
by DharamCW | Jun 30, 2025 | General, Project-Program-Portfolio Management Knowledge
🔵 Mental Health in Project Management: A Conversation We Must Have 🔵
Project managers are trained to deliver results, but what happens when the pressure becomes too much to bear?
In my 30+ years of mentoring, I’ve seen even the most capable professionals silently battle stress, burnout, and mental health challenges. It’s time we open up the conversation – because behind every successful project is a human being managing emotions, expectations, and exhaustion.
Here are 8 common mental health challenges faced by project professionals:
-> Stress
Tight deadlines, pressure, job insecurity, long hours, and heavy workloads are key causes of workplace stress.
-> Insufficient Assistance for Workers
Lack of support fuels these problems. Encouraging openness and honest dialogue boosts employee well-being.
-> Burnout
Burnout is common in many careers, marked by low energy, frustration, and dissatisfaction with work goals.
-> Anxiety
Workplace stress can lead to anxiety, often showing as social discomfort, avoidance, or conflict with coworkers.
-> Insufficient Leadership or Clarity
Poor role clarity and weak communication create a stressful work environment.
-> OCD
OCD causes unwanted thoughts and behaviors like over-checking or task delays, leading to stress at work.
-> Depression
It can be triggered by home problems, stress, and feelings of incompetence or insignificance.
-> Substance Use Disorder
Work stress can lead to substance use, with alcohol, marijuana, and painkillers being commonly abused.

Project success shouldn’t come at the cost of mental health. Let’s talk about stress, burnout, and wellness in project leadership.
👉 These are real issues. Let’s not pretend otherwise.
🔁 Save & Share this if it resonates.
💬 What mental health challenges do you or your team face in high-pressure project environments?
Let’s open up – your voice could help someone else find theirs.
Free Consultation (Career, PMI Certifications):
Book a free 15-minute session with me, http://talktodharam.com
Subscribe for More:
Certification Success Stories https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
My Podcasts and Interviews: https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
Contact Us:
Call us: +1 9722927588 / +1 6502830123
#MentalHealthAwareness #ProjectManagement #BurnoutPrevention #WorkplaceStress #PMOLife #DharamSingh #vCareProjectManagement #LeadershipWellbeing #ProjectManagerSupport #PMICommunity #StressManagement #WorkplaceMentalHealth #AnxietyRelief #TeamWellbeing #PortfolioLeadership #ProgramManagement #PfMP #PgMP #PMP #PMO

by DharamCW | May 28, 2025 | General, Leadership in Project Management
Driving change is never easy — but having a structured approach makes all the difference.
In my mentoring and consulting experience across 57+ countries, I’ve seen how organizations thrive when they follow a well-defined change framework.
Here’s a widely recognized and practical 8-Step Process for Leading Change that can support your transformation journey:
🔹 Step 1: Create urgency
Identify potential threats and opportunities that drive the need for change.
🔹 Step 2: Form a powerful coalition
Identify the change leaders. Change leaders are not necessarily based on hierarchy. The change leaders should be influential people from a variety of roles, expertise, social, and political importance.
🔹 Step 3: Create a vision for change
Identify the values that are central to the change. Then create a brief vision statement that summarizes the change. Next, identify a strategy to realize the vision.
🔹 Step 4: Communicate the vision
Communicate the vision throughout the change process. Apply the vision throughout all aspects of the organization. Senior management and the change coalition should consistently communicate the vision and demonstrate the urgency and benefits of the change.
🔹 Step 5: Remove obstacles
All change comes with obstacles. Sometimes the obstacles are outdated processes, sometimes they are based on the organizational structure, and sometimes they are people resistant to change. Regardless, all obstacles need to be addressed.
🔹 Step 6: Create short-term wins
Identify quick and easy wins to build momentum and support for the change.
🔹 Step 7: Build on the change
Once the short-term wins are complete, the organization needs to set goals for continued improvement.
🔹 Step 8: Anchor the changes in corporate culture
Ensure the change becomes ingrained into the culture: continue to communicate the vision, tell success stories, recognize people in the organization who embody and empower the change, and continue to support the change coalition.
At vCare Project Management, I work closely with professionals navigating change at project, program, and portfolio levels.
💬 How does your team ensure that change efforts are sustained long term?
Let’s discuss below.
View our upcoming PMP Programs
Online → https://bit.ly/2BU0mFp
Direct → http://bit.ly/3ic7GRF
View our upcoming PgMP® Programs
Online → http://bit.ly/2oBKQXQ
Direct → http://bit.ly/2oCfpg0
View our upcoming PfMP® Programs:
Online → http://bit.ly/39jOZSf
Direct → http://bit.ly/38er2M3
🎙️ Got questions about your Project Management career or PMI certifications?
Book your FREE 15-min session with me at 👉 www.talktodharam.com
📞 Contact Us
Call: 650-283-0123
Email: info@vcareprojectmanagement.com
🎧 Subscribe & Stay Ahead
Webinars & Success Stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
Podcasts & Interviews: https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
#ChangeLeadership #PgMP #PfMP #vCareProjectManagement #ProgramManagement #StrategyExecution #PortfolioManagement #DharamSingh #ProjectManagement #LeadingChange #OrganizationalTransformation #LeadershipFramework #ChangeManagement #MentorshipMatters #ProjectSuccess #SustainableChange #ChangeChampions #KotterModel

by DharamCW | May 25, 2025 | General, Leadership in Project Management, Personal, Professional Resilience and Inspiration Stories
Project management is a challenging yet rewarding task in the corporate world, requiring multitasking, team dynamics, and timely delivery. Project managers are responsible for enhancing team wellbeing and stress reduction, benefiting both the team and themselves. They can achieve this by providing realistic timeframes, budgets, and fostering high-performing teams. They also monitor team performance to identify signs of burnout and stress, offering coping mechanisms when needed. Project managers must prioritize their teams’ welfare by engaging in their duties to manage projects and lead teams.

Great project managers don’t just lead projects—they lead people. Supporting team wellbeing drives sustainable success and peak performance.
Project management is a demanding field that requires balancing deadlines, team relations, and excellence. The corporate culture often overlooks the importance of mental health treatment, creating an artificial opposition between vulnerability and toughness. Project managers can model a new leadership culture that prioritizes project success and mental health. This requires a more nuanced definition of resilience, focusing on emotional intelligence, adaptability, and an active attitude towards mental health.
To address this issue, project managers should promote open conversations about mental health and implement policies that enhance team members’ welfare. This article is aimed at project managers and organizations looking to build leadership skills and create a culture where mental health is a key element of success.
Why Mental Health Matters in Project Management?
Mental health is essential in project management since an anxious or burnt-out team will be able to significantly contribute to the failure of a project by causing low productivity, bad decisions, increased turnover, and ultimately, project failure; hence, giving mental health priority in a project team is very important to get best project outcomes.

Strong project management starts with strong minds. Learn why prioritizing mental health leads to resilient, high-performing teams.
Important factors why mental health is important in project management:
1. High-pressure environment: Project management is most frequently marked by tight schedules, complicated activities, and high expectations, which readily create burnout, stress, and anxiety if not properly handled.
2. Effect on productivity: When employees are suffering from mental health problems, their attention, concentration, and overall performance are diminished, leading to a deceleration in project progress.
3. Team dynamics: Having an employee with mental issues can ruin team morale and collaboration, leading to a dysfunctional working environment.
4. Decision-making: Stress and anxiety can undermine critical thinking and decision-making with adverse effects on project success.
5. Absence and turnover: Mental illness workers will likely take more sick leave or leave the company, causing disruption to operations and adding workloads to other employees.
6. Employee retention: Effective workplace health with regard to mental health can promote good employees to be retained.
Common Mental Health Challenges in Project Management
Common mental health problems faced by the project managers are stress, anxiety, burnout, depression, and sleep disturbance, typically triggered by problems like tight deadlines, high stakes, complex demands of the projects, scope changes, and inadequate resource allocation, which leave the managers feel overwhelmed and out of control.
Discussions on mental health are becoming increasingly common in the workplace, since 15% of workers between the ages of 18 and 29 believe their mental health is severely bad. 70% of senior staff members lack the requisite training to have conversations with their teams on mental health, according to a recent National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) survey. Also, The World Health Organization estimates that depression and anxiety cause 12 billion lost working days a year, which translates into $1 trillion in lost productivity. This means that an employee’s mental health has a big influence on their company. As a result, workplace mental health has to be given more attention.
The following are some professional mental health risk factors:

Recognize the warning signs. From stress and burnout to anxiety and OCD—mental health challenges are real and manageable in the workplace.
· Stress – This is the primary cause of poor mental health at work. Deadlines, pressure from supervisors or coworkers, job uncertainty, long hours, and a high workload are all sources of stress.
·Burnout – The majority of employees encounter burnout at some point throughout their career. Lack of drive and enthusiasm, impatience, irritation, and dissatisfaction with work objectives and achievements are all signs of job burnout.
· Insufficient leadership or clarity – A stressful work atmosphere is created when roles and duties are not clearly defined, or when management and staff do not communicate effectively.
· Insufficient assistance for workers – The root cause of all of these issues and more is a lack of employees support. By offering forums for employees to voice their thoughts, complaints, and opinions, being transparent about mental health concerns are all ways to support employees.
· Depression – Depression, a major depressive disorder, affects 17.3 million adults in the U.S., including 7.1% of people aged 18 and older. It can be triggered by home problems, stress, and feelings of incompetence or insignificance.
· Anxiety – Anxiety is a common mental health issue in the workplace, often resulting from stress. It can manifest as social anxiety, which involves avoiding happy hours, difficulty confronting co-workers, or interpersonal struggles. General anxiety, on the other hand, is characterized by worry about the future at the company, constant stress over deadlines or tasks, or perceived tension and disaster.
· OCD – Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a serious disorder that can manifest as persistent, unwanted thoughts or obsessions, multiple rereads of a project, or difficulty completing daily tasks. These issues can lead to significant stress and strain in the workplace.
· Substance Use Disorder – Triggered by stress or negative work-related issues, often leads to substance use. Commonly abused substances include alcohol, marijuana, and painkillers. This is not just a one-time event; it’s a mental disorder involving brain rewiring and chemical imbalances. 9.5% of working adults have a substance use disorder, and it can lead to poor decision-making, missed work, increased conflict, and other negative outcomes.
Reasons why mental illness peaked in project management in recent times
· Unrealistic timelines: Tight deadlines might create unnecessary tension and lead to rushed decisions.
· Scope creep: Ongoing variations in project scope can lead to confusion and cumulative workload.
· Lack of adequate communication: Unclear communication to stakeholders can develop misunderstandings and tension.
· Poor resource allocation: Insufficient human resources or necessary competencies to carry out a project might lead to frustration and burnout.
· Work-life imbalance: Failure to separate work life and personal life with long work hours and unnecessary demands.
Ways to minimize mental health problems in project management
· Healthy work-life balance: Support normal breaks, holidays, and flexible working hours.
· Open communication: Build an open atmosphere where staff members are free to openly speak about problems and concerns.
· Good project planning: Set attainable objectives, handle expectations, and forecast potential risks.
· Stress management methods: Provide exposure to mindfulness instruction, relaxation training, and staff aid schemes.
· Leadership development: Provide project managers with the ability to handle stress, delegation, and assistance of team members.
The Role of Project Managers in Supporting Mental Health of their team members
Project managers play a crucial role in fostering a healthy workplace by addressing the mental health of their team members. Overwork, poor management techniques, and lack of support can lead to stress, anxiety, and despair, resulting in a toxic atmosphere. Bullying and harassment may also contribute to these issues. To overcome these issues, project managers should identify their root causes and adopt proactive measures such as stress management resources, leadership training, anti-harassment measures, and a positive work atmosphere. This not only improves team performance and project success but also fosters a healthier workplace by ensuring that excessive demands do not worsen team members’ mental health.
Project Managers’ Role in Mental Health
Project managers can shape a healthier workplace. From awareness to access—lead the change for better mental wellbeing in your teams.
· Awareness and Training:Project managers must be able to identify the early signs of mental stress. Training that emphasizes mental health awareness may provide managers the tools they need to properly assist their personnel.
· Creating a Supportive Work Environment:It’s critical to have a culture at work that values employees’ well-being. Realistic expectations, breaks, and open discussions regarding mental health issues should all be promoted by managers.
· Access to Mental Health resources:It’s critical to guarantee that team members have access to mental health assistance. This entails forming relationships with healthcare providers and providing resources in an accessible manner.
Facts that Long-Term Effects of Ignoring Team’s Mental Health in project management
· Impact on Productivity:Long-term stress and burnout impair team productivity and project success in addition to lowering individual performance.
· Issues with Retention and Turnover: An expensive and disruptive cycle of training and retraining can result from high turnover rates, which are a result of high stress conditions.
· Organizational Reputation:Businesses that have a bad reputation for handling work-related stress may have trouble attracting top people, which might hurt their ability to compete in the market.
Ways to Improve Mental Health amongst the team members in project management

Effective leadership goes beyond task management. Learn five ways project leaders can nurture mental health and build resilient, thriving teams.
1. Developing an Engagement Culture
Leadership principles have a significant impact on a team’s culture. For example, democratic and transformative leaders frequently promote an environment of transparency and participation. These settings foster initiative and idea sharing among team members, which can boost their commitment to project results and job happiness. Effective communication, mutual support, and a shared goal are all characteristics of engaged teams that lower the risk of burnout.
2. Leadership Adaptability
The flexibility of leadership styles is a crucial element that isn’t specifically addressed in the table. In order to better address the demands of their team under changing conditions, effective leaders frequently combine aspects of several styles. For instance, in order to swiftly establish precise goals and standards in the early phases of a project, a more autocratic approach may be required. Including democratic components can assist the team stay engaged and motivated as the project moves forward, lowering the stress and powerlessness that cause burnout.
3. Leadership & Emotional Intelligence
In order to manage stress and avoid burnout, leaders must possess emotional intelligence. Emotionally intelligent leaders are able to identify the psychological and emotional requirements of their team members. They are skilled at adapting their support, encouragement, and communication tactics to the moods of the team and the individual. This skill is especially helpful in high-stress situations when customized support may reduce tension before it becomes burnout.
4. Proactive leadership and preventative measures
The goal of proactive leadership is to foresee certain stressors and put plans in place to lessen them before they have an adverse effect on the team. By proactively identifying the symptoms of burnout, leaders may reduce stress by adjusting workloads, project scopes, and deadlines. Furthermore, providing tools for mental health assistance, such as stress management classes and access to counseling, may improve team well-being.
5. Leadership Development Programs
Project managers and leaders may successfully modify their management style to meet the demands of their team by investing in leadership development programs. The range of conflict resolution, emotional intelligence, stress management, and leadership styles should all be included in these programs. A more thorough knowledge of how leadership affects mental health might help organizations better equip their leaders to build wholesome, effective teams.
Many people still fail to recognize the intensity of stress at work, concentrating only on results and ignoring the human factor. Project managers who are unable to adequately manage workload risk not only team burnout but also leadership failure.
Including Mental Health Wellness Techniques in Project Management
· Proactive Mental Health Initiatives:Implementing proactive mental health efforts, including as wellness programs, stress management seminars, and routine mental health check-ins, can aid in the early detection and treatment of mental health and stress-related problems.
· Flexible Work Schedules:Promoting remote work and flexible work schedules may greatly lower stress, enhance work-life balance, and, consequently, improve mental health.
· Systems for Acknowledgment and Compensation:A more balanced attitude to work is encouraged by putting in place procedures that acknowledge and reward both results and good work habits, which highlights the significance of mental health.
Project managers are tasked with protecting their team’s mental health, preventing stress and fostering a productive work environment. They must prioritize their teams’ mental and emotional health above any project milestone. By broadening their focus to include these crucial components, project managers can ensure their teams are not only successful but also content and healthy in their work environments, ensuring a healthy and productive work environment.
Toolkit for Project Managers and Teams on Mental Health
Building a Mental Health Toolkit for company employees entails gathering tools and tactics to promote workers’ mental health.
Here are some essential components to incorporate:

Equip your project team with the right tools. This mental health toolkit empowers leaders to build supportive, resilient, and high-performing workplaces.
1. Educational Materials: This document provides information on mental health disorders, workplace stigma reduction, stress management resources, resilience building, and self-care.
2. Policy and Procedure Guidelines: Sample policies for mental health support and accommodations, workplace crisis handling procedures, and guidelines for confidentiality and privacy regarding mental health issues.
3. Training Modules: Training sessions for managers and employees on mental health, communication skills, empathy, active listening, and promoting work-life balance are being conducted to prevent burnout.
4. Supportive Resources: This document provides contact information for mental health professionals, EAPs, helplines, referral pathways for counseling, therapy, or psychiatric services, and information on insurance coverage for mental health treatment.
5. Promotion and Communication Strategies: This document provides materials for raising mental health awareness, communication strategies for promoting initiatives, and platforms for sharing success stories, testimonials, and best practices within an organization.
6. Crisis Management Resources: This document provides protocols for handling workplace mental health emergencies, emergency contact information, and immediate support and follow-up care for employees in crisis.
7. Evaluation and Feedback Mechanisms: The toolkit involves surveys for feedback on mental health initiatives’ effectiveness, monitoring metrics like absenteeism and turnover rates, and regular reviews and updates to the toolkit based on feedback and organizational needs.
8. Risk Assessment and Prevention: This document provides tools for assessing workplace stressors, strategies for preventing bullying, harassment, and discrimination, and resources for promoting psychological safety and inclusion.
9. Peer Support Networks: The text suggests implementing peer support systems, training employees to offer mental health guidance, and promoting open discussions and forums for employees to discuss challenges and coping strategies.
10. Wellness Initiatives: Programs promoting physical activity, healthy eating, and sleep hygiene, as well as supportive work environments like flexible schedules and remote work options, are essential for a healthy lifestyle.
Real-world examples of organizations successfully addressing mental health

From Google to Nike—these 10 companies are redefining how workplace mental health is approached through proactive, supportive, and sustainable practices.
1. Google – Employee Assistance & Mental Health Days
Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs), peer support groups like “Blue Dot” where employees may openly discuss mental health concerns, and on-site counseling services are just a few of the mental health initiatives that Google has implemented. It also organizes company-wide mental health days, such as the “Day of Reflection,” to motivate staff to prioritize their health and take breaks.
2. Microsoft – Mental Health Leave & Well-being Support
In order to provide employees more time to concentrate on their mental health, Microsoft provides five extra paid mental health days annually. They offer free access to mental wellness coaching for employees and treatment via telemedicine services. Microsoft also offers a wellness reimbursement program that pays for things like exercise classes and meditation applications that promote mental and emotional well-being.
3. Unilever – Mental Health Champions & Flexible Work
Unilever has created a global network of Mental Health Champions, which consists of trained staff members who provide peer support and help create a psychologically safe workplace. They promote “agile working” as well, which enables employees to design flexible work schedules that accommodate their needs for both personal and mental well-being.
4. Deloitte – Mental Health Ambassadors & DE stigmatization Campaigns
Deloitte has taken the lead in addressing workplace mental health by appointing mental health champions and initiating awareness campaigns to reduce the stigma attached to discussing mental health. Their “This is Me” initiative encourages employees to submit personal stories regarding mental health in order to foster an open and supportive work environment.
5. Starbucks – Free Therapy & Mental Health Training
Through the Lyra Health platform, Starbucks offers 20 complimentary therapy sessions annually to all U.S. employees and their families. Additionally, the company provides shop managers with mental health first aid training, enabling them to identify symptoms of distress and provide team members with the right kind of assistance.
6. PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers) – Mental Health Coaching & Well-being Apps
By providing subsidized therapy sessions and one-on-one mental health coaching, PwC has incorporated mental health into its overall well-being plan. Additionally, employees have access to applications for mental health like Headspace and Thrive, which offer stress-reduction techniques, mindfulness training, and guided meditation.
7. Accenture – Employee Assistance & Resilience Training
Comprehensive Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) from Accenture include mindfulness training, round-the-clock counseling, and individualized mental resilience training. Additionally, they have a “Truly Human” campaign that highlights the value of mental health and self-care in a high-achieving workplace.
8. Johnson & Johnson – Holistic Mental Health Approach
With an emphasis on physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual well-being, Johnson & Johnson incorporates mental health into their “Energy for Performance” program. Employees have access to mental fitness training, on-site mental health counseling, and company-sponsored mindfulness and meditation programs.
9. Salesforce – Mindfulness Rooms & Employee Well-being Grants
Salesforce supports workplace mental health by providing employee well-being grants that enable staff members to receive financial assistance for mental health services like coaching, therapy, or wellness retreats, as well as by creating “Mindfulness Zones,” which are quiet areas in offices where staff members can meditate or take breaks.
10. Nike – Global Mental Health Training & Paid Rest Days
Nike started a program called “Mental Health First Aid” to teach employees and managers how to identify and handle mental health issues. In order to minimize burnout and promote mental recuperation, they also instituted paid rest days for the whole organization, such as a full week off for corporate workers.
Strategies for a Balanced Approach in Project Management
So, from all the real-world examples of organizations successfully addressing mental health, an effective project management is now crucial for businesses to keep ahead of the competition in the increasingly complicated and competitive business sector. The capacity to properly manage a project is crucial to its success, regardless of its size.
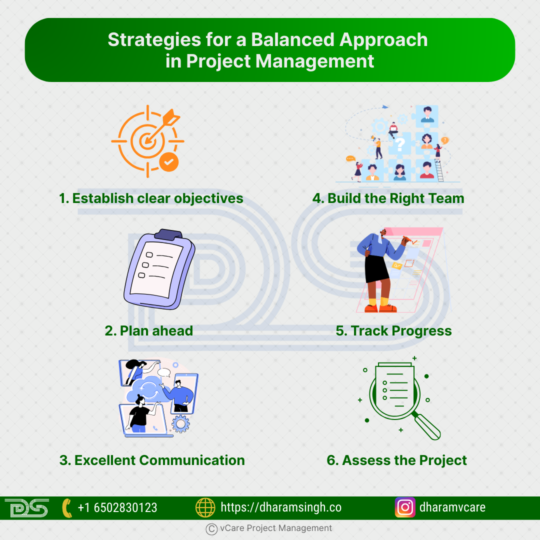
A successful project isn’t just about deadlines—it’s about clarity, teamwork, communication, and care. Here’s how to strike the right balance.
· Establish clear objectives: Having well-defined objectives is important for effective project management. Make sure that everyone engaged is aware of the project’s goals and that they are clearly defined.
· Plan ahead: Developing a strategy that details the actions necessary to accomplish your project’s objectives is the next stage. Create backup plans to deal with any obstacles that may arise. A project’s budget, schedule, and necessary resources should all be included in a solid plan.
· Excellent Communication: The keys to successful project management is excellent communication. Continually update all stakeholders on the status of the project and any modifications to its scope or schedule. Organize frequent check-ins or meetings to make sure everyone is in agreement.
· Build the Right Team: The team that works on a project has a big impact on its success. For each activity, make sure you have the appropriate individuals with the requisite training and expertise. Promote cooperation and teamwork to create a happy workplace.
· Track Progress: Monitoring progress is crucial to making sure the project is proceeding as planned and that objectives are being fulfilled. To monitor developments, spot any bottlenecks, and make necessary corrections, use project management software.
· Assess the Project: After the project is finished, spend some time assessing its effectiveness. Determine what needs to be improved, then make the necessary adjustments for next projects.
Conclusion
In project management, mental health is not only a primary issue, rather it is a critical component that affects team output, performance, and project success as a whole. The necessity for project managers to provide a supportive atmosphere where team members feel heard, respected, and capable of managing stress has been highlighted by the increased awareness of mental health issues in the workplace.
Project managers need to think about these important concerns in order to address these challenges:
· How to successfully strike a balance between team well-being and high performance standards in order to avoid burnout?
· What techniques may employ to foster a psychologically healthy workplace?
· What is the effect of emotional intelligence on a project manager’s capacity to encourage team morale and motivation?
· What part does risk management play in recognizing and reducing mental health risks?
· How to help teams who are dealing with unpredictability and short timelines become more resilient and adaptable?
The first step in addressing the influence of mental health on both individuals and teams in project management is to comprehend why it matters. Burnout, short deadlines, and a poor work-life balance are common issues that can lower morale and productivity. This emphasizes how important it is for project managers to foster an environment of open communication, psychological safety, and proactive assistance.
In order to enhance the well-being of team members, businesses need to put into practice useful tactics, such as mental health toolkits, organized support systems, and training courses that enable managers to identify and successfully handle mental health issues. Furthermore, a comprehensive strategy that incorporates flexible work arrangements, stress management programs, and practical project planning is needed to strike a balance between project needs and employee well-being.
Organizations have shown that prioritizing mental health initiatives leads to stronger teams and better project outcomes. By embedding mental health awareness into project management practices, organizations can create a healthier, sustainable work environment that benefits both employees and project success. Fostering a culture of mental well-being should be an integral part of the project leadership.
#ProjectManagement #MentalHealthAwareness #TeamWellbeing #BurnoutPrevention #LeadershipDevelopment #vCareProjectManagement #DharamSingh #PMICertification #ProjectSuccess #EmployeeSupport #WorkplaceWellness #LeadershipMatters #HealthyTeams #MentalHealthToolkit #EmotionalIntelligence #FlexibleWork #CorporateCulture #StressManagement #ProjectLeadership #WellbeingAtWork

by DharamCW | May 15, 2025 | General, Leadership in Project Management
⏱️ In the rush to deliver fast, are you forgetting to deliver right?
After mentoring hundreds of project, program, and portfolio managers, I’ve seen one truth stand out: Speed means nothing without thoughtfulness. Swipe through these 5 essential principles to help you find that balance 👇
✅ Prioritize What Matters
– Identify the most critical tasks and focus your resources there
– Not everything needs to be done quickly — some things need to be done right
✅ Plan for Agility
– Use flexible frameworks like Agile or iterative planning
– This helps you adapt to changes while maintaining a thoughtful approach
✅ Communicate Clearly
– Keep your team aligned with clear, concise updates on priorities and timelines
– Thoughtfulness in communication reduces confusion and builds trust
✅ Evaluate Risks Carefully
– Weigh the trade-offs between speed and long-term impact
– Take calculated risks but avoid shortcuts that could lead to project failures
✅ Reflect and Refine
– After each phase, review what worked and what didn’t
– Continuous improvement ensures that speed and thoughtfulness remain balanced throughout the project
💭 Fast isn’t always forward.
👉 How do you personally balance speed with thoughtfulness in your projects?
Let’s open the conversation.
View our upcoming PMP Programs
Online → https://bit.ly/2BU0mFp
Direct → http://bit.ly/3ic7GRF
View our upcoming PgMP® Programs
Online → http://bit.ly/2oBKQXQ
Direct → http://bit.ly/2oCfpg0
View our upcoming PfMP® Programs:
Online → http://bit.ly/39jOZSf
Direct → http://bit.ly/38er2M3
🎙️ Got questions about your Project Management career or PMI certifications?
Book your FREE 15-min session with me at 👉 www.talktodharam.com
📞 Contact Us
Call: 650-283-0123
Email: info@vcareprojectmanagement.com
🎧 Subscribe & Stay Ahead
Webinars & Success Stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
Podcasts & Interviews: https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
#ProjectManagement #PgMP #PfMP #PMP #Agile #Leadership #StrategicThinking #DharamSingh #vCareProjectManagement #SpeedVsQuality #PMICertifications #ContinuousImprovement #RiskManagement #TeamAlignment #ProjectLeadership

by DharamCW | May 11, 2025 | General, Industry Trends and Insights, Leadership in Project Management, PMI Certification Insights, Program Management
🎯 Is Program Management Professional (PgMP) certification the next step in your leadership journey? Before you jump in! Do you know which path you’re eligible through?
Let me make it simple for you 👇
✅ Set A – High School / Secondary Diploma
📌 48 months of project management experience (or PMP®)
📌 84 months of program management experience
🕒 All within the past 15 years
✅ Set B – Bachelor’s Degree or Higher (Global Equivalent)
📌 48 months of project management experience (or PMP®)
📌 48 months of program management experience
🕒 All within the past 15 years
✅ Set C – GAC-Accredited Degree (Bachelor’s or Master’s)
📌 36 months of project management experience (or PMP®)
📌 36 months of program management experience
🕒 All within the past 15 years
🚀 I’ve personally mentored 551+ PgMP® certified professionals across 57+ countries, including 168+ from the United States alone.
View our upcoming PgMP Programs
Online – http://bit.ly/2oBKQXQ
Direct – http://bit.ly/2oCfpg0
📅 If you’re unsure where you fit or how to prepare,
👉 Book a 15-minute, obligation-free session with me:
http://talktodharam.com
📞 For queries: +1 650-283-0123
💬 Which set do YOU fall under—A, B, or C?
Comment below and let’s discuss your PgMP® path!
#PgMP #ProgramManagement #PgMPEligibility #DharamSingh #vCareProjectManagement #StrategicLeadership #PMICertifications #PMI #PgMP2025 #CareerAdvancement #LeadershipJourney #ProjectToProgram #pgmpexamprep

by DharamCW | May 1, 2025 | General, Industry Trends and Insights, Leadership in Project Management

GEICO program managers and Dharam Singh united for strategic PgMP excellence at Maryland HQ

by DharamCW | Apr 24, 2025 | General, Project Management, Project-Program-Portfolio Management Knowledge
🔍 Top Leadership Skills for a Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Role
The role of a CTO goes far beyond just overseeing technology.
✅ Driving innovation
✅ Aligning tech with business goals
✅ Leading technical teams with expertise and vision
Here are 4 key leadership skills every aspiring or current CTO must master:
1️⃣ Mastering Strategic Thinking
Anticipate trends, align technology with business goals, and drive growth through informed decisions.
2️⃣ Excelling in Communication and Collaboration
Align stakeholders, inspire teams, and simplify technical concepts into actionable insights.
3️⃣ Staying Ahead with Technical Expertise
Balance leadership with up-to-date knowledge to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge.
4️⃣ Leading and Developing High-Performing Teams
Empower employees, foster growth, and build a positive, performance-driven culture.
💬 Which of these skills do you believe is most critical for a CTO today?
Comment below and let’s spark a conversation.
🔁 Don’t forget to Like, Share, and Save this post if you found it insightful.
🔗 Want to explore more?
View our upcoming PgMP Programs
Online Training → http://bit.ly/2oBKQXQ
Direct Training → http://bit.ly/2oCfpg0
Explore Our PfMP Programs:
Online Training → http://bit.ly/39jOZSf
Direct Training → http://bit.ly/38er2M3
📞 For queries: +1 650-283-0123
🎥 Free Consultation with Me: https://lnkd.in/gwD-52JH
#CTO #LeadershipSkills #StrategicThinking #TechLeadership #Innovation #HighPerformingTeams #vCareProjectManagement #DharamSingh #TechnologyLeadership #BusinessStrategy #DigitalTransformation #ExecutiveLeadership #TeamDevelopment #CLevelSkills #CTORole #TechVision #InspireTeams #TechManagement #FutureLeadership #CTOSuccess

by DharamCW | Mar 26, 2025 | General, Industry Trends and Insights, Project-Program-Portfolio Management Knowledge
🚀 PfMPs – A High-Impact Opportunity Awaits in the Tech Sector!
I’ve received job requirements for 2-3 Portfolio Managers from a well-established technology company in Ohio, USA. These are onsite roles ideal for professionals who can lead from the front and drive strategic execution across programs and initiatives.
🛠️ PfMP® certification is a must – organizations are now actively seeking certified Portfolio Management Professionals to elevate their strategic decision-making.
🌍 Why PfMP® Matters Today:
With business landscapes becoming more complex and value-driven, companies are turning to PfMP®-certified professionals who bring a structured approach to aligning portfolios with organizational strategy, optimizing ROI, and enhancing governance. The PfMP® is no longer just a credential – it’s a mark of enterprise-level leadership and strategic impact.
📌 Key Details:
Role: Portfolio Manager (PfMP® Required)
Location: Onsite – Ohio, USA
Experience Levels:
• Level 1: 8+ years + PfMP
• Level 2: 15+ years + PfMP
📅 Deadline to Apply: April 4th, 2025
📩 Send resumes to: support@vcareprojectmanagement.com

Seeking PfMP-certified leaders! Apply now for onsite portfolio manager roles in Ohio’s growing tech industry – deadline April 4, 2025.
🎯 If you’re looking to contribute to a technology-driven environment and lead strategic portfolio execution – this is your moment.
📌 Explore Our PfMP® Programs:
🌐 Online Training → http://bit.ly/39jOZSf
🏛 Direct Training → http://bit.ly/38er2M3
📌 Join Our PfMP® Community:
PfMP4U LinkedIn Group → http://bit.ly/31P7GKR
📌Need expert guidance? Book a free consultation with me: http://talktodharam.com
Let’s drive portfolio excellence together.
For more details, feel free to connect with me directly.
#PfMP #PortfolioManager #StrategicLeadership #vCareProjectManagement #DharamSingh #PMI #OhioJobs #TechCareers #PfMPJob #PortfolioLeadership

by DharamCW | Feb 27, 2025 | General, Leadership in Project Management, Project-Program-Portfolio Management Knowledge
Mastering Problem-Solving: Techniques for Every Professional 🔍💡
Every challenge has a solution – you just need the right approach! Complex problems may seem overwhelming, but the right tools can help you analyze, innovate, and resolve issues effectively.
Here are some powerful problem-solving techniques to enhance your decision-making process:
✅ 5 Whys – Keep asking “Why?” to drill down to the root cause of the problem.
✅ Fishbone Analysis – A visual tool to identify multiple causes of an issue. Works well with ‘5 Whys’ and ‘Mind Mapping’ for structured brainstorming.
✅ Silent Brainstorming – Encourages equal participation, ensuring that both quiet and outspoken team members contribute meaningfully.
✅ Mind Maps – A structured way to visually organize thoughts, explore solutions, and drive team alignment.
✅ Six Thinking Hats – Helps teams evaluate problems from different perspectives—facts, risks, creativity, and logic.
✅ Agreement Certainty Matrix – Categorizes problems into simple, complicated, complex, or chaotic, helping teams decide the best approach.
✅ Conversation Café – Facilitates meaningful discussions with active listening to reach better team consensus.
✅ Design Thinking – A five-step method (Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test) to unlock creative solutions for complex challenges.
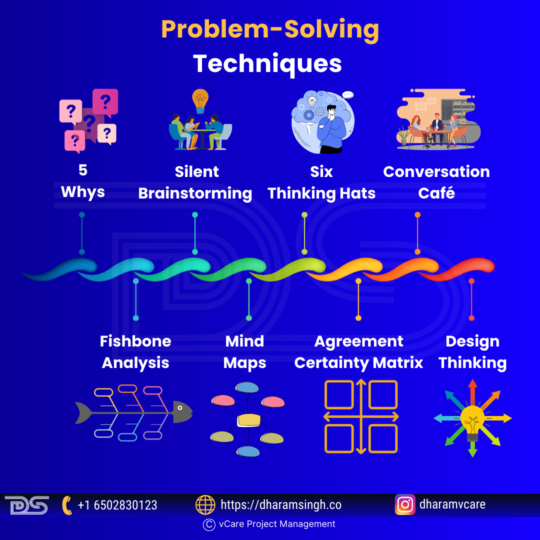
Master problem-solving with these expert techniques to enhance decision-making and innovation in any professional role.
💬 Which problem-solving technique do you use the most? Drop a comment below! 👇
🚀 Want to enhance your problem-solving skills?
Join me in these upcoming webinars featuring global experts:
🔹 Turning Business Goals into Reality with Marcelo Pessotto → https://bit.ly/4hhH4Yu
🔹 Resilient Leadership in Cyber-Driven Programs: Strategies from a Transformation Expert with Dr. Maria Sette → https://bit.ly/4j9fmPA
🎯 Explore More:
🔹 Book a free consultation on Project Management career, training & certifications → http://talktodharam.com
🔹 Exclusive training & certification discounts → https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
🔹 Get Q&A insights & success stories on my YouTube channel → https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
🔹 Listen to expert interviews on my podcast → https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
#PgMP #PfMP #PMP #ProblemSolving #CriticalThinking #CreativeThinking #Brainstorming #5Whys #FishboneAnalysis #MindMapping #Leadership

by DharamCW | Jan 28, 2025 | General, Project Management
Traditional businesses worldwide have long recognized that digital transformation is the key to thriving in a fast-paced world. Digital transformation involves integrating digital technology into all aspects of a business. It fundamentally alters how businesses operate and provide value to customers. It increases efficiency, transparency, customer experience, employee engagement, and culture and saves time and money. Modern digital tools have elevated the project management process to new heights.
The following are the seven critical elements of a successful strategic digital transformation framework:
1. Strategy and Leadership
2. Culture Change and Communication
3. Optimization of the Process
4. Data Curation
5. Technologies to be Implemented
6. Team Structure
7. Results – How to Measure the Success of Your Digital Transformation Strategy
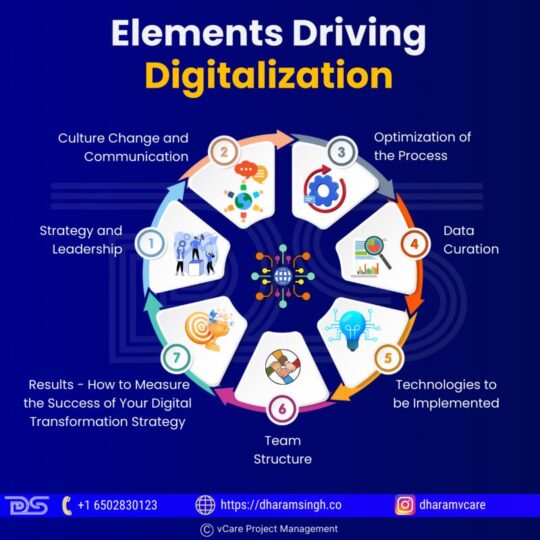
Elevate your business with a strong digital transformation strategy! Learn the 7 critical success factors.
🚀 Looking to deepen your knowledge? Check out our upcoming webinars featuring global experts,
1. PMO Digital Transformation Leadership: Insights and Success featuring Sherwyn Cambridge – https://bit.ly/4iMvyWE
2. Culture, People, Programs, Risks: Leadership Redefined featuring Lucie Ellis – https://bit.ly/3VXv4mW
3. Turning Business Goals into Reality featuring Marcelo Pessotto – https://bit.ly/4hhH4Yu
4. Resilient Leadership in Cyber-Driven Programs: Strategies from a Transformation Expert featuring Dr. Maria Sette – https://bit.ly/4j9fmPA
– Book an obligation-free consultation session on Project management Career, training, and certifications: http://talktodharam.com
– Discover training offers and certification discounts: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
– Stay updated with our Q&A series and certification success stories by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube channel at https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
– Follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
#DigitalTransformation #BusinessStrategy #TechInnovation #CultureChange #ProcessOptimization #DataDriven #DigitalStrategy #TechLeadership #AskDharam #DharamSingh

by DharamCW | Dec 25, 2024 | General
As we celebrate this season of giving and joy, I want to take a moment to thank all of you for being a part of my professional journey. May your Christmas be as bright and inspiring as your dedication to your goals. Cheers to a season of celebration and a year ahead full of opportunities!

Wishing you a bright and joyful Christmas! Cheers to a season of giving and a year full of opportunities.
#Christmas2024 #MerryChristmas #HolidayCheers #GratefulHeart #ChristmasJoy #FestiveSeason #ProfessionalJourney #YearOfOpportunities #ChristmasSpirit

by DharamCW | Oct 28, 2024 | General
Program/portfolio managers must make significant and minor decisions in the ever-changing project management environment. In many instances, their judgments and actions due to their more critical decisions may significantly influence their well-being and the prospects of clients and team members. Moreover, such decisions can impact the very nature of our jobs and even the lives of others who rely on them.
As equal to decision-making, problem-solving skills are essential in project management. Problem-solving is a project management skill that combines creative thinking and strong analytical abilities to assist effective problem solutions. This skill allows the project leader to look at challenges from a different angle and assist in designing and implementing successful solutions for making great decisions.
It’s easy to understand how, in problem-solving, recognizing simple solutions to complicated challenges might benefit the project and the company. Still, not all competent Project Leaders are capable of doing so. To be an effective problem solver and decision maker, the program/portfolio manager must possess specific skills and techniques to manage the project successfully.
Understanding the Decision Making Process in Project Management
All managers and other interested stakeholders must have a thorough grasp of decision-making in project management. The project will only then be able to progress toward the final delivery phase while maintaining the established timelines. The project runs a significant risk of stagnating or moving extremely slowly in this absence.
However, many businesses need help on several fronts because they need to recognize the value of decision-making in their management teams.
A McKinsey survey found that roughly 80% of professionals thought their firms’ decision-making processes could have been more efficient. Furthermore, the firms that demonstrated superior decision-making skills and topped the survey had better financial and performance outcomes.
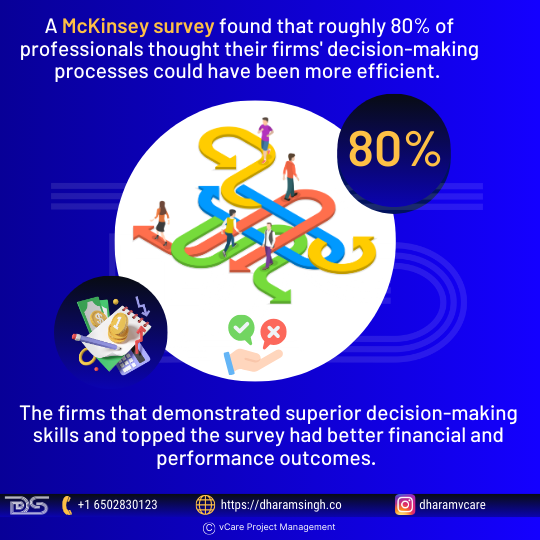
Why Efficient Decision-Making Matters for Firms
Decision-Making Types in Program/Portfolio Management
Decisions need to be made regularly in project management. Most are minor, but others are significant and will determine whether the project succeeds or fails. The same applies to program/portfolio management. Final choices can be reached using either an intuitive or logical method or a combination of the two. More intricate conclusions typically need a more formal, systematic approach incorporating intuition and reasoning. Not all decisions are the same. Management must make many decisions during a project, and each decision-maker is unique. The most common ones are listed below:
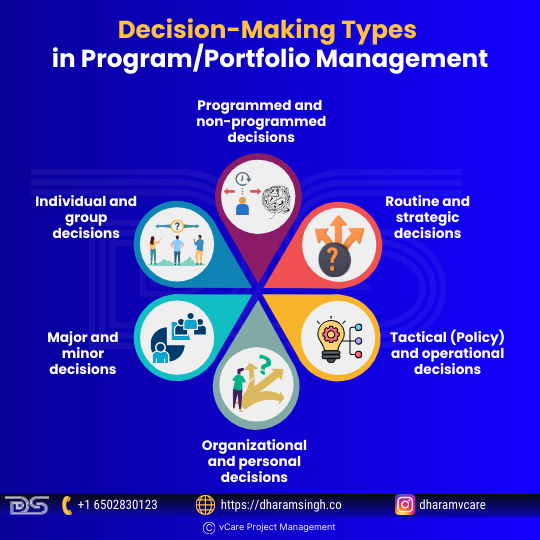
Decision-Making Types in Program/Portfolio Management
- Programmed and non-programmed decisions
Programmed decisions are concerned with problems of a repetitive nature or routine type matters. For example, decisions of this type may pertain to purchasing raw materials, granting leave, and supplying goods to the employee. Non-programmed decisions are made in challenging situations with no clear solution. These decisions need more attention, resources, and time and are usually made at a higher level.
- Routine and strategic decisions
Routine decisions affect the overall operation of a project and can be made rapidly. Within the broad policy framework of the project manager or the organization, ample powers are granted to lower ranks to make these decisions. However, strategic decisions are essential and affect objectives, organizational goals, and other important policy matters. These decisions usually involve a program’s orientation or huge investments in portfolios, are non-repetitive, and are taken after careful analysis and evaluation of alternatives.
- Tactical (Policy) and operational decisions
Portfolio managers make policy decisions that have a long-term impact on the functioning of the concern. For example, decisions regarding how many projects can be run each time according to the budget are policy decisions. On the other hand, operational decisions relate to the day-to-day functioning or operations of the business. Middle—and lower-level managers make these decisions. For example, decisions concerning the payment of bonuses to employees are operational rather than policy decisions.
- Organizational and personal decisions
When an individual decides their responsibilities and tasks within the project, it is an organizational decision. But, if the individual decides on personal matters, it’s a personal decision. The authority to make organizational decisions may be delegated, whereas personal decisions cannot.
- Major and minor decisions
A decision related to increasing the number of resources by 50% is a major decision. A minor decision, for example, is that the superintendent can purchase office stationery.
- Individual and group decisions
When an individual decides within an organization, it is known as an individual decision. However, when it comes to more crucial decisions, more stakeholders need to engage and assist in making a decision. Therefore, it is interesting to investigate in which cases a project manager should involve other project members.
Decision-making Tools and Techniques
Project managers frequently employ additional measures to support the validity of their decisions. While the fundamental concepts remain the same, hundreds of distinct ways and tools are available. A mixture of these strategies can also be employed to make better decisions. Project managers would benefit from knowing which are appropriate and applicable in any given situation.
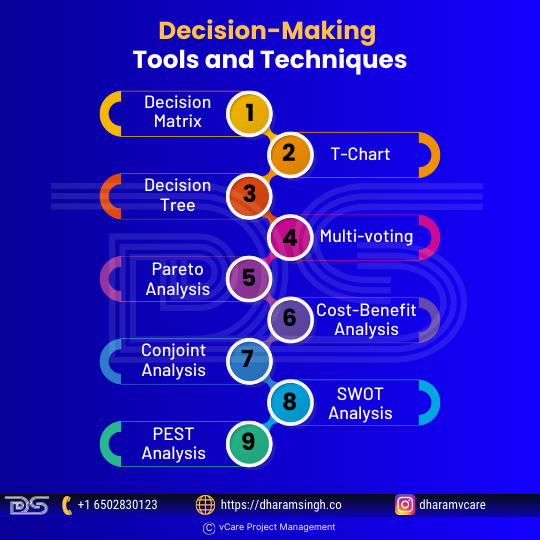
Decision-making Tools and Techniques
- Decision Matrix: A decision matrix examines all of a choice’s possibilities. When utilizing the matrix, create a table with all the alternatives in the first column and the criteria influencing the decision in the first row. Users then rate each choice and choose which criteria are most important. After that, a final score is calculated to determine the best option.
- T-Chart: This chart analyzes the benefits and drawbacks of the alternatives. It guarantees that all of the advantages and downsides are considered when deciding.
- Decision Tree: This is a graph or model for assessing each option and its outcomes. This approach is also used for statistical analysis.
- Multi-Voting: This is utilized when multiple people decide. It helps narrow down many possibilities to a smaller one that leads to the final decision.
- Pareto Analysis: This technique is used when making many decisions. This analysis aids in selecting which decisions should be made first by calculating which ones will have the largest overall impact.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: This strategy assesses the financial implications of each feasible alternative to arrive at the most economical conclusion.
- Conjoint Analysis: Business leaders use this strategy to assess consumer preferences when making decisions.
- SWOT Analysis: This planning tool examines SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats).
- PEST Analysis: PEST, which stands for political, economic, social, and technical aspects, can help decision-making and timing by analyzing external factors. This method takes current trends into account to forecast future ones.
Importance of Decision-Making
Decision-making is an acquired skill rather than an inherent one that is in high demand in the workplace. However, employers consider it an appealing trait as it signifies a good leader. Therefore, demonstrating your decision-making abilities can help you advance your career and accomplish company objectives and goals.
Here are some of the benefits of making correct decisions:
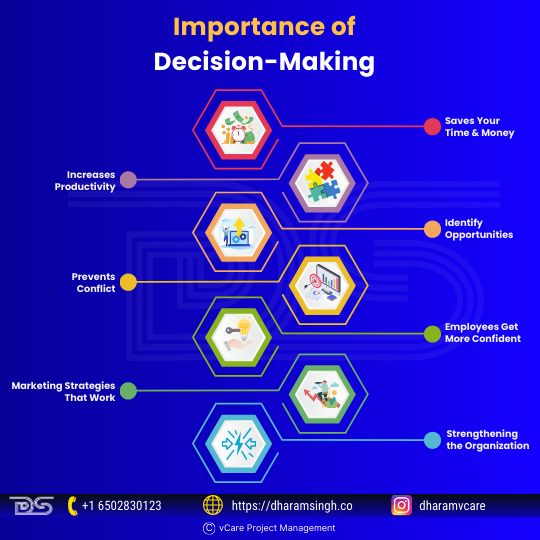
Importance of Decision-Making
- Saves Your Time & Money
Ineffective decision-making requires some time and depletes the motivation of those engaged. The less time you waste making rapid decisions, the better. When it comes to running a business, time is money. Wasting time is the same as wasting money.
- Increases Productivity
When management excels at making decisions and developing good ones, it will boost the workforce’s productivity. Employees will be motivated, for one thing, since they know where the organization is heading. They will strive with the conviction that their efforts will succeed. All time is preserved because the management team is convinced that their activities will correctly guide their organization.
- Identify Opportunities
The key is to recognize the opportunities in front of you and be able to act on them. If there is a great demand for a product in the market and your firm can offer it, wrong or delayed decision-making may prevent you from focusing on it. On the other hand, poor decision-making can make opportunities appear non-existent.
- Prevents Conflict
A manager’s failure to make strong, fair decisions can lead to workplace conflict. Conflicts in the lower tiers also occur when management needs to be more assertive and leave more decisions to their employees. Good decision-making skills can prevent employee conflicts regarding which idea is better for their team or how to maintain a project.
- Employees Get More Confident
Project leaders can become role models and show their employees they are good decision-makers. As a result, employees will trust and follow them confidently, even in the darkest times. When their staff feels that they trust their decisions at every moment, they are more likely to develop new innovative ideas that could benefit the overall business.
- Marketing Strategies That Work
Several critical considerations must be made when implementing successful marketing campaigns. Decision-making is the most important factor in developing strategies and making them stand out. No matter how good the products or services are, the firm will only reach its full potential if it can effectively advertise its brand.
- Strengthening the Organization
Everyone has an equal right to participate in the management of the organization. This aspect fosters a spirit of teamwork and solidarity among those who work there, improving the organization’s overall productivity and strengthening its general structure. Decision-making allows individuals working in an organization to convey their ideas equally.
Decision-making and its impact on problem-solving
The importance of decision-making in problem-solving is apparent and an essential component of efficient project management. A project manager’s capacity to make sound decisions and solve problems correctly is critical since it influences organizational functioning. Problem-solving and decision-making are sometimes inextricably linked; one must better decide to solve a problem.
Problem-solving is a key skill that makes one an excellent project leader. Problems are unavoidable when it comes to project management. Because we all encounter similar scenarios in our everyday lives, what makes a difference is knowledge and how well we use it to tackle a present or looming problem. In project management, problem-solving and resolution are strategic processes. As a result, one won’t be able to master that talent overnight. Instead, it requires incremental learning, using a framework, and preserving some critical factors.
Why are problem-solving skills necessary?
When potential employers discuss problem-solving, they aim to assess how team members use this talent to assist decision-making in the company’s day-to-day operations. Here are four reasons why problem-solving skills are vital in the workplace:

Why are problem-solving skills necessary?
- Strategy prioritization, planning, and execution
Efficient problem solvers may thoroughly examine consumer requirements and devise a strategy that allows them to give outstanding service to their intended audience. Their expertise is in simplifying procedures by eliminating bottlenecks.
- Out-of-the-box thinking
Problem-solving and creative thinking are inextricably linked. Finding a dynamic and innovative solution to a problem is not a matter of finding an instant solution but a dynamic and innovative solution. This mindset assists the company in staying ahead of the curve and gradually improving the workforce’s competence.
- Better time management
When an issue emerges, it must be resolved as soon as possible. Employees with strong problem-solving abilities are laser-focused on what is critical to the organization, can roll with the punches, and can meet tight deadlines.
- Risk management
Effective planning is a necessary problem-solving ability. Problem solvers may respond rapidly to short-term circumstances while keeping an eye on the future. Their positive approach toward learning agility enables them to foresee future challenges based on prior experiences, industry trends and patterns, and current events.
Problem-solving Techniques
Complex problems might be challenging to solve, yet difficulties can be addressed when the correct tools are used. Aside from sophisticated management tools, here are some tools and technologies that can help with problem-solving approaches in your everyday work.
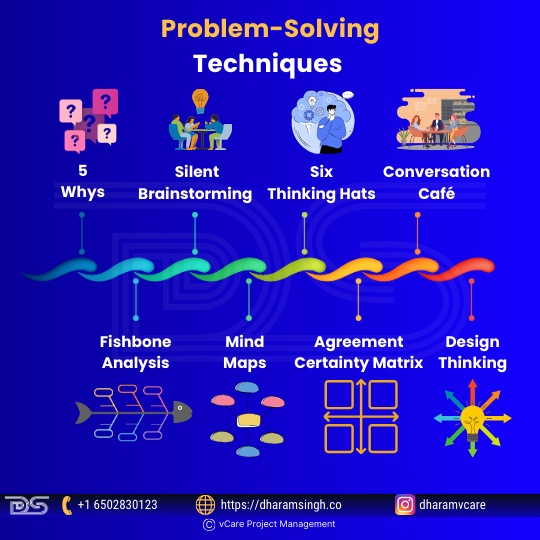
Problem-solving Techniques
- 5 Whys – Understanding the problem better is a wonderful strategy to find the core cause.
- Fishbone analysis – used to visualize the fundamental causes of an issue. Simple to use in conjunction with ‘5 Whys’ or ‘Mind mapping’ to brainstorm and discover the source and impact of any problem.
- Silent brainstorming – allows everyone to engage in idea generation since the loudest and quietest persons will contribute equally. This technique is useful because everyone’s point of view is equally valid.
- Mind maps – are organized visual representations that allow one to exchange ideas, thoughts, and solutions like your brain does. You immediately describe the issues, discuss new ideas, and eventually reach a team agreement that can lead to a successful solution.
- Six thinking hats – This technique allows your team to approach challenges from several perspectives, concentrating on facts, creative ideas, or why some solutions may not work.
- Agreement certainty matrix—another fantastic visual tool for brainstorming issues and challenges. It categorizes them as simple, complicated, complex, or chaotic domains to help teams agree on what technique should be utilized to handle the real problems impacting them.
- Conversation café: This allows the team to have constructive conversations with less argument and more active listening. The problem is addressed in rounds of dialogues until a consensus is reached on the best problem-solving technique.
- Design thinking: When you’re stuck for new ideas, the 5-step approach will help you empathize with the problem, then define and create new concepts before prototyping and testing them.
What are the critical problem-solving skills?
Problem-solving skills enable firms to seek and recruit intellectually equipped personnel who can handle anything their professions throw at them. Problem solvers can watch, assess, and act quickly when the situation demands it- without negatively impacting the business. The following are the top problem-solving skills in the workplace:
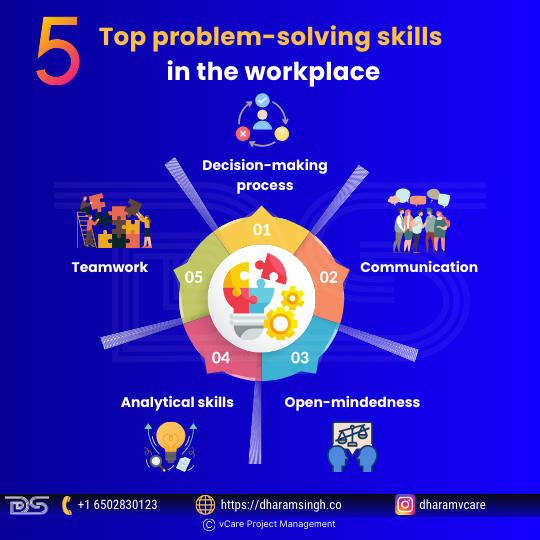
Top problem-solving skills in the workplace
- Decision-making process
Problem-solving requires the ability to make decisions. One can only solve it if one fully comprehends the issue and decides to take action. Decision-making abilities enable experts to rapidly choose between two or more solutions after weighing the benefits and drawbacks of each.
- Communication
Communicating the problem and offering remedies vocally and in writing is an art in and of itself. However, proper communication ensures that solutions are implemented successfully and that all parties engaged in the disagreement agree.
- Open-mindedness
Open-mindedness is the readiness to explore new ideas and look at things from a new viewpoint. When faced with an issue, consider all of its viable solutions. Being curious and observant allows one to be a better problem solver.
- Analytical skills
Almost all problem-solving scenarios need analysis, such as predicting, critical thinking, or troubleshooting. Analytical skills allow one to comprehend the situation better and generate effective answers based on facts and data.
- Teamwork
Collaboration is essential for keeping communication lines open, problems cooperatively addressed, and the team aims before personal ambitions.
Team dynamics are important in problem-solving because they allow one to work together with others toward a common objective.
Final Thoughts
The majority of problems start modestly. Creative program/portfolio managers are responsible for finding solutions as quickly as feasible. The longer they wait, the worse the situation will get.
They may break out of that cycle with a strategic problem-solving framework and quickly find solutions to difficulties using ideal project management automation technology. However, making decisions is crucial to solving problems. Making decisions may be a painstaking process in project management. However, the decisions made inside the team significantly impact a project’s success.
In the future of employment, net new jobs will be created at the same pace as dying jobs. Human talents such as creativity, decision-making, problem-solving, invention, and critical thinking will become more in demand as technology replaces employment requiring repetitive and boring operations. Organizations that get a head start on measuring these human talents in their workforce now and provide strategic learning and development opportunities to upskill them will gain a competitive edge as we enter the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Jobs we will never see coming will rise rapidly in the future of work (or what many call “The Fourth Industrial Revolution”). The “proper” professional path or education of an ideal individual for these professions will not be clear. We will need to quantify people’s human talents to position them in positions; not only are these skills transferable across unconventional career choices, but these distinctive human skills will also be protected against automation.
Thus, advanced certifications like PMP®, Agile, PgMP®, and PfMP® certifications can help one develop project management skills, be a good problem solver, be a more competitive candidate for positions, and be a successful project leader. In today’s competitive business world, one must be skilled and experienced to succeed and grow one’s career.


































Are your program managers equipped to lead strategic transformations — or just managing projects?
At GEICO, we took this challenge head-on. And the results were nothing short of inspiring.
📍Location: GEICO Headquarters, Maryland, USA
💼 Event: PgMP® Bootcamp – Elevating Program Management Excellence
When Beatrice D. opened our session with a powerful vision — “You’re already great program managers, but the goal is to become Exceptional Program Managers” — she set the tone for an unforgettable learning experience.
Over three energizing days, I had the honor of mentoring 16 outstanding program managers at GEICO. We moved beyond theory — diving into real-world insights, challenging conversations, and practical strategies to lead enterprise-level programs with purpose and precision.
Their passion, discipline, and commitment to excellence were truly admirable. The gift of the GEICO mascots, the GECKOs — will always symbolize the relationships and results we built together.
🌟 To the GEICO team: Thank you for your trust and energy. The future is bright, and you’re ready for it. Special thanks to PMTraining for making this collaboration possible and for supporting organizations in upskilling their program management talent.