
Transparent Supply Chain in Post-Pandemic World
The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed numerous long-standing vulnerabilities and risks in organizations’ supply chains. As a result, it has sometimes prompted businesses to rethink their processes and business models. Also, it has created new opportunities for post-pandemic innovation, growth, and competitive advantage.
The challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic did not reveal the interconnected or global nature of supply chains; instead, they highlighted that most organizations are not prepared to manage this interconnectivity when adverse impacts occur. In short, the pandemic has demonstrated that if businesses are to thrive in the future, they must adapt. However, supply chain leaders seeking to prepare their organizations’ supply chain processes for thriving post-pandemic can focus on three key areas to “get there”:
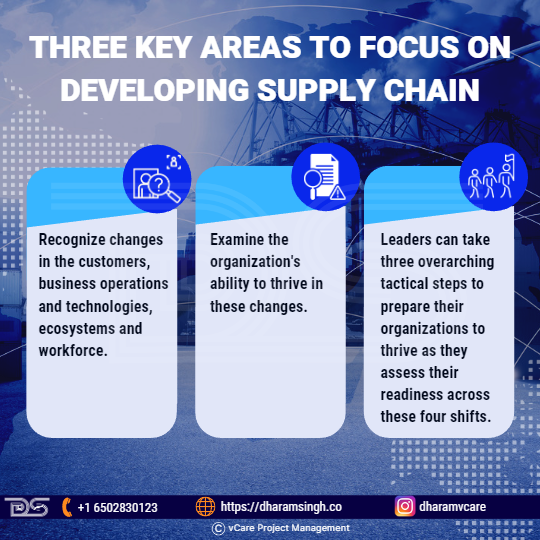
Three key areas to focus on developing supply chain
- Recognize changes in the customers, business operations and technologies, ecosystems, and workforce: Four fundamental realities have shifted dramatically due to COVID-19. Each of these shifts has direct and indirect implications for supply chains.
- Examine the organization’s ability to thrive in these changes: Supply chain leaders can ask questions to assess their organization’s readiness to deliver in the face of these shifts.
- Leaders can take three overarching tactical steps to prepare their organizations to thrive as they assess their readiness across these four shifts.
Better rebuilding: the importance of long-term supply chains in a post-pandemic world
The pandemic has served as a wake-up call to businesses concerned about the fragility of modern global supply chains. As a result, managing supply chain economic, social, and environmental impacts has become a strategic priority.
According to the World Economic Forum, COVID-19 is the final blow to supply chains that revered reliability and efficiency over resilience and sustainability. Enterprises cannot effectively monitor inputs and outputs for sustainable practices unless they have visibility into how materials and products advance via the supply chain.
Supply Chain 4.0
Customers are increasingly demanding faster service, fulfillment, and delivery. As a result, organizations that invest in industry 4.0 and supply chain practices and procedures to assist in meeting these demands.
Supply chain 4.0 includes using new technologies to crunch data streams across departments and organizations to identify new opportunities, highlight any difficulties in the process, and identify system-wide trends in the works. By combining and integrating new technology, business organizations can gain a more comprehensive view of internal and external data while bridging departmental silos.

Gartner Report
According to a Gartner report, more than half of large global companies will use IoT, artificial intelligence, and advanced analytics in supply-chain operations by 2023. According to the report, this shift toward digitizing supply chain processes will be overseen by humans who will collaborate with new technologies.
Moving Supply Chain 4.0 Forward
While many organizations are implementing supply chain processes and procedure digitization, others have not yet made the switch. But progressing with supply chain 4.0 is essential.
Without taking steps to optimize the supply chain digitally, one risks impairing their ability to synchronize their systems into a cohesive whole.
Tracking and labeling are critical components of supply chain 4.0. The first step is to implement a secure, dependable labeling system that integrates with the supply chain 4.0 practices. One must use a labeling solution that works alongside the internal workflows and systems to improve data management accuracy and evolve with the ongoing business practices. A successful product labeling system will be critical in the organization’s progress toward digitizing supply chain processes.
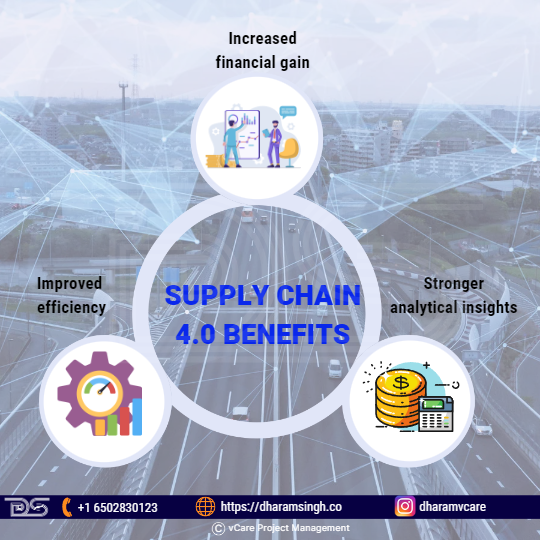
Supply Chain 4.0 benefits
Supply Chain 4.0 benefits
- Stronger analytical insights
A focused, digitized supply chain provides stronger analytical insights. This increased visibility improves communication and data transparency among manufacturers, warehouses, vendors, operations, and distribution centers. As a result, operational efficiency, customer experiences, and revenue increase occurs.
- Increased financial gain
Organizations expect a financial benefit when they invest strategically in digitizing the supply chain. Strong financial results can be the optimal result of smart supply chain investment, according to a 2019 McKinsey & Co. report.
- Improved efficiency
Moving from a paper-based supply chain to a digitized supply chain will increase the organization’s efficiency. More precise data, greater transparency, and fewer pitfalls and errors exist. In addition, electronic sensors and scans can speed up supply chain practices by eliminating labor-intensive manual processes.
Digitizing supply chains in the supply chain 4.0 era inevitably accounts for greater ordering and spending accuracy. Artificial intelligence models, machine learning processes, and other automated technology can accelerate the business’s innovation, resulting in more precise data and accurate shipments, all topped off with proper labeling for successful distribution.

Challenges faced in Supply Chain
Challenges faced in Supply Chain
A healthy supply chain should operate smoothly, with goods being received and delivered between parties. However, today’s market is becoming increasingly volatile. As a result, the supply chain is bottlenecked or completely obstructed at every turn, affecting brands, manufacturers, suppliers, and the consumer. However, here are some of the current supply chain issues and challenges:
- Keeping up with consumers and buying behaviors
- Delivery and Logistics
- Material Scarcity
- Global Port Congestion and blockage of choke points
- Increasing freight and transportation Costs
- Digitizing and Automating key processes
- Geo-economics and Geopolitics
Impact of Logistics & Supply Chain Drivers – Multi Billon Dollar Projects/Programs
For a firm’s project to succeed, its supply chain and competitive strategies must share a common goal. Strategic fit necessitates alignment between the competitive strategy’s customer priorities and the capabilities the supply chain aims to develop. In other words, strategic fit necessitates that a company achieves the optimal balance of responsiveness and efficiency in its supply chain to meet the needs of the company’s competitive strategy. Here are the seven supply chain performance drivers:
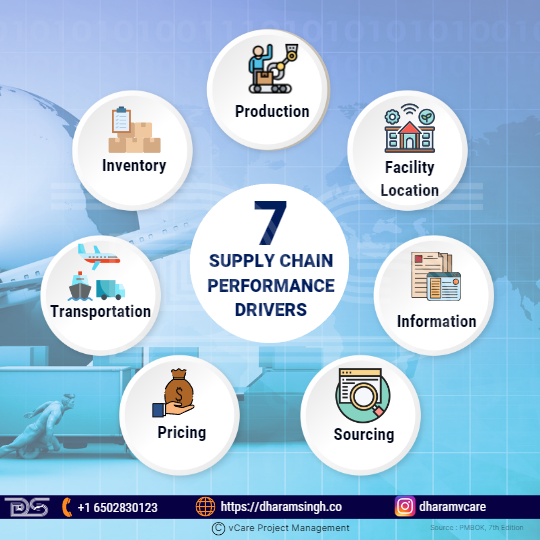
7 Supply Chain Performance Drivers
- Production: Factors like what is produced, how it is made (the manufacturing process used), and when it must be produced all significantly impact the supply chain’s performance.
- Inventory: Inventory refers to all raw materials, work in progress, and finished goods in a supply chain. Any change in inventory policies can have a significant impact on the supply chain’s efficiency and responsiveness. Decisions such as how much to store, where to store (at the firm’s or warehouse’s premises or the retailer’s premises) etc., must be made. Reducing inventory, on the other hand, will increase the retailer’s efficiency but decrease its responsiveness.
- Transportation: Inventory has been transported along the supply chain using multimodal transportation facilities, each with its performance requirements. Consequently, the choice of transportation modes and routes significantly impacts the supply chain’s responsiveness and efficiency (affecting the speed and cost of transportation). Decisions about the movement of products from one location to another and by what mode of transportation are typically trade-off decisions. On the one hand, the associated economies need evaluation, and on the other hand, the desired level of customer satisfaction needs consideration.
- Facility Location: Facilities are locations in the supply chain network where inventory is stored, parts are manufactured, and finished goods are assembled. The location of the facilities (plant), capacity, and flexibility significantly impact the supply chain’s performance. On the other hand, fewer service centers and distributors of spare parts could boost the responsiveness of the supply chain network at the expense of efficiency.
- Information: Throughout the supply chain, information consists of data and analysis about inventory, facilities (location, capacity, etc.), transportation, and customers. Because information affects all other drivers, it is the most important driver of supply chain performance. Information is useful in making the supply more efficient and responsive.
- Sourcing: Purchasing or obtaining the right materials in the right quantities, from the right supplier, in the right conditions, at the right time, and at the right price is known as sourcing. Purchasing in bulk allows suppliers to improve economies of scale while investing in capacity or processes to improve customer service. However, when a buyer firm relies on a single source of supply, it is more likely to run out of stock if supply is delayed. Managers are responsible for making “make or buy” decisions and deciding which tasks to outsource, whether to a single supplier or a group of suppliers. Managers then choose suppliers and negotiate contracts with each one to improve supply chain performance (flow of materials, information, and funds). The following are examples of crucial sourcing decisions made within a company:
- In-house manufacture or outsourcing
- Supplier selection
- Procurement
Logistics and supply chain management are driven by the sourcing and outsourcing decisions made by managers.
- Pricing: Pricing is how a company determines how much it will charge customers for its goods and services. Pricing has an impact on the price-sensitive customer segment. Customers’ expectations are also influenced by the prices they pay for goods purchased. As a result, pricing impacts supply chains regarding the level of responsiveness required and the demand profile that the supply chain tries to meet. Pricing is also used as a lever to balance supply and demand.
Understanding “Supply Chain Disruption” along with “Digital Disruption”
A supply chain disruption is a break in the flow of a process involving any entities involved in the production, sale, or distribution of specific goods or services. A well-organized supply chain is critical for maintaining product quality from beginning to end and ensuring that all resources are of the highest or required quality. To effectively manage supply chain disruptions, one must be able to respond quickly when adverse events occur in your operations. Here are a few essential steps:
- Rapidly evaluate critical events
- Determine any risks associated with the delivery of goods from your suppliers
- Examine your suppliers’ viability
- Ensure supply and your ability to meet customer commitments
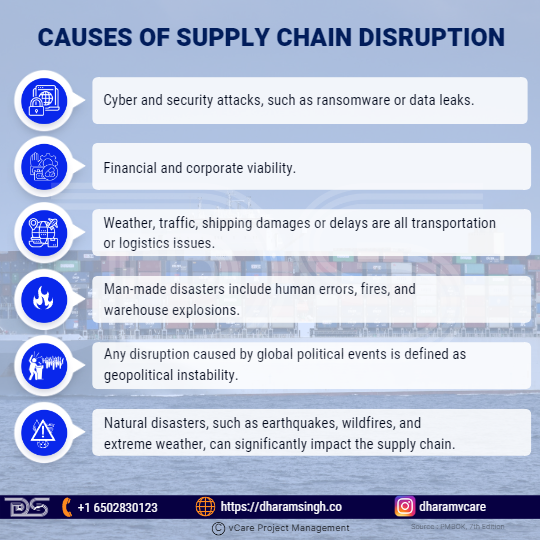
Causes of Supply Chain Disruption
Causes of Supply Chain Disruption
Internal or external factors can be the source of supply chain disruption in various industries. The following are the typical factors that may cause these disruptions and should be considered by businesses and organizations:
- Cyber and security attacks, such as ransomware or data leaks
- Financial and corporate viability – any internal or corporate concern that may impede production, including revenue forecast
- Weather, traffic, shipping damages, or delays are all transportation or logistics issues.
- Man-made disasters include human errors, fires, and warehouse explosions.
- Any disruption caused by global political events is defined as geopolitical instability.
- Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, wildfires, and extreme weather, can significantly impact the supply chain.
Three ways to manage disruption in your supply chain
The pandemic’s effects on the economy, various industries, government bodies, and societies are constantly manifesting — it is not a stretch to say that they are here to stay. But companies must make their supply chains more resilient and strategic to keep up with changing conditions. The following are some factors that businesses should consider when dealing with disruption:
- Be aware of the risks of supply chain disruptions and the potential consequences for production. This understanding can aid in proactively identifying and resolving issues. A predictive analytics tool is an excellent way to accomplish this.
- Diversifying supply chains and evaluating sourcing strategies: Businesses should have secondary to tertiary backup plans for material resources to mitigate disruption if the primary supplier is compromised.
- Reallocating capital as needed – the sudden lockdowns at the start of the pandemic reinforced the need for employees to be able to work from home, causing a shift in business capital allocation that would most likely continue post-pandemic.
- Following good distribution practices will protect distributors from situations that will not only harm their industry reputation but may also harm consumers and result in a significant loss of customers.
- Enterprises should essentially have an effective Business Continuity Plan to ensure continuous production during a business disruption.
- Use big data, intelligent systems, and connected ecosystems to implement Supply Chain Transparency. The advantages of doing so are as follows:
- This allows for the accessible communication of shortages/issues at any point in the supply chain, making it adaptable.
- Secure consumer delight and brand allegiance by ensuring the products’ origins.
- Improve industry practices that are not limited to a single business but can benefit the entire industry.
Building Digital Resilience with Supply Chain
Global disruptions have significantly impacted supply chain management in recent years. Labor shortages worsen as more workers reach retirement age, for example, forcing businesses to reconsider how to compensate and distribute labor. At the same period, the e-commerce mania has heightened customer expectations, with more customers demanding faster delivery times. As a result, supply chains must become faster, more granular, and more precise to keep up with these trends. Digitization provides one solution, allowing businesses to meet changing expectations while remaining efficient in the face of disruption.
Supply Chain 5.0
Supply Chain 5.0 addresses hyper-personalization and hyper-customization of customer needs, which necessitates the right combination of human creativity and machine efficiency. While machines do the grunt work, humans can concentrate on creative tasks and cognitive problem-solving.
Robots are frequently used in the manufacturing industry to perform repetitive tasks, thereby streamlining the assembly workflow. In that sense, using robots is extremely valuable for manufacturers attempting to maintain both product standards and a high production volume. However, what robots cannot do is interact with customers who require additional assistance and guidance. This space is where the human factor comes into play. More importantly, human-machine collaboration can enable the flexibility and efficiency needed to achieve resilience in a changing world.
Implementing a Collaborative Supply Chain
Supply Chain 5.0’s hybrid human-machine model assists businesses in surviving disruption without compromising competitiveness or profitability. Digitization and human collaboration are critical for building resilience in the supply chain without changing personnel or asking the customers or suppliers to change their processes. Here are some of the best practices:
- Automate data management and acquisition: Manual data entry takes time, is prone to errors, and is rarely up to date. Digital data management enables businesses to collect more robust data and analyze it in real time, all while saving valuable labor time. Accurate data is essential for workflow automation, reporting, and AI.
- Collaborate on process optimization: Many businesses have implemented an integrated planning process in silos. Ensure that each business sector knows what the others are doing and why. Digitization can make real-time information accessible across an organization, allowing all departments to stay up-to-date and collaborate on solutions. Everyone in the company might get benefited from this type of collaboration.
- Begin small and work your way up: Empower employees who thoroughly understand the company’s goals to take on mentoring roles. Do provide them with the tools and authority to communicate the corporate mission effectively. More employees will have learned from their superior’s guidance over time and will pass on that knowledge to the next wave of new employees.
Is disruption ever beneficial? It certainly could be. Because digital disruption enables businesses to capitalize on and create new opportunities, digitalization can be categorized as disruptive supply chain technology. And using artificial intelligence might assist leaders in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risk.
Hybrid Supply Chain – Advantages and Disadvantages
Hybrid supply chains are an evolution of agile supply chains that produce product components before determining final demand levels. A hybrid approach uses forecasting and real-time data to assist in making better decisions. A hybrid supply chain strategy combines Lean and agile practices. A hybrid supply chain strategy may be appropriate for a company attempting to become a “mass customizer,” producing progressively smaller batch sizes (sometimes as little as one item) specific to customers’ sometimes unique needs.
The age of mass customization has replaced the age of mass production. Mass customization refers to producing customized goods to meet customers’ specific needs while keeping production costs per unit low, as in mass production. Companies must cater to the needs of various customer segments in today’s highly competitive industry environment. A hybrid supply chain allows far more efficient production of smaller batches. Companies with such a strategy can also effectively respond to changing demand situations.
Companies can reduce their inventory holdings by utilizing supply chain agility. Such agility reduces inventory carrying costs. In addition, eliminating waste in the supply chain adds to businesses’ cost advantage from a hybrid supply chain. In today’s business environment, this cost is a major competitive factor.
According to a Gartner survey, 61% of supply chain leaders anticipate a permanent hybrid work model for frontline workers. As a result, supply Chain Management has become one of many businesses’ most important sources of long-term competitive advantage. The right supply chain plan can make or break a business. A hybrid approach to supply chain management is a comprehensive approach that can reduce costs, improve product quality, and boost customer satisfaction.

Hybrid Supply Chain – Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Alignment of corporate and divisional objectives
- Functional knowledge and efficiency
- Divisions must be adaptable and flexible
Disadvantages
- Disagreements between corporate departments and units
- Administrative overhead is excessive
- Slow reaction to exceptional circumstances
Final Thoughts
To create a supply chain ready to thrive in the future, supply chain leaders should consider how key forces of change will affect their supply chains and look to evolve their supply chain management strategies accordingly. This tipping point represents an opportunity for forward-thinking supply chain leaders to build future-fit supply chains that drive progress on top procurement priorities while advancing the sustainable business agenda. Though considerable uncertainty about how these forces of change will manifest, supply chain leaders can take concrete steps to plan for a wide range of possible future scenarios.
The following are five recommendations for how businesses can embrace and capitalize on the key forces of change that are changing supply chains while also achieving their top procurement priorities.
- Plan for the effects of Automation and Migration on the Supply Chain
- Build Responsible Regional Sourcing Hubs
- Digitalize Supplier Assessment and Engagement
- Strengthen Supply Chain Transparency and Disclosure
- Embed Climate-Smart Supply Chain Planning
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd










Recent Comments