
by Dharam CW2 | Aug 11, 2023 | General
A project manager or leader is much more than someone who develops a strategy and controls all operations within a project. These experts, for example, must be skilled in communication and connection-building because the work requires them to do it frequently. The capacity to develop long-term, trusted relationships with stakeholders is a critical component of project managers’ and leaders’ success. Whether they like it or not, diverse stakeholders directly impact the business. As a result, companies with managers who can foster a deep connection with their stakeholders have a substantial competitive edge in today’s interconnected business environment.

Stakeholders
Why Stakeholders are Important to a Project
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization whose interests are affected by the success of a business venture or project. As the name suggests, stakeholders are interested in a project’s success. They might be internal or external to the entity funding the initiative. Stakeholder relationships may positively or negatively impact the project’s life cycle. Therefore you’ll need to identify your key stakeholders and develop a stakeholder management plan to fulfill the requirements.
Every project you manage has stakeholders, whether internal or external. One of the most common reasons for project failure is that the deliverables differ from what the customer requested or did not meet the customer’s demands. To guarantee project success, one should be familiar with the project’s main stakeholders, how they communicate their needs, and what acceptable results are.
Engaging stakeholders throughout the project, especially at the start, will assist, reduce and discover hazards and boost overall “buy-in.” When stakeholders are fully engaged, their impact is amplified. Stakeholders are vital to a project in the following ways.

Importance Of Stakeholders In Project
- Providing Expertise
Stakeholders are a source of information about current processes, historical data, and industry expertise. When gathering and documenting requirements, it is critical to include all essential stakeholders. Project managers and those in charge of deliverables may be experts on only a few projects. Key stakeholders can contribute to industry-specific needs or limitations that can be useful in identifying project constraints and risks.
- Reducing and Uncovering Risk
The more one engages and involves stakeholders in the project, the more they will decrease and identify risks. For example, during discussions, stakeholders may raise concerns regarding satisfying original specifications, project demands, and limits. Identifying risks and developing a plan to manage them before issues arise will significantly improve your initiatives’ success.
- Increasing Project Success
Stakeholders should be aware of the project scope, significant milestones, and when they will be asked to evaluate deliverables before final acceptance. Set expectations early in the project life cycle if the business must satisfy stakeholders’ demands due to competing needs or priorities. This move will assist in maintaining the relationship throughout the process.
- Granting Project Acceptance
The more frequently you interact and include stakeholders from the beginning, the more likely you will have a successful project outcome. By the end of the project, team members should be aware of delivery expectations and risks and how to reduce those risks. The final acceptance is their last stamp of approval at the project completion phase.
Stakeholder Relationships are key
Building relationships with stakeholders leads to improved trust. People collaborate more readily and successfully when there is trust. Investing time and effort in discovering and cultivating stakeholder connections may boost project confidence, reduce uncertainty, and accelerate issue resolution and decision-making. This concept recommends making a deliberate decision to devote time, attention, and effort to stakeholder relationships. In addition, personal qualities such as self-awareness, mindfulness, respect for others, and courage may be essential to developing trustworthy, open, and honest relationships.

Ways To Approach Stakeholder Relationships
How could we approach it?
- Determine the stakeholder hierarchy.
- Create profiles for individual and group stakeholders.
- Create relationship maps.
- Determine who should interact with whom and when.
- Always maintain a professional and genuine demeanor.
- Build trust and confidence through controlling and satisfying expectations, acting with integrity, honoring commitments, and being trustworthy.
- Consider how you can assist your stakeholders rather than just how they can assist your project.
Risks of overlooking this concept include:

Risks Of Overlooking Into Stakeholders Relationship Concept
- Increased project risk in terms of time, cost, and quality.
- Greater known and unknown project opposition.
- Project management is shattered.
- Reduced team motivation.
- Low cohesiveness within the project community.
- Personal and corporate reputational damage, as well as recrimination.
The benefits of applying this concept include the following:
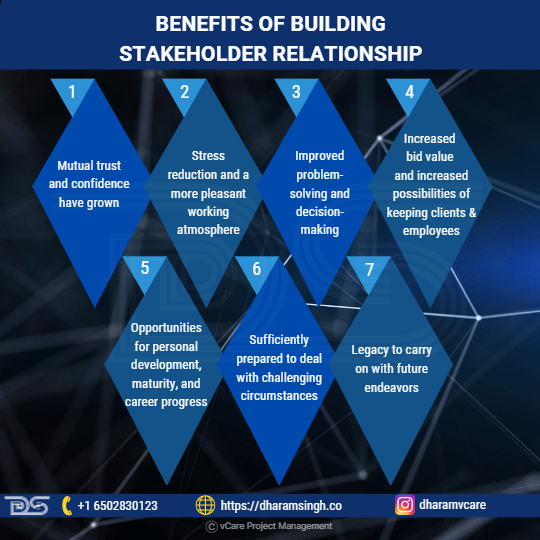
Benefits Of Building Stakeholder Relationship
- Mutual trust and confidence have grown.
- Stress reduction and a more pleasant working atmosphere.
- Improved problem-solving and decision-making.
- Increased bid value and increased possibilities of keeping clients and employees.
- Opportunities for personal development, maturity, and career progress.
- Sufficiently prepared to deal with challenging circumstances.
- Legacy to carry on with future endeavors.
Ways to build good relationships with Project Stakeholders
Stakeholders must be effectively taken care of for any firm to succeed. These include the customers, suppliers, partners, investors, workers, and the general public interested in your company. When a stakeholder is neglected, the organization can feel the consequences. Building great connections with stakeholders requires work, time, and a well-thought-out action plan.
Building trusted relationships with key stakeholders and maintaining communication throughout your project is essential. Through active engagement and speedy resolution, engaged stakeholders motivate individuals and keep the project on track.
Project managers establish trust and interact with important stakeholders at the outset. However, as the project progresses and the team size rises, we need to catch up on the importance of maintaining those connections. If unengaged, it usually results in communication failures, a mismatch of expectations, delayed decision-making, and, in extreme cases, misaligned project goals with company strategic objectives.
Here are six suggestions for developing and maintaining effective stakeholder relationships.
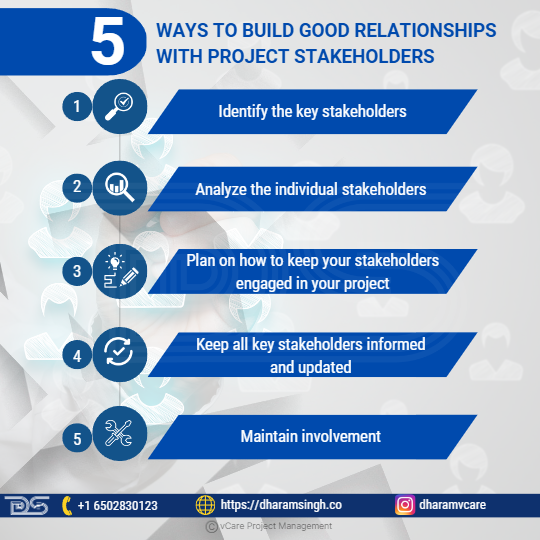
Ways To Build Good Relationships With Project Stakeholders
- Identify the key stakeholders.
In every project or program, the project manager oversees the initiative and identifies all stakeholders involved in planning, status reporting, or managing the dependencies. However, the focus here is on how you engage your important stakeholders. Who are the most important stakeholders? It is determined by project type, organizational structure, industry, and internal and external relationships.
Key stakeholders in project engagement are:
- Persons who have decision-making authority.
- Influence.
- A vested interest in the project’s result.
They might be part of your project’s organizational structure (such as a project sponsor or business sponsor) or an extended stakeholder (like external customers or funding partners).
Identifying these important stakeholders early in the project allows the PM and team to build trusted relationships and understand their expectations of project deliverables, their role, and their level of engagement on an ongoing basis.
- Analyze the individual stakeholders
Analyze the individual stakeholders identified at the previous stage to determine the amount of involvement and time required to create the connection. Historical data, team brainstorming sessions, focus groups, and interviews might provide the necessary knowledge for analysis. Next, each important stakeholder is examined to determine their attitude toward the initiative, level of support, influence, and acceptance of the change.
The project manager would decide on the amount of engagement based on their interest in the project and their ability to affect change. When there is more ambiguity about the program’s scope, objectives, and expected outcome, the PM’s role in managing expectations and relationships is more significant.
- Plan on how to keep your stakeholders engaged in your project
Consider organizational culture and attitudes toward the project while developing an engagement plan. For example, understand the stakeholder’s level of support or resistance to team talks.
Define how you will assess when a stakeholder becomes disengaged as part of your strategy; the metric may be anything like the number of mandatory meetings missed by the stakeholder in a month. When a significant stakeholder consistently skips a needed meeting or fails to make timely decisions, it is a source of contention. If not handled, this disengagement will begin to undermine the project.
- Keep all key stakeholders informed and updated
The project manager is responsible for keeping all key stakeholders informed and updated as frequently and as early as feasible during the project. Therefore, maintain a proactive approach in your discussions with them.
To build a standardized onboarding process, new stakeholders should become acquainted with a collection of standard artifacts (like the charter, communication plan, business case, and risk register). Also, take the chance to hear from current stakeholders. Feedback from stakeholders who no longer have a vested interest in your endeavor may help you adjust your path.
- Maintain involvement
It is critical to maintain your involvement, especially in long-term initiatives. At the end of a project, we’ve seen project teams wear out, with stakeholders eager to move on to the next big thing. The project manager must keep the engagement going. The connections and reputation you build via this involvement can help you succeed in future efforts in large businesses. Maintain contact with your key stakeholders long after the project has been completed and delivered.
Project Management Trends That Will Shape the Future
Project management is crucial in deciding how businesses and organizations will fare in the marketplace. Projects might include implementing a corporate plan, running marketing efforts, or organizing business events. Teams work to interact, manage, and communicate as effectively as possible to complete tasks and meet deadlines.
Organizations flexibly responded to the pandemic’s disruption by developing new methods of operation. However, they were thrust into the era of digitization and had to reconsider their methods of operation. These top 6 project management trends in the future demonstrate the ongoing need for technical innovation and digital transformation regarding the function of project management software in the future by building great stakeholder relationships.

Future Project Management Trends
- AI Automation and Implementation
The use and usage of artificial intelligence are the most obvious of the new current trends in project management. Knowing which initiatives are more successful enables teams to precisely determine which aspects are vital if the firm is to reduce costs and risks. As a result, organizations may increase transparency and productivity. The main factor driving the current increase in the adoption of such software is this characteristic of project management systems.
Let’s look at a few instances:
- A few businesses currently use automated and machine learning technologies to get alerts about potential issues the company could run into. For instance, suppliers might now get notifications about possible obstacles like bad weather and traffic.
- Building machine learning algorithms to support a project manager’s decision-making capabilities by evaluating data from several projects in the project portfolio is a promising study area.
- Globalized Project Management
As working circumstances got more flexible due to the forced work from home caused by the worldwide pandemic, businesses and teams became even more globalized. It has long since established roots. Mercer estimates that 70% of businesses want to use the hybrid work model.
Although the remote work and hybrid model trend allows for the employment of creative and inventive individuals worldwide, project management has to keep up with it. Collaboration, for example, is challenging when team members are unavailable due to competing schedules created by different time zones.
Software for project management provides a tool that could address this issue. The platform enables all brainstorming sessions and discussions to take place in a single setting, allowing businesses to access talent worldwide.
- Hybrid Project Management
The third new development in project management is the rising use of the hybrid approach, which refers to how project teams combine the Waterfall methodology, the systematic approach, with the Agile methodology, which is the quick-moving methodology. A hybrid approach aims to elevate teams to become aware of the specific project lifecycle while providing the ability to support them in changing the plan as necessary.
How do you know what will work for you, and how can you prepare for this trend?
PMs must learn about the most recent techniques, examine some of the fundamentals, and analyze how to use them correctly to obtain a greater understanding of the project situation and its aspects, such as the clients, the corporate objectives, and the purpose of the project, and the team’s attitude.
There is an increasing requirement to adapt your strategy and develop a project plan that enables you to lead projects unconventionally and comprehend different components of multiple techniques that cater to the demands of your team, perceived timeline, environment, end goals, etc.
- Stakeholder-Centered design
The fourth most recent trend in project management is an emphasis on delivering transparency for the benefit of the company’s stakeholders and developing products centered on the human perspective. Project managers may communicate with, collaborate with, and inform stakeholders. This design makes it easy for investors and customers to support any project launched as part of a company’s business plan.
- Soft Skills
Soft skills have become an essential component of project management. Project managers must interact with stakeholders, clients, and project teams. They will mitigate risks, resolve internal disagreements, and keep the project team engaged. Having a high level of emotional intelligence will also be useful in project management. Therefore, organizations should begin investing in tools and programs that assist employees in acquiring soft skills.
- Predictive Data and Simulation-Based Analyses
The most difficult and demotivating aspect of managing several projects is when unanticipated repercussions jeopardize their success. Project managers seek a solution to give them the knowledge to account for the unexpected. Project teams with predictive and data analytics skills may fully use KPIs and benchmarks and execute them proactively by developing data-backed best practices.
Companies cannot afford to bear the repercussions of project failure, given the competitive environments of most markets. Therefore, projects must be started successfully to stand out from the competition. The most recent advancements in project management software demonstrate that technology will play a role in this element of corporate operations in the future. Suppose you want projects to succeed and businesses to thrive. In that case, you should consider introducing project management solutions to simplify your, your teams, and your stakeholders’ lives.
Final Thoughts
Stakeholder involvement will become essential to optimize success as knowing stakeholders becomes increasingly critical for firms. For example, stakeholder engagement may assess reactions, track public impressions of a company’s operations, and assure collaboration and partnership with all stakeholders. In addition, an organization’s long-term performance may be determined by its connections with stakeholders, which provide commitment and buy-in to future initiatives and difficulties. As a result, the company becomes more aware and responsive to the demands of all its users and stakeholders.
Stakeholder management must place a greater emphasis on involvement to move projects from installation to execution. Stakeholder management must be less hierarchically centered while considering companies’ changing political nature. Projects should begin by identifying diverse stakeholders, engaging with them consistently, and coordinating continuously to increase project success.
As a project proceeds, Stakeholder management processes need to account for the dynamic nature of stakeholders’ commitment to a project and the interactions between various stakeholders. As a result, project teams will get the competitive advantage they want by focusing not just on their stakeholder position but also on the other major stakeholders in a project and how they interact. To achieve more effective stakeholder involvement, follow these three steps:
- Create a stakeholder map and keep it updated as the project progresses.
- Prioritize essential stakeholders and regularly evaluate assumptions about commitment levels and impact.
- Create essential stakeholders and increase their commitment to the change.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by Dharam CW2 | Jul 24, 2023 | General
Delivering a successful project is challenging, especially when there are multiple stakeholders. However, even if a project is performed on time, on budget, and to the expected scope, it can still be regarded as a success only if the stakeholder expectations are managed appropriately.
Each project stakeholder has certain expectations. Project managers are at the forefront of potentially disastrous situations when such expectations conflict. They must address and resolve the issue or risk jeopardizing the project and their position. Because the fundamental cause of problems is only sometimes apparent, project leaders and teams must analyze links between issues and stakeholder motives using interpersonal skills such as resolving conflict, resistance to change, and trust building.

Project Stakeholders
Project Stakeholders
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization that is affected by the result of a business venture or project.
Stakeholder interactions may positively or negatively impact the project’s life cycle. Thus, a project leader must identify important stakeholders and develop a stakeholder management plan to satisfy their demands. Using project management tools and strategies to keep track of the key stakeholders is an excellent method to remain on top of things and ensure that project stakeholders remain satisfied and productive.

Types of Stakeholders
Internal Stakeholders
An internal stakeholder is somebody whose interest in the project is directly linked to their affiliation with the entity in charge. Internal stakeholders want the strategic and commercial goals of the project to be realized. They might be project managers, team members, sponsors, owners, or investors.
External Stakeholders
External stakeholders are not directly linked with the company but are important to the business or are influenced by the project in some way. Those are frequently supply chain participants, creditors, or public groups.
Stakeholder Management
The stakeholder management process includes communicating project status, expenses, and barriers to stakeholders to increase visibility, navigate changes in project direction, and manage expectations. Project stakeholders are those involved in the project or whose interests may be influenced by the project’s execution or completion.
Stakeholder management helps project managers keep change at the forefront of their thoughts while making it less intimidating. Furthermore, the stakeholder management plan is a reminder for every interaction the project managers have with direct or indirect stakeholders, helping them maintain a genuine link between the project and day-to-day operations.
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Means
An effective stakeholder management process ensures that timely and relevant feedback is provided, and that the stakeholder management strategy directs the change effort. The project manager maintains stakeholder expectations, resolves conflicts, and identifies and fixes any problems that develop throughout the project. In general, the following are the fundamental parts form the stakeholder management process:

The Necessary Elements For Successful Stakeholder Management
- Managing stakeholder expectations: The project is more likely to succeed when stakeholders’ expectations are actively managed. As a result, to ensure perfect conformance with project goals and expectations and to continue the project management effort, the project manager must continually negotiate and influence the demands of stakeholders.
- Managing stakeholder perception: It is critical for project success to ensure that stakeholders are involved in the project regularly and are kept up to date on the project’s progress. High-level stakeholder perception increases the likelihood that stakeholders will provide the necessary support and the project will be completed as intended.
- Keeping track of stakeholder activity: The project manager is primarily responsible for recording and tracking all stakeholders’ activity. As a result, to secure stakeholder acceptance and project communications plan adherence, the project manager should formally document all contacts with stakeholders and keep records of the project’s outcomes.
- Solving problems and resolving conflicts: To avoid challenges and conflicts, the project manager should address stakeholders’ concerns and identify risks and threats in collaboration with conflict management. By referring to change requests, the project manager can generate solutions.
Understanding the components of the managing stakeholder’s process enables the project manager to engage with stakeholder expectations and demands and build action plans to be used when disputes and challenges emerge. The project manager can utilize the following tools to assess conflicts and challenges, as well as manage stakeholders on an individual and group level:

Tools To Assess Conflicts And Challenges In Managing Stakeholder’s Process
- Issue logs: An issue log is a tool for assessing issues and documenting resolutions. It is a document with a rigid categories structure that allows each issue to be placed in the appropriate category (issue group). The project manager uses problem logs to ensure that each stakeholder understands the project and maintains positive working interactions among all stakeholders, including project team members.
- Change Logs: It is a tool for documenting any changes that occur throughout a project. The project manager uses change logs to track changes and their impact on project goals and deliverables. A change log should be provided to project stakeholders and should include data on changes to risks, uncertainties, costs, and budgets.
A change request for project deliverables may result from the technique for managing and engaging stakeholders. Changes to the stakeholder management approach and registry are also feasible. The method of managing stakeholders allows for evaluating and modifying stakeholder benefits created earlier in the project’s life cycle.
Five pitfalls to address while dealing with the expectations of stakeholders
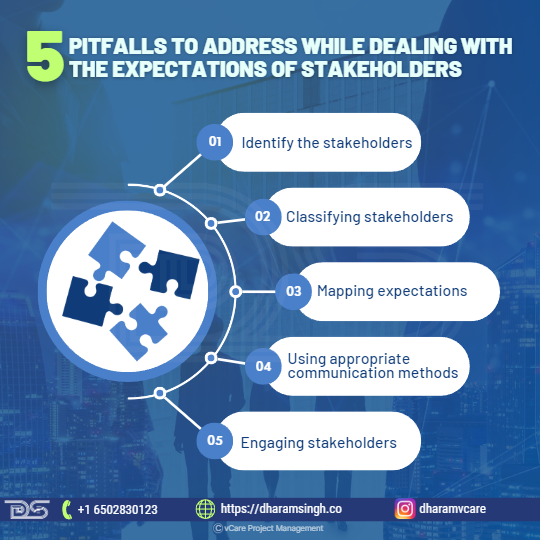
5 Pitfalls To Address While Dealing With The Expectations Of Stakeholders
- Identify the stakeholders
A project often involves many stakeholders, and it can take time to identify all of them. A stakeholder is a person, a group, an organization, or a set of organizations that are actively involved in or may be affected by the project. Stakeholders can have an impact on a project in a variety of ways.
For example, if a stakeholder is top management in an organization and is not completely committed to a project, it may drastically limit buy-in throughout the business. Founders and C-suites are also stakeholders who can positively or negatively impact a project. Therefore, the identification of stakeholders is a critical step in managing expectations.
- Classifying stakeholders
Effective stakeholder management necessitates a project manager categorizing stakeholders based on their role in project completion. A project manager must determine which stakeholders are supporters and which may be obstacles to the project. It might be challenging to define the types of risks, where and when each risk exists, the impact on the project, or how to build strategies to handle possible risks if stakeholders cannot be classified.
- Mapping expectations
Project managers must resolve possible concerns, keep stakeholders involved and motivated, and finish the project on time. A project manager must have a good understanding of all stakeholders’ expectations. Stakeholder analysis and adequate documentation can be useful in mapping expectations. Stakeholders may have different priorities when completing tasks, milestones, or the full project. Their interests may be interpreted differently and have different definitions of success.
For example, one stakeholder may prioritize project completion on time, while another defines success as keeping it under budget. Mapping expectations and obtaining clarity among all stakeholders enhances the possibility that a project manager and their team can effectively complete a project.
- Using appropriate communication methods
Stakeholder management requires determining and implementing appropriate communication methods. To successfully manage stakeholder expectations, a project manager must establish the available and preferred communication mechanisms for stakeholders. A poor or incorrect communication approach can lead to distrust and dissatisfaction between stakeholders and a project manager. It is also essential to adjust communication tactics and frequency based on elements such as time, message, purpose, secrecy, or changes based on stakeholder contexts.
- Engaging stakeholders
Stakeholder engagement during the project with frequent updates boosts stakeholder confidence, which is essential for project success. In addition, efficient stakeholder management necessitates the involvement of stakeholders in decision-making by the project manager.
Although a project manager may believe they have already determined the optimal course of action, they should incorporate stakeholders in procedures and pertinent talks to ensure all options have been examined; otherwise, key possibilities and expectations may be missed.
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Methods
Before beginning a new project, start by identifying all stakeholders. First, identify those impacted by the project and the organizations that will influence the project. Then, using the strategy outlined below, begin developing strong relationships with each stakeholder.
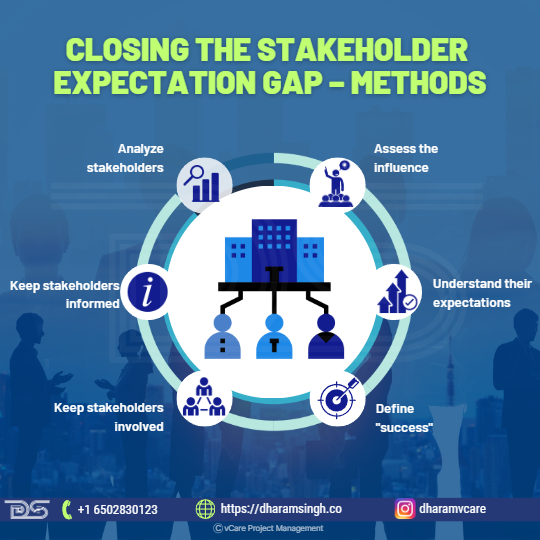
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Methods
- Analyze stakeholders
Conduct a stakeholder analysis or an evaluation of the key participants in a project and how the initiative will affect their issues and requirements. Determine their unique qualities and interests. Find out what motivates them and what frustrates them. Define responsibilities and levels of engagement, and assess whether there are any disputes among stakeholders.
- Assess the influence
Determine the extent to which stakeholders can have an impact on the project. The more powerful a stakeholder is, the more a project manager will require assistance. When evaluating stakeholders, consider the question, “What’s in it for them?” Knowing what each stakeholder needs or desires from the project allows the project manager to measure their degree of support. Remember to weigh support against influence, like Is it more necessary to have strong support from a low-level stakeholder or moderate support from a high-level stakeholder?
- Understand their expectations
Determine the exact expectations of stakeholders. Then, when necessary, seek clarification to ensure they are thoroughly understood.
- Define “success”
Every stakeholder may have a distinct definition of project success. Discovering this towards the end of the project is a potential disaster. Instead, gather definitions and integrate them into the objectives to guarantee that all stakeholders support the final results.
- Keep stakeholders involved
- Don’t just provide updates to stakeholders.
- Solicit their opinions.
- Schedule time for brief meetings to get to know them better.
- Determine each stakeholder’s ability to engage while keeping time restrictions in mind.
- Keep stakeholders informed
- Send regular status updates.
- One update each week is generally adequate.
- Hold project meetings as appropriate, but allow enough time between them.
- Respond to stakeholders’ inquiries and emails as soon as possible.
- Regular contact is usually valued – and may help ease the impact when you have unpleasant news to deliver.
These are some of the fundamentals of developing effective stakeholder connections. However, like with any relationship, there are subtleties that every effective project manager knows, such as understanding the distinctions and responding successfully to various types of stakeholders.
Final Thoughts
There is a link between resolving conflicts in stakeholder expectations and project success. Similarly, the faster project teams defuse a potentially dangerous situation by recognizing the source of conflicts, the link between issues, and the motivations of stakeholders, the simpler it is to develop trust, settle conflicts, and overcome resistance to change.
Using diverse modes of communication between the project team, senior management, and stakeholders improves prospects for mutual understanding. These methods may help the project managers to meet the stakeholder expectations and reduce the risk of project disaster.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by Dharam CW2 | Jul 19, 2023 | General
Project management is a fulfilling career choice that may offer competitive pay and a wide range of job opportunities. As a result, project managers are constantly in demand: Qualified individuals are always needed to plan and provide work in every business.
Over the next ten years, demand for project managers is one of the roles which will expand faster than the need for workers in other roles. But on the other hand, organizations may face risks due to the talent gap.
Understanding PMOE
Projects are becoming an increasingly important component of business completion. The acceleration of business evolution, increasing emphasis on digital transformation, and ever-changing consumer expectations and competitor offers are here to stay. As a result, project management skills and talents are becoming increasingly important in organizations.
Organizations will not invest in training the people in those positions to accomplish that work if those roles are not recognized as contributing to project management. As a result, they will not foster an environment where employees may develop experience, and they will eventually find themselves unable to sustain the number of projects that must be delivered.
One of the reasons that technical roles are considered part of PMOE is the growing adoption of agile ways to deliver work. However, many organizations still see agile as a ‘project management free’ delivery method, where the self-organized nature of agile teams eliminates the need for project management. But, again, this thinking must change if there is any hope of closing the skills gap.
Organizations must assess their skill profiles for all roles and determine if project management competencies should be included. Even roles that do not entail daily project delivery or where employees are more frequent contributors than leaders are likely to benefit from project management skills and experience. Unless that is ‘built in’ to job profiles, hiring and development methods will remain the same, and the shortage will remain unaddressed.
Talent Gap Report 2021
Successful projects are a significant contributor to global economic growth. As more industries become projectized, the demand for qualified project managers will likely rise over the next decade.

The Talent Gap Report 2021
The Talent Gap Report 2021 has been released by the Project Management Institute. The headline is the scarcity of qualified candidates for project management-oriented employment (PMOE). As a result, around 25 million more employees will be required by 2030 than in 2019. To put this in context, there were 90 million workers in those positions in 2019, implying a 30% increase.
Simultaneously, 13 million existing project management-oriented employees will retire, with the vast majority nearing the top of the experience curve. This phenomenon implies that enterprises will lose significant knowledge and skill. And this will happen when they increase the need for that experience by introducing a large number of new project-related staff who must progress quickly. In developed economies, on the other hand, retirement is the primary source of job possibilities for younger workers.
The report’s most critical statement comes near the end: “Global demand for project management expertise is unlikely to be addressed by 2030 unless firms encourage a culture of continuous learning.” As a result, firms confront a huge growth in PMOE roles and an inability to address that requirement based on current business processes.
Addressing challenges of this magnitude demands a strategic approach backed by financial commitments and constant responsibility for performance. In some circumstances, it may also necessitate a transformation in how leaders understand their companies and roles.

3 Reasons For The Project management Talent Gap
Why and where is the Talent Gap?
There are three reasons for the project management talent gap:
- The number of positions requiring project management skills is increasing.
- Project managers are in high demand in emerging and developing companies.
- Project managers are retiring faster than young talent can replace them.
Upskill the people
Unless firms foster a culture of continuous learning, the worldwide need for project management skills is unlikely to be met by 2030. The most resilient firms will prioritize reimagined employee capability-building.
According to a McKinsey report, over 80% of business leaders consider skill building to be “very” or “very” vital to their organization’s growth, up from 59% before the pandemic. As a result, organizations will need to support new learning initiatives and seek partnerships to equip employees with the appropriate project management skills to develop their talent. These talents include power skills like teamwork and leadership; business acumen to develop well-rounded employees; and mastering new methods of working, such as growing use of tech-enhanced problem-solving tools.
Gaining a Competitive Advantage in the Talent Acquisition Race: The Front-Runners
According to PMI and PwC study, a cohort of 250 organizations face fewer challenges in attracting and retaining talent than their counterparts. Their project management offices (PMOs) are better connected with corporate strategy—three quarters have a C-suite presence, and 90% are seen as strategic partners by their executive leaders. As a result, they have an easier time recruiting people with important project skills. They are more successful at developing project managers. They are also twice as likely to have outperformed in revenue growth, customer acquisition, customer happiness, and environmental, sustainability, and governance (ESG) indicators.
Facilitating project-based organizations
The concept of stable operations is unlikely to exist at any scale by 2030, which is one of the most important factors driving the demand for more individuals in PMOE roles. The rapid growth of technology has resulted in much shorter lifecycles for both customer-facing and internal solutions. This trend is expected to continue as digital transformations drive organizations to the point where technology is vital in managing every business area.
Future of project management
Project management is being massively disrupted by management technology. As a result, forward-thinking professionals are questioning how to effectively prepare for the upcoming tidal wave of change caused by technological innovation.
Here are four skills that project managers of the future might need:
- Data Science
- Conflict resolution
- Entrepreneurship
- Resource management
Project Management’s Future in the Age of Advanced Technology
Because of emerging trends such as remote teams, digitalization, and automation, project management has changed dramatically in recent years. As a result, companies now rely significantly on technology to plan, execute, and monitor work. As an example:
- Big data and artificial intelligence for better risk forecasting
- Remote progress tracking using digitization technologies
- Automation software for more efficient execution
These innovations have improved firms’ management capacities and altered project management’s future. According to Gartner research, 80% of management duties will be automated by 2030, and future managers will need more technological abilities. They must be knowledgeable about cybersecurity, blockchains, machine learning, and robots, all of which are expected to play larger roles in management.
Future Trends of Project Management
Consider project management ten years ago: fewer tools, smaller teams, and more straightforward tasks. Since then, the project landscape has changed dramatically, with major trends such as:
- Blockchain
- Artificial intelligence
- Sustainability
- Remote teams

Future Trends of Project Management
Trend 1 – Blockchain
More companies use blockchain technologies for management, such as when conducting dispute investigations. The capacity of blockchain to automatically update data makes it ideal for reconciling records and transactions. One of the most significant contributions of blockchain to project management will be smart contracts, which are effectively self-executing contracts powered by computer code.
Smart contracts reduce the number of key functions within the project manager’s scope, such as checking on project milestones and assigning new ones, which speeds up management processes. As a result, quicker workflow assures project completion on time and improves a company’s overall performance.
Trend 2 – Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence quickly infiltrates project management systems, handling anything from predictive analysis to risk management. Because of its efficacy, AI is expected to contribute:
- $42.7 B (7.7%) to Egypt’s economy
- $135.2 B (12.4%) to Saudi Arabia’s economy
- $96.3 B (13.6%) to the UAE economy
The primary capacity of AI is to provide data insights for decision-making, which increases the agility of any given project. For example, assume a manager considers which product features to include; AI finds correlations and patterns in consumer data and then recommends which product features are more likely to sell. Such insights improve an organization’s competitiveness by avoiding commitment to poorly planned, hazardous ventures.
Trend 3 – Sustainability
Today, project sustainability is more crucial than ever. Governments and societies all around the world are demanding greener approaches throughout the life cycle of a project.
Green initiatives are cost-cutting methods from a business standpoint. For example, energy is required for project execution, and shifting to renewable sources reduces costs. In addition, this frees up resources for other essential areas, such as innovation and research. Meanwhile, sustainable practices improve a company’s brand and foster consumer loyalty.
Trend 4 – Remote Teams
Remote teams have been the norm since the advent of communication technology. As a result, businesses gain from a more diverse and borderless talent pool easily available through contracts. In addition, they spend less on office space, travel, and other administrative expenses.
As a result, it’s not unexpected that 65% of workers anticipate that workplaces will become entirely virtual over the next several years. In general, remote working arrangements enable businesses to extend their resources while increasing operational efficiency. As such, they are crucial in developing lean, competitive firms.
Skills Future Project Professionals Need
To stay up with modern project management trends, a fundamental understanding of ideas such as data science, conflict resolution, and entrepreneurship is required. For example, understanding data science may assist a manager in incorporating AI into more elements of the project life cycle.
Here’s a closer look at what these talents comprise and how they’ll stay up with future project management improvements.

4 Skills Future Project Professionals Need
Skill 1 – Data Science
Big data insights are essential management tools, particularly for large projects with extensive life cycles. Insights from previous projects show inefficiencies that guide the current project, such as the number of slack hours and their causes. Data analysis assesses progress and uncovers deviations early, such as changes in material costs and currency rates that exceed expectations. As a result, project managers must comprehend topics such as statistical inference and regression analysis.
Skill 2 – Conflict Resolution
Today’s projects are extremely complicated, with constantly changing deliverables. As a result, conflicts are never far away. These issues, if left unaddressed, can undermine the team’s performance, resulting in delays and missed deliverables. Managers must thus grasp the various aspects of conflict resolution, such as:
- A conducive work environment’s behavioral and organizational components
- Effective communication
- Effective contingency planning
Skill 3 – Entrepreneurship
Project managers are, in essence, CEOs. On the one hand, they manage project deliverables. Yet, simultaneously, they negotiate with shareholders and set goals based on estimates. As a result, being effective requires more than technical and administrative skills.
Entrepreneurial skills, such as strategic thinking and market insight, are also required of project leaders. Such skills are especially important when modifying deliverables, typical in agile projects like software development.
Skill 4 – Resource Management
Budgets and timeframes became tighter as projects became larger and more complicated. Today’s project managers must balance budgetary constraints, quality delivery, and achieving deadlines with limited resources. They are entrusted with creating a lean organization.
For optimal efficacy, a precise balance of resource allocation is required, as over-allocation to one activity inhibits the others. As a result, managers must understand resource management principles such as equilibrium shifts and flexibility.
Bridging the talent gap
The PMI Talent Gap report delves into a decade’s worth of project management-related job trends, costs, and global implications. PMI has completed its most recent study of the “projectized” businesses that leverage these talents better to understand talent and employment trends in project management. Using data from selected areas, the PMI Talent Gap report provides a birds-eye perspective of the most in-demand talents and the magnitude of the talent shortfall.
PMI data shows a continuing gap between the global demand for project management skills and talent availability. This data translates into many new career prospects in PMOE for job-seeking project professionals. However, the skill shortage is a significant issue for firms that rely on project leaders and changemakers. For example, by 2030, this skill gap is anticipated to affect every area, resulting in a potential global GDP loss of up to US$345.5 billion.
Here is a summary of the top three reasons for the skill gap, as identified by PMI research and explained in the report:
- An increase in the number of professions that need project management expertise.
- Economic growth drives demand for project managers in emerging and developing countries.
- The rate of labor-force retirement
Final Thoughts
Project management has a bright future. There is still a high demand for change agents. PM will transition from being viewed as an administrative function by some executives to the strategic partnership that it has the potential to be in every organization, not just those enlightened businesses with high levels of program management maturity.
For many years, the skills of project managers have migrated toward “soft” skills. However, given how the future of work is shaping, this will become much more important. Project managers will need to be team players. As a result, we’ll need to interact with people who have the skills that the technical companion lacks:

Skills That The Technical Companion Lacks
- Empathy
- Strategic thinking
- Fun
- Creativity
- Motivation and persuasion
- Thoughtful customer service
- Listening
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by Dharam CW2 | Jun 4, 2023 | General
Project management may be challenging. Addressing changing business demands, allocating limited resources, and managing team workloads can all result in dealing with complicated project management aspects on a day-to-day basis. However, having high-level assistance and guidance can be a lifesaver. Steering committees accomplish precisely that. Project management steering committees give administrative assistance and troubleshoot issues to keep projects on schedule to achieve their objectives.

Steering Committee
Steering Committee
A steering committee is an advisory body of important stakeholders overseeing and supporting a project to ensure its success. Project steering committees are also known as stakeholder boards, senior leadership teams, and project working groups. They manage projects from beginning to end, offering direction and assistance throughout the project’s lifecycle.
A steering committee’s primary concern is the organization’s direction, scope, budget, timeline, and techniques. Steering committees will meet regularly to discuss these issues to identify where they are and where they want to go to stay on track.

Project Steering Committee
Project Steering Committee
A steering committee may also be a group working together on initiatives. In this case, steering committees assist project managers in ensuring that projects are aligned with business objectives. They identify and manage risks, maintain project quality, and track progress and timeframes. In addition, the committee can approve changes to the project scope, budget, and strategy.
A project steering committee is a part of a larger organization for project governance. Companies that plan major projects that need collaboration across departments and include multiple stakeholders gain from a steering committee that can direct project management. The committee supervises the team’s progress toward fulfilling benchmarks and goals in this role.
The committee is in charge of project management, financial analysis, and recognizing changes that influence the project’s original scope. Furthermore, the project steering committee ensures that all points of view are heard and that any problems between stakeholders or departments are resolved.
Role of a Steering Committee
A steering committee can accomplish its core goal by utilizing a range of group and individual functions. When a steering committee gives advice and guarantees that items are delivered on time and in good condition, a company may reap significant benefits from its project successes. Some of the most important group-based steering committee positions that influence a business’s and consumers’ satisfaction with a product include:
- Providing input on the growth or development of a business or initiative.
- Addressing concerns and offering guidance on budgeting, marketing, recruiting, and other financial issues.
- Identifying the outcomes or objectives that the project must achieve.
- Prioritize the steps and objectives that must be completed to meet the project’s objectives.
- Assisting in the formulation of business-related policies, processes, and guidelines.
- Identifying, monitoring, and eliminating potential operational risks.
- Setting project deadlines or timelines and keeping track of progress.
- Monitoring the final work’s quality.
- Making plans for how a client or consumer will react to a product or service.
- Analyzing and discussing changes that have occurred or will occur to guarantee the project’s success.
- In the workplace, encouraging team members to collaborate.
- Where relevant, providing further insights on business or project concerns.
Members of the steering committee generally do not work on the project directly; nevertheless, committee members may perform various tasks individually to help assure the project’s success. Therefore, individual steering committee members should understand and strive to improve the strategies used to achieve project goals, be genuinely interested in the project and its outcome, promote the project whenever possible, and maintain a broad understanding of project management concerns, in addition to attending team meetings.

Key Functions of The Steering Committee
A steering committee is an advisory committee made up of various stakeholders and firm officials. They assist in making choices on various initiatives, with members directly interacting with project managers. Here are some of the key functions of the Steering Committee:
- Advocacy
A steering committee advocates for the organization’s varied goals and programs. Remember that it is generally composed of top management and specialists.
- Setting strategies and goals.
Steering committees develop strategic directions for initiatives. They also provide advice and opinions on budgeting, assets, money, time, facilities, marketing, and hiring. Goals and project scope are established as part of their employment.
- Coming up with ways of measuring success
There are several metrics for measuring performance. The steering committee is in charge of establishing how a product’s success is measured.
- Monitoring
The steering committee serves as an advisory body as well as a monitoring body. It ensures that projects fulfill the necessary quality standards and monitors any changes. It also keeps track of project processes and plans, which is critical to project success. The committee also analyzes and monitors project or company hazards before devising solutions to mitigate them.
- Offering expert opinion
The steering committee comprises experts who provide expert opinions on various issues concerning projects or the entire business. Their involvement is generally required, especially while working on a complex project.
- Conflict resolution
Disagreements are normal, mainly while working on a specific project. However, to ensure that issues do not disrupt the overall project, these committees resolve disputes between stakeholders, giving them more time to focus on what is best.
- Problem-solving
One of the functions of any advisory body is to discover solutions to problems the organization may be experiencing. It can generate various problem-solving ideas due to the experts on the strategy committee.
- Decision making
Although the steering committee’s primary function is to provide counsel, it also participates in decision-making. For example, it can analyze, accept, or reject project plans or recommend revisions to the supplied plans based on the members’ feedback.
The committee also engages in role allocation because its members can appoint project managers and other professionals to complete assigned tasks.
Ways to prepare for the project steering committee meeting
Important information and documents must be communicated with all steering committee members before the planned meeting, including:
- Meeting agenda
- Minutes of the previous steering committee meeting
- Project progress report from the project manager
Certain team members should be in charge of creating steering committee meeting documents and scheduling meetings. The steering committee is led by a chairperson who runs the meeting according to the agenda. They also ensure that all committee members express their viewpoints and ideas.
A basic meeting agenda would include the following:
- Recognizing and distributing the previous steering committee meeting minutes with other committee members.
- Conduct a thorough review of action items decided at previous sessions.
- Analyze the project status report filed by the project manager.
- Have a thorough discussion about any additional issues of concern or project requests.
- Select a date, time, and location for the next steering committee meeting.

Steering committee Best Practices For Project Success
Steering committee best practices for project success
Consider the following steering committee best practices for project success, whether you hold your meeting online or in person:
- Allow adequate time for the project team and committee members to prepare.
- Focus on the most important project KPIs and milestones and deliver them to the committee members in a format that everyone can agree on, such as a presentation, report, or infographic.
- Present project facts that are factual, contextual, and relevant. Share any inconsistencies or difficulties as soon as possible before they become significant issues.
- Schedule meetings in advance and automate meeting alerts to go out a week and a day ahead.
- Ensure comprehensive documentation of all meeting discussions and distribute it to committee members before the next meeting.
- Maintain the project charter and refer to it whenever there is doubt about authority, accountability, or strategic direction.

Challenges for Steering Committees
Challenges for Steering Committees
Because project management steering committees are comprised of employees from various backgrounds and functions, they will almost always experience certain challenges. These are some examples:
- Conflicting interests:As the committee includes cross-functional representatives, they will frequently have opposing ideas and interests. People think differently, which may be shown in their behavior, activities, and perspectives.
- Slow decision-making:Team decision-making is typically slower than individual decision-making.
- Lack of clarity in roles:Many committee members may need to know their individual or team responsibilities. A clearly defined charter for the steering committee ensures transparency and clarity about their duties in the project.
Final Thoughts
Every organization needs a Project Steering Committee to lead its transformation initiatives, beginning with a contemporary approach to project management. It may be instantly productive by initiating the process of managing project priorities. Steering committees are extremely crucial in efficient project management. They add value by keeping projects on pace, reducing risks, and resolving problems. When creating one, it is essential to evaluate the overall composition.
The steering committee plays a crucial role in project management that should be considered. The steering committee is the project’s administrator. This functionality does not exonerate the project of responsibility. On the contrary, this role necessitates that the steering committee participates in the project and not simply monitors the project group’s performance from the sidelines. This move will strain the steering committee’s multiple tasks and the time spent on the project.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by Dharam CW2 | May 19, 2023 | General
Emotional intelligence in the workplace is becoming increasingly important for leaders and project managers as remote work became more prevalent due to the pandemic. Success in project management and managing cross-functional remote teams is only possible with emotional intelligence.

Capterra Survey
According to a Capterra survey, emotionally intelligent project managers (PMs) are approximately 11% more successful at managing processes, engaging stakeholders, avoiding scope creep, and efficiently using resources than PMs who lack this skill.

Emotional Intelligence
What is Emotional Intelligence?
Emotional intelligence refers to our ability to recognize, control, and communicate emotions. People with high emotional intelligence understand how they feel, what their feelings imply, and how their feelings affect others. In interpersonal situations, it is also the ability to empathize with others. Emotional intelligence is about creating a positive work environment, which is critical to the success of any project.
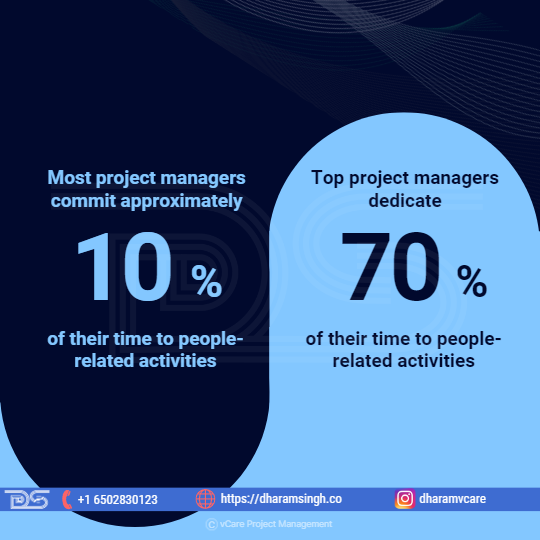
As Per LiquidPlanner Study
According to a LiquidPlanner study, most project managers commit approximately 10% of their time to people-related activities. Top project managers dedicate 70% of their time to these activities. As a result, we can conclude that emotional intelligence is crucial for project success.

Importance of Emotional Intelligence for Project Managers
Importance of Emotional Intelligence for Project Managers
- Emotional intelligence is essential for leading cohesive, high-performing teams.
- According to researchers and behavioral scientists, Emotional intelligence impacts how leaders communicate with their teams and how team members interact.
- Emotionally intelligent leaders and managers understand how to control their emotions and behavior at work, which includes providing safe environments for exchanging ideas and feedback, productive teamwork and performance, good morale, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. They manage workplace stress and conflict with care and educate their team members to do the same.
Characteristics of Emotional Intelligence
What can project managers do to help themselves develop and become more aware? First, let’s examine five abilities for raising emotional intelligence:
- Self-Awareness – The ability to sense, identify, and comprehend emotions is self-awareness. Unfortunately, many of us were taught to ignore our emotions in the past. However, it is critical to be aware of your feelings to make appropriate decisions and act accordingly. Those with high self-awareness are self-assured, authentic, open to feedback, and capable of maintaining perspective throughout all project phases.

Characteristics of Emotional Intelligence
- Self-Management – Self-management is the ability to reason well while understanding feelings. Many frequently react based on their frame of reference rather than selecting a response based on their current unique circumstances. Self-managers are deliberate in decision-making, taking the initiative, framing events appropriately, maintaining perspective, and responding quickly. They understand their feelings and why they have them and effectively manage their responses.
- Self-Motivation – Self-motivation is the ability to channel the power of your emotions toward a specific goal. When project teams have a purpose, these ‘P’s follow peace, passion, power, perspective, and potential leverage. Self-motivators who are influential are optimistic and have a positive attitude. They can delay gratification and assert themselves.
- Interpersonal Management – The capability to identify and respond properly to the emotions of others is referred to as interpersonal management. If you can connect with people and acknowledge their humanity, they will answer openly, leading to common trust.
- Leadership – An emotionally intelligent project manager inspires guides, challenges, and supports the team. Leadership is defined as the ability to create and communicate vision and passion for assisting individuals and organizations in reaching their full potential.
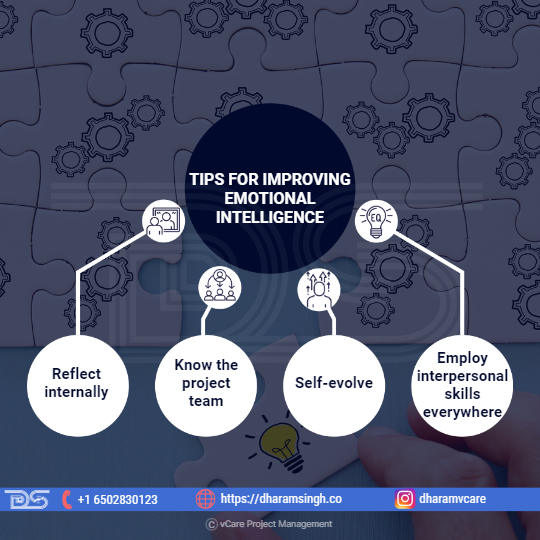
Tips for improving Emotional Intelligence
Tips for improving Emotional Intelligence
- Reflect internally – To become more emotionally aware, one must first understand their emotions and then regulate them in stressful situations. Next, they have to figure out what motivates them. Finally, authenticity is necessary to develop emotional intelligence by leading a successful project team and establishing meaningful relationships with stakeholders.
- Know the project team – Project managers are usually aware of the people they must contact when working on a project. However, understanding the project team, from team dynamics to personalities to dealing with conflict and stress, is just as important. To improve emotional intelligence, one must first get to know their team, communicate with them, and understand their emotions. It will also help the success of their project. This job becomes even more important for teams that operate in multiple locations and are diverse.
- Self-evolve – Along with other important leadership talents, project managers should work to improve their emotional intelligence regularly. Conditions surrounding a project frequently change; its scope may shift, the number of stakeholders may increase, and projects may eventually end.Every project is distinct, and no project manager can complete a project independently. Therefore, it is advantageous for project managers to consider what they learn during and after a project. For example, consider how a project team operated, what they witnessed during critical times with stakeholders, and their team’s performance.
- Employ interpersonal skills everywhere – Emotional intelligence can be helpful in almost any project management situation. For example, people may feel compelled to sign off on a strategy to minimize delays while managing scope changes or project risk. Following the resolution of such issues, an emotionally intelligent project manager would pursue people because they notice that this could lead to more severe problems in the future.
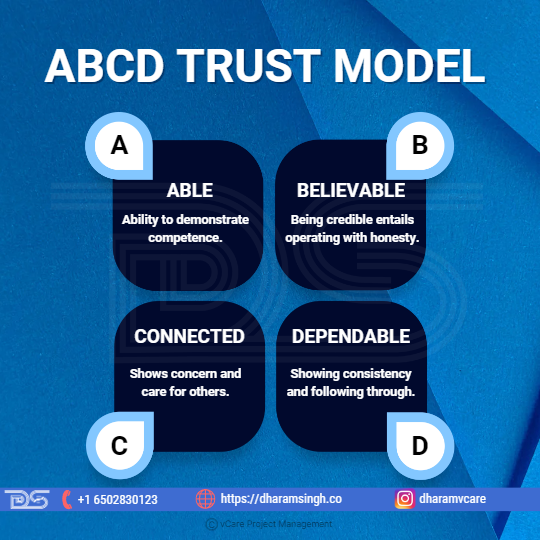
ABCD Trust model
ABCD Trust model
Better relationships will result in better outcomes. That is why developing trusted connections is critical to the success of your organization. When individuals trust one another, they may work efficiently together.
It is well known that low trust harms morale, productivity, and turnover. To prevent these traps, Ken Blanchard created the ABCD Trust Model to help executives understand the activities that affect creating trustworthy relationships.
Blanchard suggests four critical aspects for leaders to develop trust with people: Able, Believable, Connected, and Dependable.
- Able – The term able refers to the ability to demonstrate competence. Leaders demonstrate competence by possessing the necessary skills, education, credentials, and experience. They also exhibit their capacity to lead by accomplishing achievements. Able leaders can encourage people and collaborate with them to achieve goals.
- Believable – Being credible entails operating with honesty. Believable leaders adhere to a set of core beliefs. They know what they stand for and will not compromise their principles under pressure. Being credible also means maintaining promises and not lying or stretching the truth.
- Connected – Connected shows concern and care for others. This aspect fosters trust and contributes to a more engaged workplace atmosphere. Being linked entails attending to people’s needs and promoting their well-being. Leaders also build relationships by giving information not only about the organization but also about themselves. Employees are significantly more likely to provide their best effort when they feel linked to leaders.
- Dependable – Dependable means showing consistency and following through. It entails holding oneself and others accountable for commitments. A trustworthy leader will accept responsibility for their acts and help their followers face adversity.
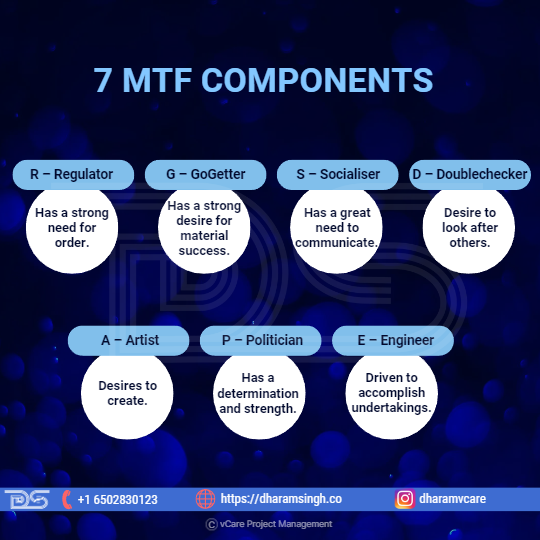
7MTF Components
7MTF Components
The 7MTF model is composed of seven components. We all have all 7 in our personalities; as adults, 2 to 4 will be strong, some will be weak, and others will be ordinary. This mix of elements is one of the most significant variables in deciding our temperament – our emotional predisposition.
- The R – Regulator (formerly known as the Normal) – A person with a ‘strong R’ has a strong need for Order. They will be mature, responsible, calm, and emotionless. You may hear the words ‘should,’ ‘ought,’ and ‘logical’ in their language. They have high expectations of themselves and others, including those with whom they live and work.
- The G – GoGetter (formerly known as the Hustler) – A person with a ‘strong G’ has a strong desire for material success. This individual entails enjoying money and the things it can purchase. The G is quick, opportunistic, intelligent, enterprising, and charming. They are short-term in nature, expecting results immediately or very soon. Promising a G a large monetary reward next year is unlikely to pique their attention.
- The S – Socialiser (formerly known as the Mover) – The ‘strong S’ personality has a great need to communicate. This aspect implies talking about people, fun, events, what you did over the weekend, or anything related to life. Hence, their straightforward, friendly, and frequent grin immediately.
- The D – Doublechecker – The ‘strong D’ is characterized by a desire to look after others and ensure everyone is safe. When you encounter a strong D, expect someone obedient, loyal, and concerned with doing the right thing. One of their greatest assets is their ability to anticipate difficulties and hazards.
- The A – Artist – A person with a ‘strong A’ desires to create. “I want to be different,” is what they would say. These hardworking individuals are conscientious and do not wish to offend anyone. Seek for anything unusual about their attire, such as innovative earrings, cufflinks, a six-button jacket, or an all-black ensemble!
- The P – Politician – A solid handshake and direct eye contact indicate that the ‘strong P’ is determined to win. This person has a determination and strength that others may find challenging. The spoken word is the strong P’s stock in trade – look for status markers like the huge Mercedes in metallic blue.
- The E – Engineer – A person with a ‘strong E’ personality is driven to accomplish undertakings. The strong E has traits such as process, detail, and procedure. This individual can form a strategy and make it happen as soon as they see anything. The E is concerned with completion. So, unless you can assist, you should avoid getting in the way!
Wisdom – strive for mental stability and individual resilience – 10 Competencies
Wikipedia defines wisdom as the “ability to contemplate and act using knowledge, experience, understanding, common sense, and insight.” Psychologists have created a list of ten competencies that are typical therapies in their field and are referred to as wisdom. Self-awareness, self-control, and empathy are the three components of emotional intelligence (EI). Although the fourth component of EI is not formally mentioned among the ten competencies, social influence or influencing others may be considered a result of being highly effective in the other areas.
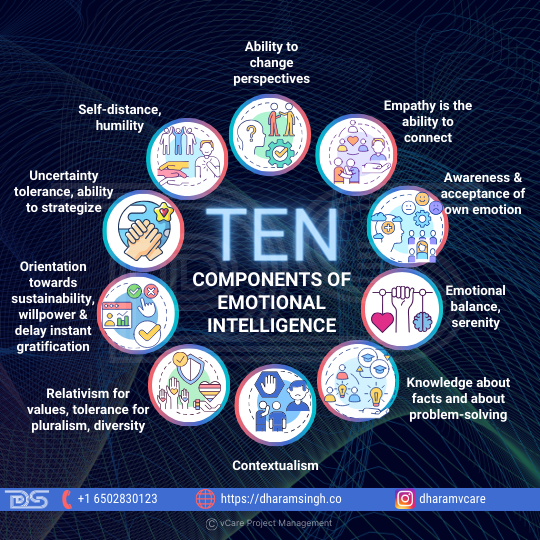
Ten Components of Emotional Intelligence
- Ability to change perspectives – In a bipolar environment, it is possible to remain trapped in one thought and dislike the other viewpoint with strong emotions, which may lead to violence. The ability to look for and identify more points of view implies a shift in viewpoint. Some of the therapies used to treat mental illnesses can help with this. Examples include role-playing, acting, visiting people in various countries, learning about diverse cultures, and brainstorming.
- Empathy is the ability to connect – Understanding people’s intentions, current state of mind, emotions, and mindsets is necessary for being heard, establishing trust, and influencing others. In addition, active listening techniques may help you focus outside yourself and view others as humans who vary from ourselves.
- Awareness & acceptance of own emotions (self-awareness) – Self-awareness leads to increased self-confidence and sincerity. It refers to mindfulness, or being aware of one’s feelings, and is required for self-control and emotional balance.
- Emotional balance, serenity (self-control) – Patience, serenity, and avoiding knee-jerk reactions make you more popular and respected and contribute to mental tranquility. Having a mentor can help you develop and fine-tune this skill.
- Knowledge about facts (know what, assimilation) and about problem-solving (know-how, accommodation) – Wisdom includes knowledge; therefore, it has two components.
- On the one hand, we have factual knowledge about a topic; on the other, we may be specialists in a (typically technical) area. This heuristic knowledge and assimilation are how we apply established systems to circumstances.
- On the other hand, when we encounter new situations or topics, we use accommodation to apply our problem-solving skills. We employ our epistemic intelligence and heuristics to do this.
- Contextualism (consider the situation, timeline, and social relevance) – Even though we have theories and may find similarities in new scenarios, each situation is unique and depends on the circumstances, the context in which the problem develops, and the societal importance. This capacity is achieved via awareness and avoiding picking a solution that works in another context without first examining the present dependencies of the situation.
- Relativism for values, tolerance for pluralism, diversity (which is hard if you are part of the same belief systems for most of your life, like nations and churches) – There are many truths (this is known as non-monism), and yours is only one of them. Others have the right to their realities, which are based on the cultures in which they live, their beliefs and experiences, and the facts to which they have access. Value relativism allows one to accept and appreciate the values of others.
- Orientation towards sustainability, willpower, and delay instant gratification (perspective of linear and circular time flow) – We can pursue long-term goals and make decisions with both short and long-term consequences in mind.
- Uncertainty tolerance, ability to strategize (imaging solutions for scenarios) – Accept that life is unpredictable and swim through it like a river, adapting to currents and waves as they come.
- Self-distance, humility – Do not believe you are the center of the universe, which will remain when you die. Avoid being a taker rather than a giver by avoiding jealousy, bragging, pride, and greed.
Final Thoughts
For today’s project managers, emotional intelligence is a critical concept. Many companies are looking for project managers with strong technical and soft skills. Emotional intelligence is crucial in project management because it enables project managers to improve communication and collaboration in the workplace. It is essential to mention that emotional intelligence can be imparted and nurtured. This aspect implies that as a project manager, one can better oneself by controlling feelings and emotions and developing positive behaviors to influence others at work. One will make better decisions about other people’s emotions, strengths, and weaknesses once they have recognized their thoughts.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd











































Recent Comments