
by DharamCW | Aug 1, 2024 | General
Today’s organizations are structured through many time-limited programs that transform organizational strategy into action. These programs necessitate a visionary mindset to align program goals with the organization’s strategic objectives. While project managers direct project work, they ensure individual projects align with program goals. Thus, program managers see their role as strategic and play an important role in managing the implementation of the organization’s strategic objectives by ensuring that the overall mission is met through the successful completion of planned programs.
Core Competencies of Program Managers
There are many similarities between a good program manager and a good project manager. However, a program manager must have broader organizational knowledge than a project manager. In addition, programs frequently necessitate strategic visioning and planning skills to align overall program goals and benefits with the organization’s long-term goals.
Here are the top ten core competencies of Program Managers:

Top 10 Core Competencies of Program Managers
1. Leadership and Teamwork
The program manager is the team’s leader and is accountable for the program’s overall success. As a result, it is critical to have a clear vision and the ability to communicate it effectively to all employees, whether charismatic, supportive, or inspiring. The program manager’s strong leadership provides direction, builds morale, and inspires the program and project teams.
As the team leader, the program manager is responsible for engaging all team members and fostering collaboration, individual commitment, and accountability. A program manager must decide which tasks can be assigned and who can delegate them. Understanding what to delegate and how to delegate is critical.
2. Planning and Organizing
Programs frequently necessitate strategic visioning and planning skills to align overall program goals and benefits with the organization’s long-term goals. Therefore, the program manager must be skilled at planning and organizing for the best outcomes. Aside from the program schedule, creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for the program at the summary level is critical. It also allows control accounts to manage cost, schedule, and scope. In addition, a well-designed Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) helps organize the team at the start of a program and makes change management easier.
3. Communication
A program manager must be a good communicator. Effectively moving information between project resources is critical to a program’s success. To ensure the success of the team and project, the program manager must be able to negotiate effectively and use persuasion when necessary.
Thus, effective communication entails breaking down barriers within and across projects and functional departments.
Communication “hard skills” include gathering and disseminating performance data, such as status reports, progress measurements, and forecasts. In addition, the program manager must communicate effectively with the program and project teams, top management, and stakeholders. For the project’s success, vertical and horizontal communication must be fluid and transparent.
4. Ethics and Ethical Values:
One of the key aspects of effective program management is ethics.
The Code of Ethics & Professional Conduct emphasizes ethical values such as trust, honesty, accountability, respect, and fairness—these five values foster team harmony and professionalism, which leads to project success. Building trusting relationships across cultures, time zones, teams, and departments aids in the smooth operation of projects.
Trust is the common thread that connects different cultural differences, disparate work cultures spanning multiple time zones, team members with different behaviors, and departments with distinct objectives. A project leader must grasp this and cultivate trustworthy relationships.
Treating people fairly and demonstrating responsible, ethical behavior toward subordinates creates a working environment where employees feel safe, protected, and confident that there is no room for injustice or discrimination.
5. Internal and External Stakeholder Engagement
The program manager must be able to focus on both internal and external stakeholders simultaneously. Identifying and documenting all individuals or organizations impacted by the program and its projects and pertinent information about their interests and involvement significantly impacts program and project success. This process enables dealing with internal stakeholders (other project managers, senior managers, and the like) and external stakeholders (other agencies and regulators).
6. Political Understanding
Another skill that the program manager must have is the ability to understand the organization’s political environment. This understanding includes the political aspects of networking and strategic thinking to make the best decisions. With a solid understanding of the political environment, the program manager must form positive relationships to realize the program’s full benefits when the activities are transitioned to gain leverage and buy-in for overall program success. According to PMI’s The Standard for Program Management, well-managed stakeholder expectations and established buy-in can ensure program success. Knowing the firm’s working dynamic and environment is critical to the program manager’s success.
7. Knowledge management
A successful program manager should have a solid understanding of the organization and its business practices and familiarity with the technologies used in the program’s projects. In addition, program managers must have “hard skills” such as technical expertise and detailed cross-functional knowledge. This knowledge keeps the PM from being unduly influenced by functional experts who either have a plan or make decisions based on limited information.
The program manager is responsible for interpreting, implementing, and reviewing program policies, procedures, and requirements and communicating these to all program team members and project managers.
8. Financial Management
In today’s environment of scarce and competitive resources, program managers must understand how to finance their programs with speed, economy, and efficiency. Program managers are in charge of budgeting and calculating the return on investment (ROI). Therefore, they must be familiar with the program’s financial aspects to keep the budget under control at all times. In addition, they will be required to make decisions that will directly impact the budget and ROI for all projects within the program; therefore, program managers must be knowledgeable about the financial issues involved.
9. Risk management
Program management works tirelessly to reduce business risk. However, a project with no risk has little potential for reward. Effective risk management necessitates identifying risks, assessing their potential for harm, and developing plans to address the threats. Program managers are in charge of gathering all risks from functional teams and leading the team through a risk analysis exercise to determine which risks are program-level and project-level.
The program risks are then classified and prioritized based on their potential impact on the program. Finally, a similar exercise is performed to mitigate project risks throughout the life cycle to reduce overall program risk.
10. Project and Process Management
Transitioning from project management to program management necessitates a greater emphasis on the horizontal domain and less on technical capabilities. This action requires the program manager to prioritize strategic efforts over tactical skills, which can be delegated. Therefore, the program manager must have excellent project and process management skills, ideally with prior project management experience.
Managing program complexity through efficient and effective project management is critical for program management. Program management imposes structure and provides a framework that breaks down the complexity of managing a group of dynamic, time-limited projects into more manageable and cost-effective elements. This framework is critical for planning, scheduling, budgeting, and quality control. In addition, a program manager with strong core project and process management competencies can successfully lead between and across multiple projects.
Leadership Styles for Future Project/Program Managers
One of the potential success factors for both program and project managers is leadership style. A project manager can become a great project leader by understanding leadership styles and their impact. As a result, the program and project managers must determine the best leadership style for each project team. Some of the most common project management leadership styles are:

Leadership Styles for Future Project/Program Managers
1. Coaching leadership style
The coach’s leadership style is one of the most advantageous to employers and employees. But unfortunately, because it takes more time than other types of leadership, it is also one of the most underutilized.
2. Visionary leadership style
A visionary leadership style is advantageous for small, rapidly growing, and larger organizations undergoing transformations or corporate restructuring.
3. Servant leadership style
Servant leadership is an excellent leadership style for organizations of any size or industry, but it is especially common in non-profits. These leaders excel at boosting employee morale and reinvigorating employees’ interest in their work.
4. Autocratic leadership style
Autocratic leadership can benefit organizations with strict guidelines or industries that rely heavily on compliance. It can also benefit employees who require extensive supervision, such as those who need more experience. However, this leadership style can stifle creativity and make employees feel confined.
5. Laissez-faire leadership style
Unlike autocratic leadership, laissez-faire leadership focuses on delegating many tasks to team members and providing little supervision. Furthermore, because a laissez-faire leader spends less time managing employees, they often have more time to devote to other projects.
6. Democratic leadership style
The democratic leadership style is a hybrid of autocratic and laissez-faire leadership styles. Before making a decision, a democratic leader solicits and considers feedback from their team. This style is frequently credited with increasing employee engagement and workplace satisfaction because team members believe their voices are heard, and their contributions are valued.
7. Pacesetter leadership style
One of the most effective ways to achieve quick results is to set the pace. Pacesetter leaders are mainly concerned with performance, frequently setting high expectations and holding their team members accountable for meeting them.
8. Transformational leadership style
Like the coaching style, the transformational style emphasizes clear communication, goal-setting, and employee motivation. However, the transformational leader is motivated by a commitment to organizational objectives rather than putting most of one’s energy into each employee’s goals.
9. Transactional leadership style
A transactional leader, similar to a pacesetter, is laser-focused on performance. Under this leadership style, the manager establishes predetermined incentives, usually monetary rewards for success and disciplinary action for failure. However, unlike pacesetter leaders, transactional leaders are equally focused on mentorship, instruction, and training to achieve goals and reap the rewards.
10. Bureaucratic leadership style
Bureaucratic leaders, like autocratic leaders, expect their team members to adhere strictly to the rules and procedures. The bureaucratic style focuses on fixed duties within a hierarchy. Each employee has a set list of responsibilities, and collaboration and creativity are not required.
Adapting Agility during Digital Transformation
Thriving in today’s competitive environment is a difficult task. Businesses must find ways to keep up with the trends as almost every industry is rapidly evolving, fueled by technological advances. As a result, many adopt an agile mindset to remain sustainable and efficient.
The ability of a company to change or adapt quickly to market changes is referred to as business agility. The idea is to manage operations and resources flexibly and responsively to maximize business value. Concurrently, digital transformation is upgrading business processes using modern technologies to improve performance and overall efficiency.
Based on the agile project management philosophy, the business approach is gaining traction among forward-thinking organizations. It enables them to recognize and capitalize on potential opportunities ahead of the competition. Companies concentrate on three key areas for improvement:
• Strategy
• Organization
• Operations
Business agility is no longer an option in the age of digital transformation. Instead, it is an essential component of any successful business. As technology changes the world at breakneck speed, the program manager must be adaptable and develop alongside it.
Are Program Managers adapting to the agile environment?
Traditional project management entailed following a pre-defined plan to achieve pre-defined goals. However, in an agile environment, the concept of “done” is rapidly becoming obsolete. So, what does it take to manage projects effectively with constantly shifting requirements?
• Managers must first understand their organization’s goals when implementing agile workflows.
• Following that, they must reconsider their success metrics: rather than meeting a predetermined budget, timeline, or scope of work, project managers should focus on metrics such as development cycle time and the proportion of decisions made based on objective data.
• Finally, agile project managers must continuously examine their processes and seek to adapt and improve themselves to meet the evolving needs of their customers and coworkers.
Skills for a Hybrid Working Environment
Flexibility takes many forms as the world enters the “new normal” of business. However, the new flexible work models present some difficulties. To be successful in hybrid work, specific skills are required. Here is a list of five skills to concentrate on as you prepare for the new work environment.

Skills for a Hybrid Working Environment
1. Technology and Processes
2. Online Security
3. Communication
4. Team-Building
5. Leadership
Every organization’s flexible work patterns look different. Additionally, there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach to implementing a hybrid work model. But, regardless of the circumstances, one thing is certain: training will be critical to your success.
Relevant information is critical. The right delivery methods are also important if you want them to stick. Finally, reaching and engaging your employees is critical to providing meaningful training. Use the best digital solutions to level the playing field for both in-office and remote employees. No matter where your employees are, the right approach will set them up for success.
Significance of Upskilling Project/Program Managers
Project/Program managers are valuable professionals who can work in various industries. It is frequently a highly sought-after position with numerous responsibilities. According to a study by PricewaterhouseCoopers, project management is critical to business performance and organizational success for 97% of organizations.
To ensure that a project management career takes off, one must have a mix of technical and soft skills. The top eight skills are listed below.
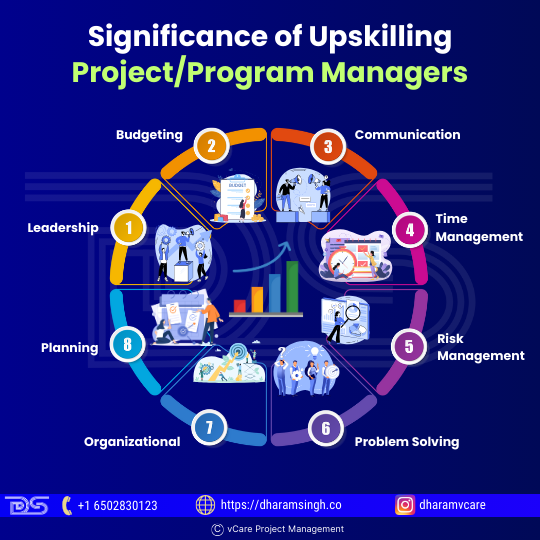
Significance of Upskilling Project/Program Managers
• Leadership
• Budgeting
• Communication
• Time Management
• Risk Management
• Problem Solving
• Organizational
• Planning
The world of project and program managers has changed significantly in the last few decades, with increased competition and the drive for efficiencies forcing companies to work differently. As project managers advance in their careers, they gain experience managing multiple related projects and making decisions that advance strategic and business objectives. As employers seek program managers to support the organization’s strategic goals, PgMP® credential holders will have a distinct advantage in employment and promotion opportunities over their peers.
How PgMP aids in gaining program managers’ knowledge
The Program Management Professional (PgMP®) certification is a visible indication of advanced experience and skill. As a result, it gives one distinct advantage in employment and promotion. As on 6th June 2024, there are 6,358 PgMP® that exist worldwide. The PgMP® is intended for professionals who have advanced in their careers and can manage multiple projects to ensure the success of a program. Furthermore, PgMP® holders are expected to manage complex tasks across multiple organizations, geographic locations, and cultures.
PgMP® Certification Benefits

PgMP Certification Benefits
Enhanced Strategic Decision-Making:
The PgMP® certification equips program managers with the skills to make strategic decisions that align with organizational goals, ensuring the successful integration and delivery of multiple projects.
Improved Stakeholder Engagement and Communication:
Certified PgMPs are trained to effectively engage and communicate with stakeholders at all levels, fostering trust and ensuring stakeholder needs are met throughout the program lifecycle.
Mastery in Benefits Management:
Gain expertise in identifying, planning, and realizing program benefits, ensuring that the program delivers measurable value to the organization and its stakeholders.
Robust Governance Frameworks:
Learn to develop and implement robust governance frameworks that ensure program alignment with strategic objectives, risk management, and compliance with organizational standards.
Also, while preparing for PgMP® Certification, you will learn the best practices for conducting your programs more efficiently and achieving great results for your organization. This aspect might assist you in securing better pay and a higher position. In addition, you will be recognized as a certified program manager.
Final Thoughts
Program management will only be effective if the anticipated benefits are realized and effective leadership is at the top. Often, programs fail to achieve the organizational goal due to a lack of management skills in dealing with the program’s complexity and demand. Competence and skills are entirely different concepts, with skills acquired through training and competence referring to the level of proficiency in applying the acquired skills. The skills and competencies of a program manager and a project manager are similar. Still, those of a program manager are expected to be deeper and much more strategic in aligning a series of projects.
When program managers use their unique perspectives and insight to guide programs in the most strategically advantageous way, they can provide long-term value for the company’s vision and direction. Any organization that manages more than one project at a time will benefit from the assistance of a program manager.

by admin | Jul 11, 2024 | General
Many PMOs recognize digitalization as an essential step in their organizations’ journey toward project management maturity. As a result, the Project Management Office (PMO) must shift its focus from project governance and delivery to supporting digital transformation.
To keep up with the evolving demands and needs of an increasingly digitized world, digital transformation has to be drifted through organizations of all shapes and sizes. However, many realize that successful digital transformation entails changing foundational cultures, structures, and methodologies and implementing digital tools. As organizations expand to accommodate this change, the PMO’s role within those organizations must change to do the same.
Digitalizing PMOs
Digital transformation is a familiar idea. Businesses constantly look for new ways to adapt and leverage emerging technologies to improve their business processes. Before the pandemic, PTC research found that 70% of organizations had or were working on a digital transformation strategy.
The PMO is crucial to achieving an organization’s strategic goals. If PMOs are to be an organization’s strategic drivers, they must expand their role beyond its traditional boundaries. They must assume their strategic role by leading change and capitalizing on opportunities in the digital space. PMOs must be at the forefront of emerging technologies, constantly evaluating opportunities and implementing new strategies. The recent pandemic and sudden shift to remote work have highlighted the challenges of developing community and culture through digital spaces. Here are some ways that PMOs can help the organization drive into digital transformation.
Five ways the PMO drives digital transformation
- PMOs can inspire and encourage change.
- PMOs act as the strategic arm
- PMOs provide support and insight.
- PMOs properly manage transformations.
- PMOs enable successful digital adoption.

Five ways the PMO drives digital transformation
How PMOs can aid an organization’s digital transformation
The nature, ownership, and stakeholders of IT strategy, governance, and management activities are changing dramatically due to digitization. According to Gartner research, 87% of organizations prioritize digitization. Furthermore, technology is now responsible for 77% of an executive’s top priorities.

Advantages of PMOs
As a result, PMOs are under intense pressure to transform. Unfortunately, their project, program, and portfolio management processes are designed for predictability and consistency rather than the speed and flexibility required to meet digital demand. Most PMOs have three significant advantages, which are either inherent due to the PMO’s role or location or have been developed through previous experience:
- A neutral enterprise perspective: As capital allocation and portfolio prioritization approaches change to enable the funding flexibility required for digital work, the PMO’s impartial, enterprise-wide perspective on demand, investment, and resource utilization is hugely valuable.
- The ability to operate via influence: As organizational boundaries become more fluid and who “owns” project management becomes less certain, influencing and enabling others, rather than direct ownership, becomes even more critical.
- Stakeholder insight: As digitization spreads throughout the business and accounts for an increasing proportion of work, there are more first-time stakeholders and greater stakeholder complexity for each piece of work. Understanding the preferences of these various stakeholders and experiencing synthesizing their feedback becomes critical in delivering results from digital work.
Elements Driving Digitalization
Traditional businesses worldwide have long recognized that digital transformation is the key to thriving in a fast-paced world. Digital transformation involves integrating digital technology into all aspects of a business. It fundamentally alters how businesses operate and provide value to customers. It increases efficiency, transparency, customer experience, employee engagement, and culture and saves time and money. Modern digital tools have elevated the project management process to new heights.
The following are the seven critical elements of a successful strategic digital transformation framework:
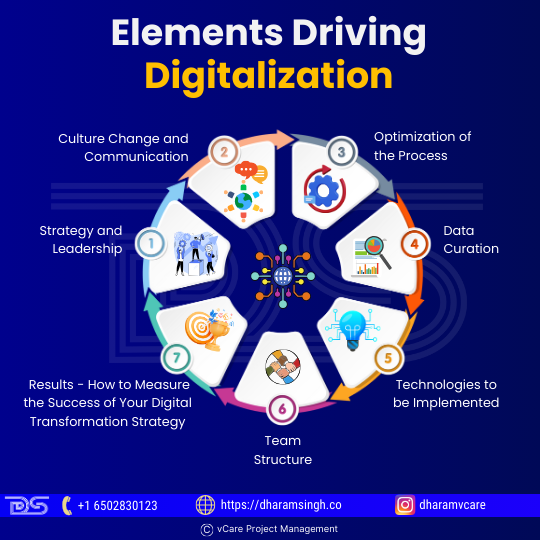
Elements Driving Digitalization
- Strategy and Leadership
An effective game plan is an obvious but frequently overlooked component of a digital transformation strategy. Instead, what matters is “how and who” formulates the strategy. A basic strategy and the appropriate technologies can help you digitize or digitalize your business, but transformation requires the right mindset and guidance. As a result, strategy combined with the right leadership is the first and most important component of an effective digital transformation strategy.
Visionary leadership combined with the appropriate digital transformation strategy can achieve a better, smoother, more cost-effective, and time-effective plan for your business’s transformation.
- Culture Change and Communication
Prepare for a massive cultural shift. A company’s clients and employees are typically resistant to significant changes, making implementing any transformation challenging. However, any successful digital transformation program must include culture. Therefore, giving your employees advanced training in good communication will be advantageous.
- Discuss the digital transformation strategy with your employees and how it will benefit all stakeholders.
- Conduct training sessions with your employees ahead of time to prepare them.
- You can prepare your employees by demonstrating the importance of aligning culture with new initiatives.
- Optimization of the Process
Every business has various processes and operations that can be improved to make workflows more efficient and effective. As a result, when developing a digital transformation strategy, consider business process optimization.
The strategy must optimize the business process while meeting customer and internal team goals. The digital transformation strategy must cover all interconnected business processes to achieve maximum output.
- Data Curation
One of the primary reasons for implementing digital transformation is to eliminate your business’s pain points for your team and your customers. But how will you know what these aches and pains are?
Data analysis and integration can assist you in locating them. People frequently choose their preferred technologies when developing transformation strategies before analyzing their data. Data analysis and the dissemination of its results can assist the team in identifying the best solutions to problems, leading to developing a better digital transformation strategy and making the most of the transformation process.
- Technologies to be Implemented
Finding the right technologies for your business is one of the most crucial steps in creating a digital transformation strategy. Introducing new technologies into your business will necessitate a significant financial investment, so it must be done correctly to avoid the need for additional funds. Any impactful strategy for digital transformation will always include options and budget constraints to help you make the best decision possible. Whether dealing with legacy system updates, application modernization, or implementing entirely new digital systems, you must find the best technology.
Some cutting-edge technologies that must be incorporated into your digital transformation strategy are:
- Cloud and Distributed Platforms
- Data Analytics & Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Experience and Digital Reality
- Team Structure
Harvard Business Review says digital transformation is about people, not tools. As a result, team structure is a determining factor in delivering results by the Digital Transformation Strategy.
The scope of the project should determine the team structure. The following components should be included in the digital transformation initiative:
- Pack of Leaders
- Business Experts
- The cast of Coders and Designers
- Results – How to Measure the Success of Your Digital Transformation Strategy
Your company’s digital transformation outcomes will greatly influence how you lay out your strategy. The outcomes will always vary depending on the practices and technologies used. Your digital transformation strategy’s success is dependent on its agility. First, of course, you must stick to your detailed strategy, but you must also be open to changes if things don’t go as planned.
By developing an effective, clear, and robust digital transformation strategy, you can ensure your company’s digital transformation goes as smoothly as possible. A digital transformation strategy is similar to a personalized road map for significant changes in your business operations. However, it requires significant financial investment, time, and technical expertise.
From Traditional PMO to Agile
Traditionally, PMOs have focused on maintaining project control to complete projects on time and within budget. However, in today’s increasingly complex and changing competitive environments, agile management is gradually displacing more traditional management methods; PMOs that remain anchored in this “classic” management model risk disappearing if they do not set the following objectives:
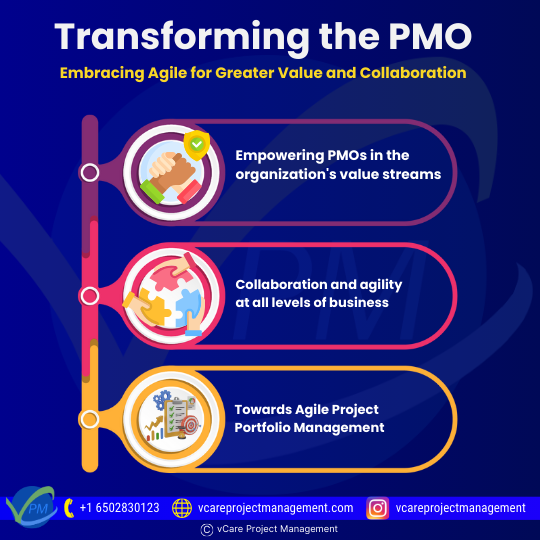
Transforming the PMO
- Empowering PMOs in the organization’s value streams
Organizations are now focusing on the value they provide to their customers and how different areas and departments contribute to that value creation. Suppose PMOs stick to their command and control model to ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget. Their contribution to the organization’s value streams will be marginal, and senior management will view them as an unnecessary expense for the company.
- Collaboration and agility at all levels of business
Silo-based organizational models need to gain ground in agile and collaborative environments. As a result, PMOs must evolve beyond simply providing Project Managers with the tools they need to complete the organization’s projects.
On the one hand, PMOs must maintain open lines of communication with senior management to align the Project Portfolio with the organization’s goals. On the other hand, it serves as a reference point for stakeholders and project work teams, providing real-time information on project status and support at all levels for proper project implementation.
- Towards Agile Project Portfolio Management
Change is the norm in this new competitive environment, with highly volatile markets demanding businesses to bring products and services to market as quickly as possible. As a result, company objectives can shift dramatically quickly, necessitating a rethinking of project portfolio prioritization. This phase is where PMOs must adapt to this new environment and manage key project management issues like prioritization, resource management, budgets, or delivery dates in an agile manner, as well as learn to react to changes in their project portfolios in an agile and efficient way without losing sight of the organization’s objectives.
Post-pandemic challenges for PMO
If PMOs establish these three goals, they might avoid extinction because senior management will no longer recognize their value to the organization.
It will be challenging, and the Project Management Office will face several challenges as it adjusts to the new reality. In particular, the PMO will face some challenges for its role to be perceived as critical to the organization’s value streams:
- Coincide the project portfolio with the overall strategy of the organization.
- Resource management is a real challenge for PMOs.
- Responsiveness to changes in the project portfolio.
- Fluent in communication with the organization’s senior management.
- Embrace Agile Leadership.
- Standardization of processes and workflows.
- Renewal of project portfolio management tools.
Mitigating mediocre implementation of Programs
There are always equal chances of success and failure in programs/projects. As a result, it is critical to understand how to avoid and overcome project failure. There are numerous reasons why a PMO succeeds or fails. Still, the most common reasons for failure are often not related to process or technology issues but to “people issues” in an organization.

How to avoid PMO Failures
Here are the most common reasons why PMOs fail:
- Adopt the Proactive Approach
After many years, project managers gain the skills and knowledge needed for the current project from their experience. As a result, an experienced and highly skilled project manager is equipped to deal with customers and avoid project failure. If you are new to project management, consult a professional mentor to discuss your concerns and receive appropriate advice based on their experience. If you have project management experience, you should apply your skills and knowledge to the project and be aware of the common causes of project failure.
- Plan the Project’s Strategy and Project Implementation
The most important stage of any project is planning. Most of the time, proper attention is not given during the planning stage. If you plan properly, you will increase the project’s chances of success. After scheduling your project, use the Project Management Life Cycle to begin project execution.
- Manage the Project Goals
It would be best to document the project’s decisions, actions, and outcomes before beginning, during, and after completion. To avoid project failure, it is always necessary to ensure project deliverables and work appropriately with customer requirements. Never rely on understanding, verbal agreements, or memory for project implementation decisions.
- Avoid Unrealistic Expectations
Always set realistic expectations and time frames with stakeholders, team members, or customers to meet your project’s deadline. This move is related to the proper project start but goes deeper until completion. To avoid project failure, realistic expectations for team members must be set based on their capabilities. It would help if you encouraged them to work enthusiastically and push themselves beyond their comfort zone to meet the project’s objectives.
- Track Project’s Progress
Project planning will assist you in determining where your project should be now. In addition, you should know how much of the work has been completed, whether your work is on schedule, proceeding as planned, and so on. These three parameters govern any project and are critical in preventing project failure.
- Identify Risk Factors
The best way to avoid risk is to identify, analyze, and respond to risk factors. So, if you identify the risks and potential issues early on in the project, your project team can avoid them with appropriate actions. In addition, identifying and resolving risk factors will assist the project manager in lowering the likelihood of project failure. As a result, you can perform proper risk management and avoid project failure.
- Use Correct Methodology
One of the most important decisions a project manager must make is the methodology to use for project management. What you choose will have a significant impact on teamwork. However, each methodology has advantages and disadvantages depending on the project type and scope. Here are some top project management methodologies to consider.
- Waterfall method
- Agile/Scrum
- Hybrid approach
- Critical Chain Project Management
- Integrated Project Management Technique
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
All project management methodologies cannot be regarded as the best for all projects, so one can understand the project requirements and select the best option. The correct methodology will assist you in achieving the project goal within the specified time frame, thereby avoiding project failure.
- Focus on Stakeholder’s Requirements
As we all know, a project will only succeed if it meets its objectives and exceeds the expectations of its stakeholders. Therefore, to be successful in project management, all team members must be actively involved in the project and committed to its success. Devoting entails writing down the following stages:
- The competent initiative assists the team in implementing various tasks throughout the project life cycle.
- Adequate funding ensures the organization’s cost-generating department has enough money to fund the projects.
Final Thoughts
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment, agile working methods might provide significant added value that should be noticed.
Digitalization is making projects more complex. As a result, the use of technology to manage projects is growing, and project teams must be cross-functional to achieve project goals. Agile project management provides an opportunity to respond quickly to new requirements and be more visible in the market. For organizations that use a traditional approach to project management, the transition to an agile PMO is part of their digital and agile transformation.
It should be noted that this is not an evaluation of “better” or “worse” methods. When used correctly, each project management method can reveal its strengths. It is critical to think about, use, and improve them.

by DharamCW | Jun 11, 2024 | General
People in the Project Economy have all the skills and capabilities required to turn ideas into reality, regardless of the type of project they are working on. It is the process by which organizations provide value to stakeholders by completing projects, delivering products, and aligning with value streams.
Project-based work has well-defined goals, milestones, deliverables, and a start and end date. Projects can last hours, months, or years, depending on the project and business needs. However, the work is focused on business needs and objectives rather than specific roles.
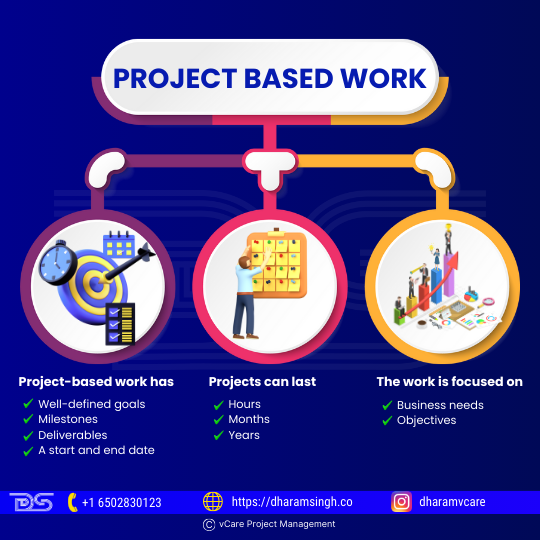
Project Based Work
Business leaders always want their teams to be agile and nimble. Adopting a project-based work mindset can help them achieve their goals. In addition, according to a recent MIT and Deloitte report, executives are increasingly viewing their workforce as an ecosystem, drawing on the diverse skill sets of their full-time employees and freelancers to meet business challenges.

Business Leaders Need
The Project Economy Has Arrived
The Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook (2021) by Antonio Nieto-Rodriguez states that:
- By 2027, nearly 88 million people worldwide are expected to be employed in project management, and the value of project-oriented economic activity is expected to reach $20 trillion.
- However, research shows that only 35% of global projects are successful, implying that project professionals waste time, money, and opportunity.
- To capitalize on the new project economy, businesses must adopt a project-driven organizational structure to ensure executives can sponsor projects and train managers in modern project management.
The Rise of the Project Economy
Berkley’s guide states that the rise of the Project Economy will play an essential role in the Future of Work. The following statistics from the below-mentioned survey make this statement more accurate:
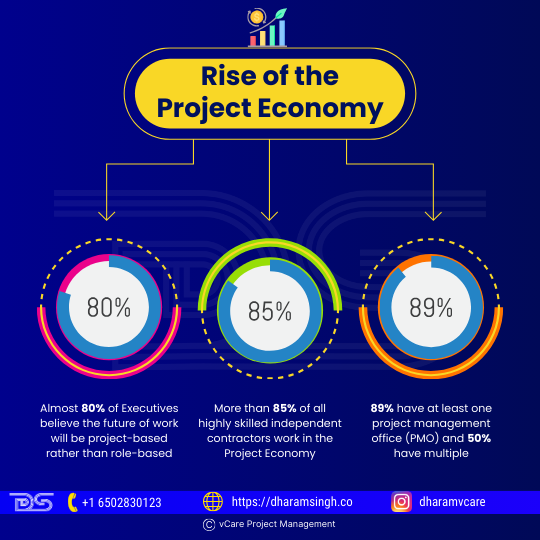
- Almost 80% of executives believe the future of work will be project-based rather than role-based.
- More than 85% of all highly skilled independent contractors work in the Project Economy.
- According to the PMI, project-based economic activity will increase by 68 percent, from $12 trillion in 2013 to $20.2 trillion in 2027. Employers will require 87.7 million PM-related specialists by 2027.

PMI Report
- 89% have at least one project management office (PMO), and 50% have multiple.
- Project work is expected to increase by 68% in the future, according to The State of Project Management report by Wellingtone.
Rise of the Project Economy
Challenges for the whole organization
The world is changing faster than ever, and businesses need help keeping up. However, savvy companies understand that the solution lies in developing and leveraging their people’s most valuable asset.
According to Global Talent Trends 2022 studies, workers are more stressed than ever. Eighty-one percent report being at risk of burnout, and one in five blame working for a company whose values do not align with theirs.
Human resource and project managers face many challenges in the whole organization.
- Close Skill Gap
Planning and managing long-term skill development will become more important as people lead longer, more diverse careers. Digital skills are now expected, and knowledge of business processes and related concepts is considered a core competency in every worker’s skill set.
Analytical and critical thinking skills have progressed from the exception to the norm, while interpersonal and leadership abilities are more valued than ever. Yet, many businesses face crucial skill shortages, particularly in retail, construction, real estate, manufacturing, education, medical and health services. According to McKinsey, 87 percent of executives report or expect skills gap challenges in the next few years.
- Initiatives to improve hiring
Hiring talented, qualified people has become critical to business success in a world of labor shortages and job-hopping. But it takes work.
- According to Josh Bersin’s study, 74 percent of businesses in the United States underperform when hiring, and only 60 percent of newly created jobs are filled.
- Businesses are attempting to attract not only talented but also diverse employees: The State of DEI Efforts report states that Finding various candidates with appropriate qualifications is the most difficult challenge for 43 percent of respondents.
- Also, Glassdoor’s Diversity and Inclusion Workplace Survey states that 76 percent of job seekers and employees value a diverse workforce when evaluating companies and job offers.
- Leadership development
Living in a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) world has become the norm. Influential leaders must be agile, constantly reevaluate and iterate their leadership practices, and strongly desire to build resilience for the future.
Organizations must adapt to new levels of complexity and ambiguity due to the COVID-19 pandemic’s disruption of the global economy and traditional modes of operation. The recovery from COVID-19 and the long-term impact of its disruption remain unknown. However, many organizations plan to meet their strategic goals and objectives as things begin normalizing. They must be especially cautious in the VUCA world.
VUCA: Companies and managers must embrace versatility, agility, and discomfort to progress. Covid-19 was the year of the phygital revolution – the physical, digital, and online-offline workplace convergence. In such a VUCA environment, managers and companies must be versatile, uncomfortable, collaborative, and agile to progress in a Phygital world. Therefore, every company and leader must be skilled in being versatile, uncomfortable, collaborative, and agile.
- Workforce retention
The ‘Great Resignation’ has resulted in historic numbers of people quitting their jobs, with the following industries suffering the most:
- Leisure and hospitality
- Trade, transportation, and utilities
- Professional and business services
- Education and health services
- Manufacturing
- Construction
Businesses are grappling with the issue of how to retain employees. One solution is to provide employees with opportunities for learning and skill-based career growth. However, employees see professional development opportunities as the most important way to improve and change the company culture.
- The Workplace Learning 2022 Report states that 46% of L&D leaders said upskilling or reskilling was a top focus area this year; internal mobility, career pathing, and employee retention fell toward the bottom.
- According to The American Upskilling Study 2021 study, 66 percent of workers aged 18-24 ranked upskilling opportunities as the third-most important benefit in evaluating a new job, and 48 percent of workers in the United States would relocate for such opportunities.
- Enterprise agility
To thrive in a highly dynamic world, organizations must quickly adapt to changing technology, markets, and customer needs. Enterprise agility denotes a shift away from traditional hierarchical structures and disconnected teams toward an operating model that optimizes strategy, structures, processes, people, and technology.
Rather than being hindered by the relentless pace of change, agile enterprises are more likely to capitalize on emerging technologies and business trends to differentiate themselves from the competition. However, as per a McKinsey report, two-thirds of businesses say they need to prepare for workforce disruptions brought on by technological and market trends.
- The transformational potential of learning
Employees and organizations are moving together as they navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing world. Workers must embrace a culture of lifelong learning to remain relevant. The benefits for businesses are evident, with skilled workers becoming more agile and motivated. In addition, Upskilling and reskilling can transform society as a whole, allowing under-represented groups to participate in the economy and be more involved.
- Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies continue to influence how we live, work, and interact in a world driven by digital solutions. Many technological advancements are beneficial: they increase productivity, make necessary services more accessible, and generally make our lives easier.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, cybersecurity, and big data can make products and services more widely available, particularly to those currently unable to use them.
Several significant benefits for business processes should also be considered. Businesses already use a variety of digital solutions to attract customers, such as applications and websites. By 2030, approximately 70% of companies worldwide will have adopted at least one type of AI technology, with other emerging technologies being implemented quickly. Thus, technological solutions will continue to automate and innovate our work.

Future Challenges for the Whole Organization
Perspective Competency and Strategic Envisioning
A better approach would be to stop thinking about today’s challenges in terms of ‘project management.’ Instead, we must reframe the question to how we can do our work most efficiently. This also entails abandoning the notion of project management as a technical discipline in favor of viewing it as a collection of skills and disciplines required to complete work today. Christoffer Ellehuus, in the article Succeeding in the Project Economy, outlines four significant components for this phase.
- Strategy
Executing a strategy must be rooted deeply in the organization and must be understood by all. The biggest challenge is selecting the right work and eliminating unnecessary tasks. In addition, identifying opportunities for innovation, growth, and value creation are critical areas for improvement.
- Work
Work completion necessitates action in three areas: process expertise, workflow management, and innovation. The most challenging priority is managing multiple priorities and interrelated work streams. Project management is a skill that should be developed in every sector.
- People
80% of managers see the need to create conditions for leading in an environment of ambiguity. 79% know the challenge of leading through change or transformation as a priority. A significant shift in how leaders approach people management is required to nurture team members and build the capacity to deal with challenges.
- Self
A well-developed ability to manage and improve your capacity is immensely valuable. Therefore, the most urgent focus areas are to build creative, problem-solving, and critical-thinking skills.
Understanding Generation Z in the workplace
A new generation brings a new outlook on work. Generation Z is already an undeniable force in shifting corporate culture. By 2025, Gen Z employees will account for 27% of the workforce, bringing their expectations and values. There may be an area where an existing employee’s opinions, ideas, and working patterns vary. So, there should be an area to bridge the gap between the experienced and Gen Z employees.
Bridging the Gap – Experienced vs. Generation Z
Today, younger generations are entering the workforce. At the same time, older employees remain in the workforce for longer due to economic necessity. In the workplace, the experienced and Generation Z employees may have noticed a few challenges and questions to the management while allocating them a task together:
- Do these coworkers have difficulty conversing with one another?
- Do they appear to have opposing processes and preferences for completing their work?
- Have their differences hampered their ability to generate complementary ideas and collaborate on projects from start to finish?
- Do they find it difficult to relate to customers of different generations and adapt to their expectations?
- Are they having trouble identifying common motivators for their team?

Challenging Questions For Experienced & Generation Z
But it might be better if the experienced employee tries to learn about Gen Z’s as they are thoroughly updated on technologies and adapted to hybrid working culture. Some aspects that may build the bond between experienced and Gen Z employees:
- Gather inputs from each other
- Live the culture
- Create opportunities for face-to-face interaction
- Facilitate frequent peer-to-peer recognition
- Form cross-generational teams
- Implement social technology for building relationships at work

Building Bonds Between Experienced & Gen Z Employees
The Skills Challenges of the Future Workforce
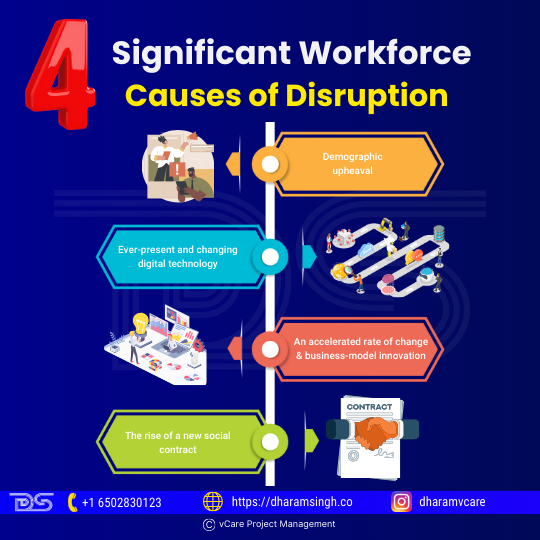
Technology, globalization, demographics, social values, and changing personal expectations of workforce participants are causing a dramatic change in the future of work and the workforce. As per The Future of the Workforce study, there are four significant workforce causes of disruption:
- Demographic upheaval
- Ever-present and changing digital technology
- An accelerated rate of change and business-model innovation
- The rise of a new social contract
Significant Workforce Causes of Disruption
To survive the hypercompetitive, fast-paced future of work, an organization must be laced with strong interpersonal connections across a diverse workforce. In the aspect of a better workforce in the future, the employees need to necessitate the combination of four key work skills:
- Digital tools and technological abilities
- Good understanding of analytics and data
- Business management abilities
- Design and creative abilities

Key Work Skills to Survive
Get adapted to change
The projectification of work has rapidly shifted the nature of most professionals’ work, moving away from routine operations and decisively toward project leadership. In this new world, executives must answer three critical questions.
- Is your organization prepared to thrive in the project-based economy?
- Do professionals in your organization have the necessary adaptive mindset to carry out critical projects?
- Do your project managers have the business skills to prioritize competing workstreams and align with shifting business priorities?
The way forward
Great projects don’t just improve work; they improve the world. Key characteristics that leaders must possess to excel in a project-driven world:
- Project management skills
- Product development and subject matter expertise
- Strategy and business acumen
- Leadership and change management skills
- Agility and adaptability
- Ethics and values
Managers and organizations must become comfortable devising strategies driven by change rather than efficiency to transform themselves and thrive in the new project economy. They must delegate more resources, budgets, and decision-making authority to projects and project teams rather than the traditional departmental hierarchy. They will need to develop project management skills and adopt new technologies. Finally, they must encourage a shift in emphasis away from inputs and outputs and toward outcomes and value.

by admin | Mar 15, 2024 | General
Managers who practice both strong management and effective leadership skills are successful project managers. Management skills are different from leadership skills. Effective leaders develop new leadership skills to enhance the ones that help them succeed as managers.
Organizations require effective leaders to achieve their strategic goals through programs and initiatives. Therefore, organizations need successful project/program managers who are also effective leaders. But what kind of leadership skills do project managers require? Are project management skills insufficient?
Project management differs from leadership. However, although project management differs from leadership, the two have some similarities. For instance, the performance of a project manager and the leader’s efficacy are both judged in terms of the performance of the followers—the team’s performance. As a result, focusing on team performance is a critical component of building project managers’ leadership skills.
Leadership Effectiveness

Leadership Effectiveness
On a macro level, leadership effectiveness is defined by a leader’s ability to gain support and influence throughout an organization to guarantee that everyone is going in the same direction to achieve common goals. It effectively measures a leader’s ability to lead, influence, manage, advice, and build their team members. The total growth and performance of the teams may be used to assess leadership effectiveness. Those who report high levels of productivity, performance, employee happiness, and well-being indicate high levels of leadership effectiveness.
A good leader inspires the best in others. These leaders understand how to create the ideal corporate vision, establish the proper values, and assist employees in focusing on and improving their skills. Great leadership reflects great performance, not just complex numbers. Workers and the organization will improve if leaders establish a great corporate culture and help employees thrive.
Program management
According to the Standard of Program Management – Fourth Edition, Program management is “the application of knowledge, skills, and principles to a program to achieve the program objectives and to obtain benefits and control not available by managing program components individually.” Program management involves aligning program components to ensure goals are achieved and benefits are optimally delivered. Program management is performed by a program manager authorized by the organization to lead the team(s) responsible for achieving program goals and objectives.
Ways to improve leadership effectiveness in Program Management

Ways to improve leadership effectiveness in Program Management
- Ensure clarity and visibility of goals
You may begin your path to improve leadership effectiveness in your business by encouraging leaders, managers, and executives to focus on objective clarity and visibility. This move has multiple aspects. First and foremost, the goals must be very clear. As a result, goals must be SMART for effective leadership, and adopting an OKR approach will make sense.
Second, for comprehensive visibility, the goals must be communicated to everybody. On the one hand, everyone in the team has to understand the organization’s goals and their role in attaining them.
- Facilitate accountability and responsibility
Second, exercising accountability and responsibility is critical for leadership success. Encourage your leaders to take accountability for their actions. The goal is to encourage them to be interested in increasing their leadership effectiveness. This aspect requires determining which skills and abilities to be acquired, as well as aspects such as emotional intelligence and empathy. When your leaders seek to improve themselves, they usually set a good example for others to follow, increasing their effectiveness as leaders since they may start a positive trend.
- Create a culture of feedback
Leadership effectiveness is heavily influenced by a leader’s desire to improve oneself. It is optional to self-assess the deficiencies and work on upskilling in this situation. Instead, it is critical to foster a feedback culture. First and foremost, it is vital to provide feedback to employees on their performance and to assist them in improving and growing along the way. This move will immediately influence organizational goals and define increased effectiveness.
Second, encourage your leaders to be receptive to employee input as well which will assist them in seeing and comprehending the gaps in their leadership style that may impede their success as a leader. Creating a feedback culture can promote improved outcomes, eventually enhancing leadership effectiveness.
- Build trust and transparency
Trust and openness are required for leaders to influence, direct, and build their teams to success. When employees trust their supervisors or leaders, they will follow them fully and offer their all. If not, following their manager will be a pointless exercise limiting leadership effectiveness.
Similarly, it is critical to be open and honest with all employees. Secrets, nepotism, preferences, and biases will be self-defeating if you want your leaders to inspire everyone collectively. Instead, everyone must be treated equitably, and all processes must be transparent to acquire team trust and influence them.
- Focus on continuous performance management
Effective leadership is not just about motivating and encouraging team members to follow a leader or manager but also about doing so in a way that leads to achieving a certain objective or high level of performance. As a result, boosting leadership effectiveness necessitates emphasizing continuous performance management.
Employees grow and develop when their leaders or managers regularly monitor and track employee performance and give frequent interventions and corrective steps to minimize risks or problems. As a result, they can motivate and inspire their team members, resulting in increased leadership effectiveness.
- Respect differences and promote inclusion
Members of each team come from various backgrounds, bringing with them different perspectives, ideas, and opinions. An effective leader accepts these differences, appreciates them, and recognizes their value. To boost leadership effectiveness, you must cultivate an inclusive culture. In addition, your leaders must understand the important skills and competencies each team member brings to the table and how the multiple views and perspectives offer the ideal breeding environment for creativity and success, resulting in leadership effectiveness.
- Foster a growth mindset
The last recommended practice for increasing leadership effectiveness is cultivating a growth mindset. It would be best to encourage your leaders to have a growth mindset during all interactions or choices they make. For example, when dealing with a team member, they must keep the employee’s personal and professional development in mind. Likewise, when making a strategic choice, they must link it with the organization’s goals and how it will eventually contribute to its success. With a development mentality, your leaders will guarantee that they lead effectively, strategically, and in the greatest way possible.
Leadership in Project Management
Leadership in project management is a vital ability for completing the project effectively. Leadership in a project setting, like leadership in other areas of business, necessitates demonstrating many talents and behaviors. Leadership is essential to ensure your initiatives’ success, from team direction to project governance.
Leadership and project management go hand in hand. You oversee the project and lead the team as the project lead. Setting the vision and encouraging the team to work together to accomplish it is a vital component of leadership. You can see how significant that is in a project environment. Delivering any project requires a team effort. While some teams work without a clear leader, in today’s business, it is more customary for someone to be in the leadership role, guiding and directing the team toward their goals.
5 Essential Project Leadership Skills
Influential leaders draw on many essential project management skills and competencies. The top five project management leadership skills are:

5 Essential Project Leadership Skills
- Communication
One of the essential project management characteristics is communication skills. Communication skills are essential for project leaders since their job requires collaboration. You can only collaborate efficiently if you can communicate clearly. Leaders can communicate ideas to people and groups in person, over the phone, or through other modes of communication. Therefore, communication is one of the most important abilities of a program manager, especially in a leadership role.
- Team leadership
The leader establishes the vision. They motivate others around them. Someone with outstanding project leadership skills fosters team agreement and togetherness while managing day-to-day team activities.
Team leadership on projects entails establishing an atmosphere in which everyone may thrive. People are drawn to the project culture that surrounds them. Stakeholders want to participate in the project because they know you will complete the task while creating a pleasant working environment.
- Motivation
Leaders inspire people to act even when they are not technically in control. As a program manager, you figure out what makes the other team members feel like they’re doing their best, and you do your best to deliver it to them.
Everyone is driven differently, and a person’s motivation can shift over time. Great leaders realize these distinctions and enable their employees to accomplish their best by fostering a happy work environment.
- Crafting solutions
Empowering the team and the larger stakeholder community to participate in developing solutions is part of fostering a positive working culture. That entails removing obstacles so each team member may fulfill their work and contribute new ideas without worrying about something getting in the way. Empowering leaders will also drive decisions down the hierarchy to the lowest possible level, allowing specialists to judge the solutions required to keep the project going.
- Conflict resolution
Conflict is inevitable when introducing or altering anything. However, effective leaders understand how to use conflict for good since the finest solutions emerge when ideas are challenged.
Conflict may benefit teams because it allows all voices to be heard and opposing viewpoints to be expressed, frequently leading to a better solution and more effective project outcomes. However, leaders must be prepared with conflict resolution tactics to recognize and address conflict before it becomes a problem for the team.
The Challenges of Leadership Effectiveness

The Challenges of Leadership Effectiveness
- Development of managerial effectiveness
To improve their leadership effectiveness, project leaders must acquire the following skills:
- Time management
- Task prioritization
- Strategic thinking
- Goal-setting ability
- Good judgment
These are essential skills for a project leader to deliver effective projects and handle the possibly competing demands of many duties. Without them, a leader is more prone to burnout from focusing on irrelevant matters and achieving little of the planned tasks and objectives.
- Inspiring and Motivating the Workforce
Motivating and inspiring others to follow you and act in a specific manner is a skill that some people appear to be born with, and others must learn. However, whether you have an inherent talent for motivating others or not, it is a skill that every project leader must have to motivate their worldwide workforce.
Passion is an important aspect of inspiring and encouraging people. Passionate leaders ignite the fire in their team members, allowing innovation to flourish and encouraging everyone to participate. In addition, effective leaders can naturally share and correctly convey their team’s and stakeholders’ enthusiasm and drive.
- Developing Employees and the Rise of “Servant Leadership.”
“Servant leadership” is based on the idea that leaders should not just delegate responsibilities but also consider themselves servants of the people they manage. As a result, their actions are driven by what is best for their team or workers rather than by what is best for themselves, which might manifest itself in the following ways:
- Close collaboration between management structures and employees
- Active participation in the growth of their teams
- Leading by example and embodying the ideals that leaders want to see in their team dynamics
- Using value systems to motivate teams to act rather than spreading fear
- This managerial style is infused with sincerity and humility.
A project leader who can find a balance between the servant-leader management style and more antiquated, authoritarian methods will be able to inspire and encourage their workforce.
- Leading a Team
All diverse cultures and viewpoints must cooperate and contribute to leading a project team effectively. Whether forming a new team or taking over an existing one, leaders must be able to give the support their team requires to cope with and navigate change or to create something entirely new.
Determining the sort of assistance required might take time and effort. Teams are as distinct as the individuals that comprise them. Project leaders must be extremely attentive to detect the demands of their workforce. What works for one person may not work for another. Leaders must be able to modify their management style in response to the demands of their teams.
Final Thoughts
In today’s firms, competent project managers must also be effective leaders. Therefore, successful project managers may use their inventive and creative skills to assist them in acquiring leadership skills that will complement their project management skills by recognizing the difference between project management and leadership and adopting the roadmap to becoming effective leaders.
The shared component of project management and leadership is the yardstick by which the performance of the project manager and the leader is measured. The performance of a project manager and the efficacy of a leader are both judged in terms of the performance of the followers, i.e., the team’s performance.
As a result, improving leadership skills for project managers with an emphasis on skills to increase team performance should be an essential factor in the project management leadership skill development process. Project managers’ essential leadership skills begin with motivating and inspiring teams and individuals. These aspects can be developed via negotiation and communication, listening and influencing, and team-building skills, emphasizing leveraging these talents to improve overall team performance.
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting https://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Jan 19, 2024 | General
Project management is becoming an essential aspect all around the world. But, many businesses need help to complete projects successfully owing to a mismatch between business strategies and project management. They require assistance in determining the relationship between business strategies and project management. Alignment is essential to get a competitive edge and meet business objectives. Therefore, project management has grown its importance and is now critical in many firms.

Constraints Confront Projects
Projects are any temporary activity with a start, an endpoint, and specific performance objectives. Three constraints confront projects:
(1) Time
(2) Budget
(3) Performance
To achieve the organization’s goals, it is considered that the above three constraints need to be fulfilled. Therefore, project management is critical to attaining corporate objectives and is regarded as the organization’s backbone. And it is critical to achieving strategy, company goals, and intended outcomes.
Project Management
Project management uses specific knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to deliver value to people. Project management has emerged as a critical concern for many worldwide businesses. Many project management implementations have been effective, while others have been deemed a failure. Projects are seen as the organization’s backbone, with success implying a great deal for an organization’s ability to compete. A project is described as a planned set of related tasks that must be completed within a specific time frame and particular costs and other constraints.
A Six-Step Technique That can be Useful in Avoiding the Worst Disasters in Project Management
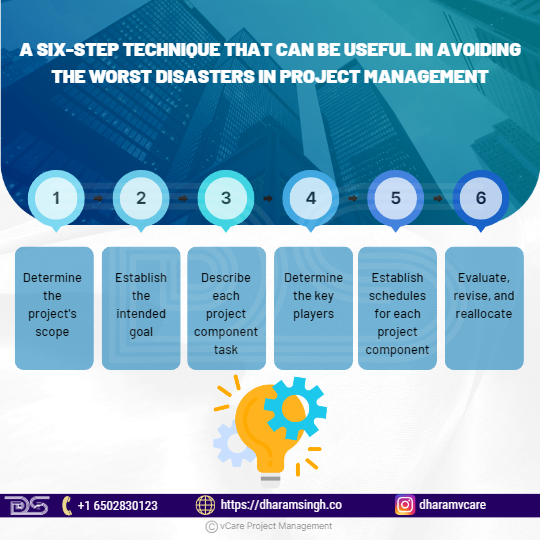
A six-step technique that can be useful in avoiding the worst disasters in project management is:
Step 1: Determine the project’s scope.
Step 2: Establish the intended goal
Step 3: Describe each project component task.
Step 4: Determine the key players.
Step 5: Establish schedules for each project component.
Step 6: Evaluate, revise, and reallocate.
The successful beginning and execution of initiatives are largely dependent on strategy. Many businesses need help with misaligned projects and a systematic approach to aligning project management with business strategy. Organizations are better equipped to achieve their organizational goals by linking their initiatives to their business strategy. Project strategy should be linked to the project’s goals and objectives to achieve its desired competitive position.
Business Strategy
Business strategy is a complete collection of actions or activities that direct the use of a firm’s resources to achieve the vision and goals of the business and provide a long-term competitive advantage. Strategic management involves translating strategy into action to operationalize strategic objectives and gain a competitive advantage.
To ensure that strategies are translated into actions, they must be operational, which includes characteristics such as structuring an organization to support successful performance and enabling success through the way an organization’s various resource areas, such as people, information, Finance, IT, and so on, are managed. As a result, companies that implement their strategic plans may do better in sales growth, profits growth, deposit growth, return on assets, return on equity, return on sales, and return on total invested capital than those that do not.

Levels of Strategies are Offered by Different Levels of a Business
However, different levels of strategies are offered by different levels of a business in every organization, including:
- Corporate Planning:It requires a high degree of strategic decision-making to meet the stakeholders’ expectations.
- Strategy for Business Units:The goal of this strategy is to acquire a competitive edge for the services and goods provided, and choices at this level are focused on product selection, acquiring a competitive advantage, meeting consumer requirements, and creating new possibilities.
- Operational strategy:It is concerned with resource coordination and improvement, resulting in the effective and efficient implementation of the business unit-level strategy.
Strategy implementation requires taking activities and accomplishing tasks and should concentrate on how to materialize these strategies.
The following major points must be considered during implementation:
- Work execution necessitates distributing resources such as finances, people, and equipment. The organizational resources are limited.
- The implementation phase necessitates the creation of a project-supportive organizational structure.
- A project selection and prioritization framework guarantee a solid relationship between projects and the strategic strategy.
Managerial challenges include:
- Connecting project management with corporate strategy.
- Encouraging individuals to collaborate in developing new ideas.
- Renew existing strategies.
Aligning Business Strategy with Projects
Aligning the company’s projects to optimize their contributions to strategic goals necessitates a highly coordinated effort. Integration requires a strategy for selecting initiatives based on their value to the strategic plan. Organizations will need business and project management experts to collaborate to achieve business objectives to become more competitive, efficient, and lucrative. Both business and project management specialists will collaborate to connect initiatives with company objectives. The alignment of company strategy with project management is a fundamental problem for every organization.
Such alignments are challenging to achieve because business strategy objectives are only sometimes explicit, adequately articulated, or compatible with project management activities. Misalignment can lead an organization to fall short of its aims and objectives. Understanding the alignment may be one of the most challenging aspects of the project management process. Alignment is a process that requires dominating leadership, top management backing, effective communication, a collaborative work atmosphere, trust, correct prioritizing, technical setup, and a thorough understanding of the business’s operations. To obtain the intended outcomes from the selected projects, the company should be able to develop capabilities and then distribute those competencies to the recommended projects. To ensure that corporate projects are linked with corporate strategy, keep the following in mind:
- Is the company committed to strategic project management?Most businesses have hundreds of projects running at any given time; therefore, there must be a corporate commitment to the art and science of project management.
- Is there a policy in place for formally preparing project charters?Because projects are the methods through which corporate plans are implemented, they must adhere to the original business philosophy, strategy, and objective. Project charters are the tool for doing so.
- Is there collaboration between the business group and those in charge of project implementation?Early engagement of project implementation personnel is required. While this theory appears logical, putting it into practice is difficult. First, corporate planners may choose to prepare without the assistance of considered “outsiders.” Then there’s a good probability that the right individuals are doing something other than brainstorming and assessing the early stages of a business strategy.
Benefits of Aligning Business Strategy with Projects
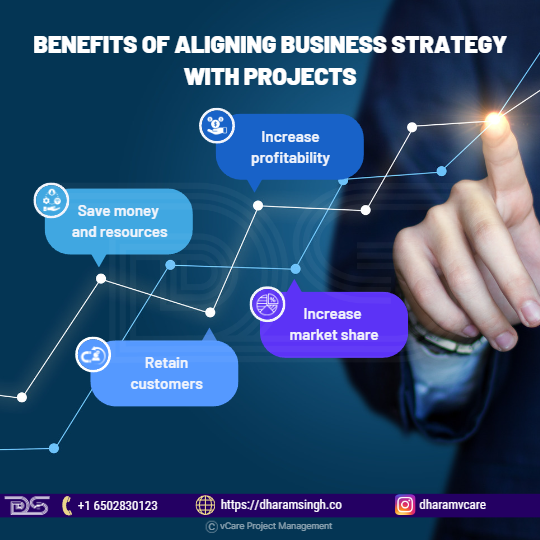
Some benefits the organizations include:
- Saved money and resources
- Increased profitability
- Retained customers
- Increased market share
Prioritizing a project based on its contribution to strategy achievement does not ensure project success. Still, consistent resource allocation is also a big responsibility. Therefore, a significant point to ensure alignment between project management and strategy is as follows:
- To carry out the suitably chosen projects efficiently
- Companies must ensure that they can implement the projects and programs.
Therefore, the alignment of projects is strongly influenced by top management.
Why Should Project Managers Care About Business Strategy?
A project manager must be able to connect their project within the larger context of the company to be truly effective. Understanding the basic business strategy is critical to achieving a great outcome. Strategic alignment and delivery should be wider than senior-level executives because the outcomes influence everyone in the business. On the other hand, a project manager should be wholly involved in all aspects of the project, including understanding and being concerned about business strategy.

Why Should Project Managers Care About Business Strategy?
Although it may appear counterproductive to focus on larger goals rather than the project itself, there are many significant reasons why project managers should be concerned with business strategy:
- Boosts Team Morale
A team will follow the project manager’s instructions. Connecting your project to a larger company goal offers everyone a feeling of purpose and connectivity. It helps people realize they are contributing to a more significant cause rather than just completing the work. It enhances team morale in this setting because it offers employees a feeling of purpose.
Furthermore, when individuals believe there is a greater good at risk, persuading them to pivot on a project is simpler. Finally, when teams can see the larger picture, they can better recognize when there is a break in activity or when resources need to be reallocated.
- Establishes Stakeholder Support
Understanding executive jargon provides you greater leverage when requesting and securing stakeholder support. A project manager will gain more cooperation if they can explain to senior team members how their participation will benefit the organization. Understanding the company’s strategy enables a project manager to structure requests in ways that are more likely to receive approval and favorable feedback. If a project manager can instill value in their team members and senior stakeholders, the odds of project success increase significantly—the greater the level of support, the more likely a favorable result.
- Outputs and Outcomes
Business strategy is about taking a step back and looking at the big picture. The traditional approach to project management held that the end of a project was about output, and what someone did with that data was their responsibility. Modern project management requires a professional to analyze the overall company strategy and what will happen with the project’s output when it goes out of your hands. It’s about remaining business-aware throughout the project so that the company’s best interests can always guide it. This awareness is how great employee morale and stakeholder support are achieved. Today’s most effective project managers can relate project outputs to successful corporate outcomes.
Final Thoughts
A good project manager should be familiar enough with their company’s strategy to utilize it to increase team morale and create a broader picture for their team. Once the team is on board, the same interactions may be used to obtain stakeholder support. Finally, the ability to link output to outcomes will guarantee that the project is successful at every step. Project managers and business leaders must formally understand how to establish, explain, and maintain strategic focus. This view will give project execution a new dimension and bring project management closer to being a competitive weapon for organizations. Choosing the right strategic focus at the start of a project and making it consistent with the company plan can help the project succeed and lead to better business results.
Projects offer an excellent opportunity to obtain a competitive advantage and bring value to the firm. Strategic project management is thus essential. Therefore, one of the most critical parts of project strategy is having a sufficient strategic focus.
Lastly, an understanding of business strategy makes for a well-rounded project manager.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting https://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Nov 24, 2023 | General
The world is becoming more aware of the destructive impacts of climate change, and many businesses have started realizing the critical importance of sustainability to their future operations. Making the projects more sustainable is important to build a more sustainable world. But how to establish it?
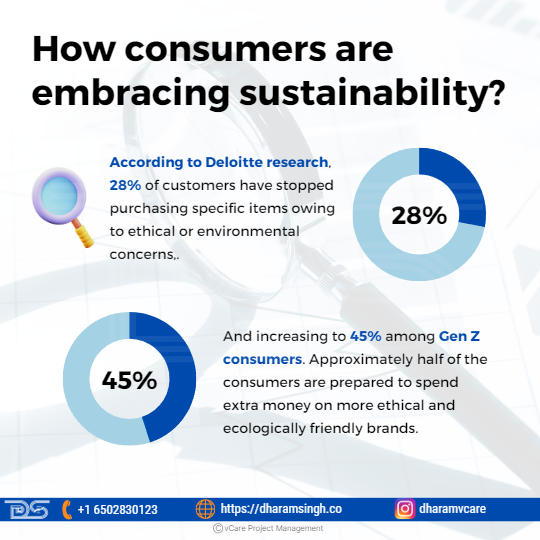
Consumer Shift to Sustainability
According to Deloitte research, 28% of customers have stopped purchasing specific items owing to ethical or environmental concerns, increasing to 45% among Gen Z consumers. Approximately half of the consumers are prepared to spend extra money on more ethical and ecologically friendly brands.
However, keeping track of and being open about an organization’s sustainability initiatives is difficult if these metrics and methodologies are not evaluated and integrated into project processes. Unfortunately, what frequently happens is a lot of greenwashing, over-promising, and under-delivering sustainability goals, which may lead to even more distrust in brands and corporations.
As a result, many organizations are adding and integrating new sustainability features into their pre-existing project processes to meet the growing need for accountability and transparency in sustainability activities. However, as regulations evolve and customers grow more attentive, this strategy may no longer be adequate. That is why the organization needs sustainable project management.
Sustainable project management
71% of the world’s top 500 companies openly disclose their greenhouse gas emissions, among other energy metrics. Sustainability has become a commercial priority for all industries, and organizations recognize that it is not responsible for ignoring the problem.

Broadening Project Management for Sustainability
However, sustainable project management is more than just being green and combating climate change. It is a duty to ensure that resources are utilized appropriately, that individuals are treated equally and fairly, and that communities are considered when making choices. Therefore, project managers in this sector will adopt a comprehensive approach, evaluating environmental, social, and economic aspects. They collaborate with environmental planners, hydrogeologists, and geotechnical engineers, to name a few of the ecological professions helping to remake our planet for the better.

Principles of Sustainable Project Management
Sustainable project management is an approach that:
- Takes into account the complete Triple Bottom Line viewpoint.
- Considers the complete life cycle of a project, from project-related activities through final deliverables.
- Engages stakeholders actively and openly rather than merely managing their expectations.
- Accepts responsibility for its actions to society and the environment.
- Considers the short and long-term consequences of all project operations and results.
Building sustainability into projects
Project managers are responsible for supervising the project delivery and support procedures. They will both strive to ensure client satisfaction while inspiring their team to deliver excellence. That is the essence of the role of a project manager.
Meanwhile, a project manager concerned with sustainability will take a more comprehensive approach. They will consider resource use, climate change mitigation, property rights, community engagement, and human rights. It’s a complicated profession that, when done correctly, can have a huge influence on civilizations. The project manager’s objective is to produce value and complete a project on time and within budget, but also to do it ethically and fairly.
Environmental management and responsible resource use have never been more popular. As a result, companies worldwide are seeking methods to cut waste and lessen the environmental effect of their operations. Being environmentally responsible not only helps firms appeal to customers, but it may also assist save costs by reducing resource requirements and minimizing exposure to potential regulatory fines.
When a company implements a “green” mindset into its project management approach, the positive impacts may spread across the organization, resulting in increased efficiency, less waste, and increased employee morale. Here are some ideas for building and carrying out sustainable projects in any industry.

Strategies for Project Sustainability Across Industries
- Start by assessing your current project’s sustainability.
Before taking measures toward increased sustainability, you must first understand where you are now. A sustainability analysis can assist the project manager in identifying the most significant development areas and measuring success as the sustainability project takes shape. First, determine if the concept of sustainability applies to a project or project management technique, and then assess the costs and effort necessary to improve.
- Develop a sustainability strategy
Once the evaluation is complete, the next stage is to develop a strategy that describes the business’s goals for enhancing sustainability, like how the goals will be achieved and what the organization wants to gain from the process. Like a project plan, the strategy should identify the people, roles, or departments that will drive the sustainability effort and the degree of power they will have in establishing project priorities.
Every day, modern organizations face new and growing obstacles. On the other hand, sustainable businesses have proven to be more resilient. But where do you begin? What steps can be taken to take your efforts to the next level? Here are the four critical steps in developing a sustainability strategy.

Crafting a Sustainability Strategy in Four Steps
Step 1: Identify the impact factors
Before developing a sustainability strategy, you must determine which factors are important to your company. Each company is unique based on the following:
- The industry you operate in
- The size of your company
- The location
- Your place in the supply chain
Different aspects will be relevant to your business.
The four pillars of sustainability
To ensure that your sustainability strategy has the greatest potential impact, you must first determine which aspects are most important to you. Companies should undertake a materiality analysis to do this. Here are the four sustainability pillars to consider in the analysis:

Core Aspects of Sustainability
- Environment
- Labour and Human Rights
- Business Ethics
- Sustainable Sourcing
Collecting data
Starting a stakeholder engagement with internal and external stakeholders is an excellent strategy for discovering your impact factors. In addition, conducting a survey or interviews will give you more profound knowledge.
Step 2: Determine the long-term vision and mission
After recognizing the crucial material issues, determine which ones you can genuinely influence. It is now time to develop a long-term purpose and vision. These two steps are critical for good strategic planning. They may give consistency and establish limits for your business and its employees.
The ideal future
A mission statement focuses on your company’s present position and briefly explains its main purpose, focus, and goals. On the other hand, a vision statement summarizes an organization’s goals and the larger influence it hopes to have in the future. As a result, your vision and mission statement must represent your fundamental materials challenges and expand on your materiality assessment results. In addition, your company’s distinct traits must be taken into account. This aspect may assist you in prioritizing the impact elements and creating long-term alignment in your organization.
Step 3: Formulate the sustainability strategy
Finally, in the third step, you can begin designing the real strategy, which is a more immediate translation of your vision and goal. It should include all of the impact elements (identified in step 1) that are relevant to your business. More precisely, you must determine short- and mid-term objectives to realize your long-term vision and purpose (identified in step 2). Breaking down these long-term high-level statements will make each step more concrete and manageable.
Setting goals
The goals should be SMART:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Realistic
- Timely
After you’ve chosen a set of relevant targets, you’ll need to decide what steps your organization will take to reach them. Project outlines and processes must be outlined in detail. It is critical to ensure that your approach promotes both horizontal and vertical cohesion.
- The alignment of multiple departments and sustainability pillars is called horizontal coherence.
- Vertical alignment, on the other hand, refers to the consistency of choices made at the management (group or entity) and operational levels.
Step 4: Implement the sustainability strategy and track success.
The next stage will be to put your thoughts into action. Developing a great plan begins with collecting relative insights and understanding your primary material concerns. Then, by following a step-by-step approach, you can create a framework that will allow you to focus on investment and drive performance while also engaging internal and external stakeholders.
- Adopt a sustainability standard
As interest in project sustainability grows, companies have established guidelines to assist senior leaders and project managers in determining if they are reaching their sustainability objectives. For example, Green Project Management has issued the P5 Standard for Sustainability in Project Management, a set of goals and measurements that businesses may use to drive their efforts.
- Look for sustainability in partners and vendors.
The larger an organization, the greater leverage it has on the firms with whom it does business. So asking vendors and suppliers to raise their sustainability can lower the organization’s environmental footprint and lead to broader changes among the vendors and customers.
- Spread the word
Communication is the key to success in every organizational activity. Begin including your project teams in the process as soon as your sustainability strategy is determined. Solicit input on your sustainability goals and fresh suggestions from staff based on prior efforts. The more engaged your team is in the sustainability project, the more determined they will see it through.
- Be adaptable
One critical component of project sustainability is the capacity to adapt to changes in the organization, technology, and competition. Because these factors might shift a company’s goals while responding to them can help you succeed. This move might also include modifying project criteria or responding quickly to problems to execute projects on schedule and budget.
- Ensure projects are manageable
Projects become sustainable when they are manageable. While you may have larger ambitions, breaking them down into smaller, more manageable tasks might help you with expenses and resource allocation over time. You may also check your ability to implement manageable initiatives, such as having the necessary teams and approval processes. When planning for the future, be sure the organization can support any system or process modifications that a project manager wants to deploy.
- Review scalability
The ability to raise or reduce your resources based on your project’s demands is called scalability. This need frequently occurs when the scope of a project grows greater than intended, necessitating the use of additional tools, funds, people, or other resources to execute it. Ensuring that you can handle changes in scale may aid in developing a long-term sustainability strategy since it provides that the result will still be worth any additional demands.
Why should every project manager prioritize sustainability?
As governments worldwide establish net-zero carbon objectives, project managers are being charged with rethinking work processes to reduce emissions. Everything from planning to procurement to team structures is being re-evaluated to achieve sustainability goals. However, it is important to realize that sustainability covers more than climate change. It entails balancing projects’ environmental, social, economic, and administrative components to fulfill the requirements of present stakeholders without compromising the needs of future generations. Far from being a burden, sustainability provides an opportunity for project professionals to demonstrate their value by connecting with company strategic objectives centered on net zero. By incorporating sustainability into all aspects of their projects, project managers may make a significant difference and increase their visibility to the organization’s leadership.
Final Thoughts
Project Sustainability Management necessitates a more comprehensive strategy. It considers resource utilization, climate change mitigation, property rights, community engagement, and human rights. The project manager’s mission is to provide value and complete a project on time and under budget and do it ethically and fairly. The intertemporal character of sustainable project management contributes to its complexity. As a result, the lifetime of a sustainable project should not end after completion; environmental and social impacts must also be monitored and regulated afterward.
Project managers are in charge of managing the project delivery and support procedures. Both will ensure client satisfaction while inspiring their teams to produce greatness.
Project managers must consequently arm themselves with new indicators, such as ISO, SA, and others, for monitoring and managing these environmental and social issues. In the end, initiatives serve as a tool for effecting change, introducing new goods and services, and shaping society. As a result, sustainability should not be an afterthought but rather one of the primary aims of any project.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting https://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Oct 13, 2023 | General
Organizations may stay profitable and competitive using project management practices that help identify process improvements or cost-cutting opportunities. Metrics may assist in discovering areas for improvement, data to focus on, and how to quantify the success and efficacy of a company’s efforts. Knowing more about project management metrics that can assess performance will help one acquire professional skills for any business and advance their career in project management.
Every organization needs to ask,
- “Are we getting the outcomes we want?”
- “Are we accomplishing our project objectives?”
- “Are we meeting the requirements for customer success?”
- “Are we getting the intended return on investment?”

Project Management Metrics May Assist
Success depends on the ability to forecast and meet product and service commitments. With projects becoming more common, it is critical to show additional value to the business using project management strategies, tools, and procedures. Therefore, a metrics program is required. Metrics may assist in identifying significant events and trends, distinguishing between challenges and opportunities, and guiding companies to make wise decisions.
How can we know whether the project management efforts make a difference and contribute to corporate success?
- It has long been known that suitable measuring methods are essential to basic management tasks, including project planning, monitoring, and control, and metrics are present at all stages of project management.
- As project management grows prominence and more firms embrace a project-based management approach, objective and performance-based management highly depend on measurement processes.
- To assist decision-making, project selection, portfolio management, and lead product and process improvement, metrics must be integrated into project life-cycle activities.
- In addition, metrics may be used to assess an organization’s project management maturity.
- Metrics aid in understanding capacities, allowing for developing strategies based on creating and delivering goods and services. They also enable people to recognize significant events and patterns and distinguish between challenges and opportunities.
- Metrics can assist in improved cost and schedule management, decrease risks, increase quality, and guarantee that objectives are met.
Measuring is an end goal in some businesses. Individuals in such businesses who have obtained project management certification and use specific project management tools and processes are the ones who often recognize the significance of project management. At the same time, individuals at the top may only accept this value partially. A metrics practice put in place is one of the best methods for successfully explaining the benefits of project management to top executives.
What are Project Management Metrics
What are Project Management Metrics?
Project management metrics are data sets, algorithms, and calculations that allow businesses to assess the performance of a project. They assist managers and organizations in reviewing how a project progresses, evaluating team productivity, project completion deadlines, and costs, and identifying, reducing, or eliminating risks. Project management metrics are numerical instruments that firms use to build successful strategies, carry out continuous improvement initiatives, and assess employee and customer sentiment.
Benefits of using metrics in project management
Project management metrics are an efficient approach to assessing a project’s progress. Measuring the project’s performance against key parameters helps to understand the management process. These indicators in project management also assist in steering project objectives, allowing teams to assess success and make improvements as needed.
Following and evaluating the right indications can provide the company with critical insights regarding the team’s performance – from both a high-level and individual standpoint. In addition, you’ll be able to identify process bottlenecks and other inefficiencies, which one can subsequently fix, adding to the project assumptions list and enhancing future project performance.
Furthermore, tracking and collecting this sort of data might be useful when the time comes for the project management performance review. Taking responsibility for the team’s work by analyzing project outcomes, identifying inefficiencies, and developing improvement plans sends a strong message to management. It displays that one can be a real leader committed to the business’s success.

Benefits of Using Metrics in Project Management
- Measure team productivity
Relevant metrics in project management can reflect a team’s productivity. For example, the on-time delivery (OTD) rate or service level agreement (SLA) rate might be used to calculate the project’s ROI.
- Optimize team performance
While it is critical to maintain the team’s performance, forward-thinking management seeks development opportunities. Relevant project metrics enable one to broaden their understanding of project-related aspects. Project performance measurement reduces uncertainty and allows individuals to make better, more informed decisions.
- Track ongoing progress
Management performance metrics also track a project’s progress over time. These metrics are critical to discover obstacles early and help adjust the track as needed.
Project Management Metrics: How to Measure and Track Success
Relevant project management metrics will help enhance our understanding by eliminating uncertainty and making well-informed decisions.
Metrics prove value
Cost-related project management indicators may demonstrate the value of a team—for example, a rate of on-time delivery or a rate of satisfying SLA. Return on Investment (ROI) is a popular statistic for demonstrating this value. If a department fails to generate or contribute to a firm’s measurable objectives, a smart business would dissolve the department and redirect resources to another area that provides results.
How to choose the Metrics
Metrics improve performance
While demonstrating value is crucial, forward-thinking management prioritizes performance improvement. Relevant metrics help you have a better grasp of project management. This aspect reduces ambiguity, allowing all parties involved to make informed decisions. For example, assume that the given slack time is causing the completion of the following task to be delayed. You can adjust the slack time to keep the project deadline.
How to choose the metrics?
Each business or project requires metrics specific to its purpose or aim. Metrics are determined in three steps:
- Understand the project’s objective or goal.
- Determine which crucial success elements must be met to succeed and reach the objective.
- Consider how you will measure the achievement of each key success factor for the project or program.

What makes a successful project?
What makes a successful project?
Before starting any project, you and your team should know what constitutes a successful project. After all, you want to avoid being known for a famous failed project. So what makes a project successful? First, you should establish a set of success criteria for your project, including the following:
- Delivers on time: Completing a project on schedule and under budget is one measure of success, especially for external parties, such as clients.
- Stays within budget: A budget is in place for all initiatives. You will have succeeded if you can finish yours without incurring more fees and expenses.
- Achieves its objectives: If your project was completed and met its objectives — as stated at the outset — that’s a huge accomplishment.
- Gets positive feedback: Assessing a project’s internal and external success is simple. But how did it fare? If stakeholders and clients offer positive feedback, the project will be considered a success.
Key Project management metrics
Project management metrics may be established based on the purpose and complexity of the project. However, the ten key project metrics listed below often cover the most important measurements:

Key Project management metrics
- Productivity
This indicator examines a company’s total skills — how well it uses its resources. Productivity demonstrates the connection between inputs and outcomes. For example, how much do you get out of a project after your efforts? The optimal productivity outcome is to produce more with less.
Productivity = Units of Input/Units of Output
- Gross Profit Margin
Numbers are more powerful than words. Indicators directly related to the bottom line indicate success or failure faster than other metrics.
The larger the profit margin, the better the business. Any program or effort done should add to a company’s financial profit. The margin is the proportion of each dollar generated after expenses are deducted.
Gross Profit Margin = (Total Profit-Total Costs)/100
- Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on investment especially considers the dollar amount earned for the amount spent on a project. This metric is a financial calculation similar to gross margin. However, instead of focusing on a total profit, it considers the specific benefit of the project divided by the costs.
To use this metric, a dollar value must be assigned to each unit of data to calculate the net benefits, which may include:
- Contribution to profit
- Cost savings
- Increased output
Costs may include resources, labor, training, and overhead.
ROI = (Net Benefits/Costs) x 100
- Earned Value
Earned value provides strategic guidance by displaying how much you have derived from the money invested in a project to date. It compares the value of work performed by a given date to the project’s approved budget.
Earned value is often called the Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP). This statistic serves as a reality check during the project’s execution.
Earned Value (EV) = % of Completed Work / Budget at Completion (BAC)
- Customer Satisfaction
A customer satisfaction score is a quality indicator for your service or product—the findings of a customer survey influence this metric. In addition, the product or service should perform as intended and meet genuine client demands.
Each organization may create a unique score by weighing each component depending on its value. Customer survey results, money earned from clients, repeat or lost clients, and complaints are examples of variables.
The Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI) is the most extensively used metric for customer satisfaction. Another technique for measuring customer satisfaction is the Net Promoter Score (NPS). NPS measures customer loyalty by determining the chance of a consumer suggesting a product or service.
Customer Satisfaction Score = (Total Survey Point Score / Total Questions) x 100
- Employee Satisfaction Score
Survey data determines employee satisfaction in the same way that customer satisfaction is. So why should workers be included while evaluating project management? The answer is straightforward: employee morale is directly related to project performance.
In the end, a satisfied employee does better work and more efficiently. In addition, the high costs of employee turnover for a firm — which may range from 50% to 200% of an employee’s salary — should be motivation enough to focus on the people closest to the project.
The Gallup Q12 Employee Engagement Survey is a well-known data collection tool. An ESI procedure yields an index score.
Employee Satisfaction Score = (Total Survey Point Score / Total Questions) x 100
- Actual Cost
The Actual cost is a simple statistic that displays how much money is spent on a project rather than simply an estimate. This cost is calculated by adding all the expenses for a specific project across the timeline.
Actual Cost (AC) = Total Costs per Time Period x Time Period
- Cost Variance
Cost variance describes the difference between the intended budget and actual expenses during a given time period. Is the estimate higher or lower than the actual costs?
- A project is over budgetif the cost variance is negative.
- A project is under budgetif the cost variance is positive(a standard measure of success).
Cost Variance (CV) = Budgeted Cost of Work – Actual Cost of Work
- Schedule Variance
The schedule variance examines both budgeted and scheduled work. Is the project running ahead of or behind schedule?
The schedule variance is the difference between work scheduled and work accomplished, calculated as the budgeted cost of work executed minus the budgeted cost of work scheduled. A negative schedule variance indicates that the project is running late.
Schedule Variance (SV) = Budgeted Cost of Work Performed – Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled
- Cost Performance
Cost performance is a cost efficiency metric. Divide the value of the work performed (earned value) by the actual costs incurred to get the earned value. Forecasting cost performance provides for more precise budget estimates.
Cost Performance Index (CPI) = Earned Value / Actual Costs
Implementing Project Metrics
Once project metrics have been established to meet the company’s goals, it’s time to apply them. First, interact with users to help them understand the process, its value, and how analytics may enhance projects. Then, provide specific examples, such as “the dashboard will indicate where we need documentation, so we may prevent delays by gathering the necessary information.”
Create a project management metrics strategy with criteria everyone can understand to help you get support. Explain the significant indicators you’ll be measuring, how you’ll track them, and the goals you intend to achieve. The strategy should then be put into action. Understand that project metrics should lead to action; else, they are worthless. As you discover unusable metrics, revise the plan.
Final Thoughts
Project management metrics are critical to the success of any organization. They track the progress of initiatives, assist managers in defining success, and verify that the team is heading in the right direction.
It is complicated to analyze and evaluate a project’s development without appropriate metrics in project management. With precise, trackable KPIs, the company can assess project progress and identify when it’s time to change strategy or where the team is experiencing difficulty. If the company does not make the essential changes, it may face serious obstacles and lead to failure. As a result, measuring important project management metrics is vital to the company’s success.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
Register today for my FREE webinar series on PgMP® and PfMP® certifications! Don’t miss out on this opportunity to advance your project management career. Click the registration link to sign up: https://bit.ly/3Z7kzMl
Are you looking for project management training and certification discounts? Check out our various offers and discounts here: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
Have questions about your project management career, training, and certifications? Book an obligation-free 15-minute session with me and get the answers you need: http://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
Stay up to date on the latest in project management by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel. Catch our Q&A series and certification success stories here: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
Want to hear from project management experts? Subscribe and follow my podcasts and interviews on YouTube here: https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Sep 29, 2023 | General
Project management is in great demand by many businesses, as are the project managers. Project management is widely used in today’s economy, regardless of the business. Why?
Today’s organizations confront tremendous competition. They must address global issues and respond to internal/external concerns in parallel. In response to obstacles, businesses require a disciplined strategy for planning, organizing, controlling, and managing their resources (including internal skills) to deliver outcomes on time. And these outcomes should be in line with goals and demands. Project managers with strong project management abilities are well-equipped to take on these initiatives. These initiatives may have varying levels of complexity. Therefore, if you are a project manager or want to start a career as a project professional and be marketable amongst other professionals to survive in this competitive environment, this article will provide a good overview.
Transforming your project management career
A project management career might be an excellent choice if you want to increase your income and professional status. Project management roles are often active and interesting, with constant new challenges and possibilities. In contrast, talented project managers are in high demand throughout the corporate sector, as many qualified candidates are looking for these opportunities.
Understanding Project Management
One of the biggest misconceptions regarding the project management profession is that it is fundamentally the same as a more traditional management position. While project managers must be great leaders, their primary responsibility is to manage projects, not people.
Unlike departmental managers, project managers are not a part of the typical supervisory structure used by most businesses. Instead, they function as a type of free agent – a project management profession entails coordinating the work of many individuals and divisions to achieve a certain assignment. Throughout a project, the project manager will communicate with individual contributors at all levels of the organization in connection to various deliverables.

Duties of a Project Manager
Project Manager Duties/Tasks
- Determines relevant goods or services to define project scope, requirements, and deliverables with clients or customers
- Develops, adjusts, or contributes to project plans
- Implements project strategies to achieve goals
- Project activities are coordinated and integrated
- Manages, Directs, or Oversees project resources
- Monitors project activity and resources to reduce risk
- Quality assurance methods are implemented or maintained
- When issues arise, the project manager makes changes, fixes them, or takes remedial action
- Presents or briefs on all aspects of the project
- Participates in the project phase, milestone, and outcome reviews
- Determines the requirements or processes for project documentation
- Creates and implements a product release strategy

Qualities that make a Project Manager in High Demand
Qualities that make a Project Manager in high demand
Effective project management may require the following qualities to become an effective project manager:
- Effective communication skills
A good communicator is one of the qualities of a successful manager since it allows them to interact with people at all levels. The project manager must clearly describe the project goals, duties, responsibilities, expectations, and feedback for each team member to obtain the project goal.
- Strong leadership skills
Effective project management requires strong leadership abilities, such as encouraging and driving the team to maximum performance to achieve their objectives.
- Good decision-maker
An effective project manager must be able to make decisions since they will always be required.
- Technical expertise
Because project management software and other associated programs are vital in achieving project goals, a good project manager must have strong technical expertise to understand technological challenges. In addition, knowledge of theory and technology may substantially assist managers in adopting strategic moves when necessary.
- Inspires a shared vision
An effective project manager can communicate the vision to the team members. A visionary can guide employees in the proper direction while effectively adapting to changes. In addition, they excel in empowering people to experience their vision for themselves.
- Team-building skills
A team must work together, or the project will face numerous relational issues that might threaten its success. Project managers must understand how to offer each of them the attention they require by emphasizing their positive characteristics.
- Handles the pressure
As the project progresses, specific events could hinder its pace and put the project manager’s patience to the test. Therefore, project managers must always remain composed and grounded to avoid losing themselves and negatively affecting their connection with the team.
- Good negotiation skills
The capacity to negotiate is one of the abilities required for efficient project management. Project managers must have strong negotiation skills to resolve disputes resulting from differences of opinion and keep the team functioning together.
- Empathetic
An empathetic leader demonstrates to their followers’ things like compassion, empathy, and gratitude for others’ assistance. Understanding the project’s and its stakeholders’ demands is a necessary step.
- Competence
A good manager can start new initiatives, manage obstacles, and knows what he is doing.
An effective project manager must possess the majority of these qualities to manage the project successfully, along with a professional certification. Professional certificates can add value to their career and aid in success in a competitive environment.
Project Management Certification
A project management certification is a certification that verifies an individual’s project management knowledge, skills, and practical expertise. Certifications like PMP®, PgMP®, PfMP®, and other advanced certifications can aid the professional’s knowledge and adds value to their career.
According to the August 2023 PMI Fact File Stats, there are 1,465,873 PMP®, 4,847 PgMP®, and 1,538 PfMP® active certified professionals globally. Thus, completing those training programs and earning a project management certification from a globally recognized standard organization such as the PMI might improve the career, including staying current with a constantly evolving field, keeping up with the latest technology and practices, and earning a better project manager salary.
A career in project management: Facts and Figures
Project management has become a highly sought-after career path in today’s agile environment. According to the Project management – Job Growth and Talent gap, 2017 – 2027 report,

Project Management – Job Growth and Talent Gap | PMI
- A growing disparity exists between the demand for experienced PMPs and their suppliers worldwide. As a result, firms and organizations are searching for qualified project management professionals. Moreover, it allows one to tailor themselves to their needs.
- By 2027, there will be a demand for 87.7 million PMP positions. Because of increased demand and high attrition, there will be a huge job opportunity for a project management role in the coming future in various sectors, including manufacturing and construction, information services and publishing, finance and insurance, management and professional services, utilities, and others.
- Apart from the fact that there will be a lot of employment for PM positions in the future, it’s also encouraging to know that PM roles will be financially rewarding. According to the report, in the United States in 2017, earnings of project management-oriented professionals in projectized sectors were 82 percent more on average than the salaries of non-project-oriented professionals.
Challenges Faced by the Project Managers
A project manager must handle challenging projects smoothly and deliver positive outcomes. It may appear that being a project manager is a simple and well-paid profession. However, a project manager must work hard and face obstacles daily to balance all parts of a complicated project.

Challenges Faced by Project Managers
As a result, a project manager must be skilled in various areas, including communication, decision-making, delegating, and risk-taking, to mention a few. In addition, project managers are constantly required to manage tasks, resources, time, and money in addition to managing projects. Here are some of the challenges that today’s project manager’s face:
- Scope creep
Scope creep expands a project’s scope beyond its intended objective or aims. It usually occurs when project stakeholders request adjustments. Any change to a project’s strategy can cause confusion, raise the cost of resources, and make meeting deadlines difficult.
- Poor communication
Strong communication is one of the keys to effectively completing a project. A project manager can successfully provide orders, acquire information, and update stakeholders if they have strong written and verbal communication skills. Otherwise, their team might need to be more organized, causing delays.
- Unclear goals
Projects can only be effective if the team works toward well-defined and quantifiable goals. Ideally, every team member is aware of each project objective and the specific expectations of each stakeholder. Otherwise, they may spend time and resources attempting to do something that does not give the necessary benefit.
- Poor budgeting
Smart financial planning and cost management are required to ensure that funds are used wisely. Poor budgeting, on the other hand, may result in unfavorable effects. Without a solid understanding of financial concerns, the team may face cost overruns, aggravating stakeholders and preventing the project from being completed successfully.
- Insufficient risk analysis
Risk analysis is forecasting probable elements that might threaten a project’s success. Although it is an important aspect of the project life cycle, the process is vulnerable to specific hazards. For example, rushing the analysis might result in oversights that fail to anticipate important difficulties. As a result, flaws in the project design, budgetary concerns, or unexpected variables may arise.
- Lack of accountability
Accountability is accepting responsibility for one’s actions and the consequences of those acts, especially when mistakes are made. As a result, responsible people are willing to confront the consequences of their actions and attempt to overcome the resulting difficulties. However, when leaders and team members are not accountable, they can interfere with development in many ways. One way is to undermine team morale, which may withstand the repercussions of a single person’s errors. The other is by decreasing production when project resources are diverted to determine the root cause of a problem.
- Unrealistic deadlines
An unrealistic deadline is impossible or unreasonable to accomplish, given the specifications and needs of the project. When a team faces unreasonable deadlines, they are obliged to compress their operations so that the quality of their work decreases. As a result, the project’s final output will likely fall short of client expectations.
- Uncertainty
Uncertainty occurs when stakeholders, including team members, need clarification about any part of the project they are working on. For example, they may be concerned about the team’s ability to accomplish goals, the project’s possible impact when finished, or the usage of project resources. When uncertainty occurs, it may damage engaged people and lead to poor project outcomes.
Ways to make yourself more marketable as a Project Manager
Making oneself necessary to a current employer or alluring to a prospective one is the key to being (and remaining) marketable. Therefore, it is a commitment to constantly broaden the skills and knowledge to remain current, competitive, and well-positioned to compete for employment in various market scenarios.

Ways to make yourself more marketable as a Project Manager
Here are some suggestions to boost your job prospects at all phases of the economic cycle.
- Upgrade your skills
Keeping your skills fresh, current, and relevant is the best way to stay marketable. Align your skillset with your company’s plans and those of potential employers, and keep up-to-date by attending workshops and conferences to expand and improve your skillset.
Identify gaps that need addressing to position yourself as a highly valuable employee. Focusing on developing your transferable skills (in leadership, communication, or technology, for example) is a smart investment in diversifying and upgrading your career.
- Expand your learning
Continuous learning demonstrates your dedication to growth. Remember that you must stay current on the industry’s best practices and technologies, even if you are not using this information in your current role. Improving your knowledge and qualifications is a vital strategy to boost your worth to a current or future company.
In-house training, distance learning, and online courses may all help you develop new skills and information. Online seminars and professional journals are also excellent ways to stay current in your field, making it simpler to transition into a new job.
- Rework your CV
Refresh your CV with recent accomplishments and current skills so you can take advantage of opportunities as they emerge. Update your CV with concrete examples of your achievements, such as improving business procedures, contributing to the bottom line, or attending key conferences or seminars. Keeping a record of your accomplishments is an excellent reminder of the value you provide to your present position.
- Be flexible
In today’s constantly changing work market, having an open mind and staying flexible about your professional choices will offer a world of extra professional prospects. However, you may need to reassess your expectations regarding industry, compensation, and employment type (permanent, contract, or temporary) to keep your alternatives open and avoid restricting your employability.
- Expand your network
One of the essential job search and career development tools you have is your network of connections. Attend chapter events, networking events, activities, and conferences whenever possible. Networking helps to keep you top of mind when possibilities occur within or outside your firm, as well as creating your reputation as a well-connected and appreciated professional.
- Stay Informed
Anticipating what talents businesses will want now and in the future is crucial. Keep current with essential trade publications, industry studies, and job postings. Staying up to date on advancements and opportunities offers you a good indication of the types of talents that are now in demand, as well as those that are likely to be relevant in the future and which are helping you to plan for future career opportunities.
- Establish a personal brand
Remember that you are ultimately marketing yourself to a potential employer, so maintain consistency in your brand. Any changes to your CV should be reflected on your LinkedIn page, and you should consider getting a professional photo taken to put in your profile.
- Showcase your work
Maintain samples of your best work, as long as they are not the intellectual property of your current employer, and create an online portfolio. This simple method demonstrates your appreciation for your work and its quality. Make sure to include the portfolio in your LinkedIn profile so future employers can see your capabilities.
- Get a mentor
Discuss obtaining a mentor with your management or someone in a career or profession you might be interested in later. Find out what helped them get to where they want to go or what they would be looking for in a comparable job when recruiting. For example, you need to focus on a certain skill set or achievement ahead of time. In that case, you can offer yourself a more suitable candidate for new employment.
Final Thoughts
The project manager’s role is critical since it determines whether a project succeeds or fails. Therefore, being the project manager places a more significant focus on essential abilities and experience; as a result, the project manager is expected to have the necessary talents and desire to perform the research required to stay current and competitive.
But not all project managers are equal. For many of us, the problem is figuring out how to stand out in a market where everyone talks about having a brand. Also, how do you differentiate yourself in a setting where selling your value to the project is frequently more essential than getting things done on the project?
Here are a few suggestions to assist you in establishing your presence as an essential component of your organization’s success and put you in line to be recognized for your achievements.
- Make sure you communicate with everyone in the organization.
- Share your thoughts inside your business and with the project management community.
- Encourage yourself to keep growing.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting https://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Sep 8, 2023 | General
From a strategic standpoint, the PMO is critical in project management. Unlike project management, which focuses on the day-to-day operations of a project team, the PMO serves as a framework for project managers, offering PMO methodologies and templates for managing programs inside an organization. In addition, it manages the project management resources required to sustain and deliver projects.
Project management offices (PMOs) are evolving from purely administrative to strategic roles. They are rethinking PMO operations, adopting new technology, and implementing new project management operating models. The evolved PMO is a new PMO concept that is gaining traction. A creative, strategic, and adaptive PMO designed to help modern organizations deal with the volatility of today’s market conditions.

Functions Of A Project Management Office
Functions of a Project Management Office (PMO)
A project management office (PMO) is the foundation of a successful project management strategy in a business. It is a function that gives decision-support information but does not make choices.
A project management office (PMO) supports project delivery mechanisms by ensuring that all business change in a company is controlled. PMOs perform various duties, and their services depend on the department’s maturity and the PMO personnel’s talents. At its most basic, the PMO assists project management teams in making funding, prioritizing, and resource choices. The most mature PMOs provide the following:
1. Governance: The PMO ensures that the appropriate individuals make the correct decisions based on pertinent information. Audits or peer reviews, designing project and program frameworks, and maintaining accountability at all levels are all part of the governance role.
2. Transparency: The PMO delivers information as a source of truth. Information should be relevant and accurate to promote good decision-making and be presented to individuals understandably.
3. Reusability: The PMO fosters knowledge sharing. This aspect prevents project teams from reinventing the wheel and positions the PMO as the hub for lessons learned, templates, and best practices.
4. Delivery support: By minimizing bureaucracy and offering training, coaching, mentoring, and quality assurance, the PMO makes it easier for project teams to accomplish their duties.
5. Traceability: The PMO manages paperwork, project history, and organizational knowledge.
In reality, most PMOs will do various tasks and offer services tailored to the organization’s requirements.
How Business Agility Drives A Shift In Focus For Today’s PMOs
Forward-thinking companies are fast learning that “simply getting the job done” will not equip them for long-term company success. To be successful in business today, firms must provide products and services that satisfy their clients while constantly innovating to grow their markets.
Historically, PMOs were responsible for managing tactical operations that supported project development and implementation. Today’s Corporate leaders recognize that to stay ahead of the market; they need to exploit new possibilities while limiting unanticipated risks – this necessitates a new approach to planning, building, and delivery. Maintaining consistent levels of project success involves more than an organized strategy; it demands a company’s collective attitude to accept required disciplines while staying flexible enough to respond to changes in their business.
1. A major project fails — badly: When an expensive, strategic initiative fails in a competitive market, it compels a company to rethink its strategy. A third of the organizations polled cited a big failure as the impetus for shifting emphasis.
2. A project goes over budget: An underlying driver is cost reduction; project success at higher-than-expected costs decreases profitability and damages customer relationships.
3. A PMO aids a strategic project to succeed: Success, on the other hand, is a catalyst for change. Therefore, the following important reason for building a strategic PMO would be to capitalize on the momentum produced by the successful project.
4. Market competition forces stronger disciplines: Maintaining market share and growing at a controllable rate encouraged larger firms to create consistency to innovate. The capacity to pivot and explore possibilities prompted smaller businesses to establish a strategic PMO.
Key Factors to a Successful PMO Transformation
Established businesses and fast-growing firms are both adapting to changing business environments brought on by competition, acquisitions, developing technology, and new risks. As a result, the importance of alignment, built-in quality, transparency, and the capacity to execute across various project endeavors has never been greater. Innovative design thinking, continuous delivery, excellent quality, and a never-ending drive for improvement are some of the essential characteristics of a modern-day PMO. Here are some causes driving PMO evolution and the seven elements required to turn a typical PMO into a transformation management office (TMO).
Drivers behind the PMO Evolution
Due to increased external business environment constraints, businesses must achieve rapid and substantial value from their projects and initiatives. This aspect means shorter delivery cycles, the adoption of developing technologies, and regularly changed priorities for the PMO. To achieve this transition, the PMO must move its focus from project execution technique to value-driven business results. Change drivers are often aligned with three fundamental needs:
Drivers behind the PMO Evolution
1. Capacity and skills:
- Specific domain areas of technical expertise required
- Extra capacity required
2. Rapid Execution:
- Organizations require rapid execution to address immediate concerns
- No time to plan, but need to execute now to meet deadlines (e.g., regulatory compliance dates)
3. Innovation:
- Legacy project management no longer meets expectations
- Value focus, agility, quality, and continuous improvement are required
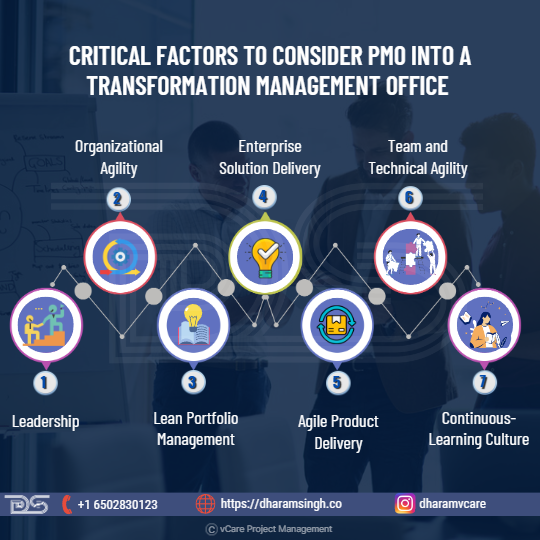
Transformation Management Office Critical Factors
Critical Factors to Consider
1. Leadership: TMO core values of alignment, built-in quality, transparency, and program execution must be completely embraced by leaders. They must adopt an agile mindset, emphasizing respect for people and culture, flow, innovation, and continuous development while cultivating a culture of trust and safety when setbacks occur.
2. Organizational Agility: Processes at the program and project levels must be improved to deliver value quickly while allowing companies to restructure and adapt to changing priorities.
3. Lean Portfolio Management: Goals for funding and execution must be aligned around workstreams that bring value to business priorities. Organizations may use this to optimize operations throughout their project portfolio. In addition, governance, monitoring, and decision-making for programs and projects should be decentralized to decrease overhead while boosting agility.
4. Enterprise Solution Delivery: The whole software development life cycle can be aligned with a DevOps methodology that refines and coordinates the work product across workstreams, supply chains, and suppliers to achieve and sustain continuous delivery.
5. Agile Product Delivery: Methods for delivering programs must begin with a customer focus and design thinking while aligning the continuous-delivery pipeline to a release cadence that provides optimum value to the customer.
6. Team and Technical Agility: Teams must be high-performing and cross-functional, with the knowledge and competence to design and execute high-quality solutions and work products aligned with customer-focused business goals.
7. Continuous-Learning Culture: Investing in being a learning organization is critical for employee transformation. Employees must be empowered to discover and uncover future value by embracing innovation and design thinking. Continuous improvement of solutions, processes, and products should be a priority at all levels of the business.
The evolving role of the PMO in digital transformation
Digital transformation has swept across organizations of all shapes and sizes to keep up with the growing expectations and needs of an increasingly digitized world. However, more people are learning that successful digital transformation entails transforming core cultures, structures, and techniques and integrating digital tools. Therefore, the function of the PMO in organizations must adapt to accommodate this shift as organizations evolve to accommodate this change.
According to a PWC study, 70% of organizations had or were working on a digital transformation strategy before the pandemic. Digital transformation may provide several benefits, ranging from better operational efficiency and product quality to increased customer satisfaction and lower development expenses.
However, PMOs have become linked with bureaucratic processes and unnecessary documentation. Their role must develop beyond the conventional limitations of “standards enforcers” to embrace their strategic role as change agents fully. Future PMOs must be at the forefront of emerging technology and implement various tactics that will allow the organization to make the most of available technologies.
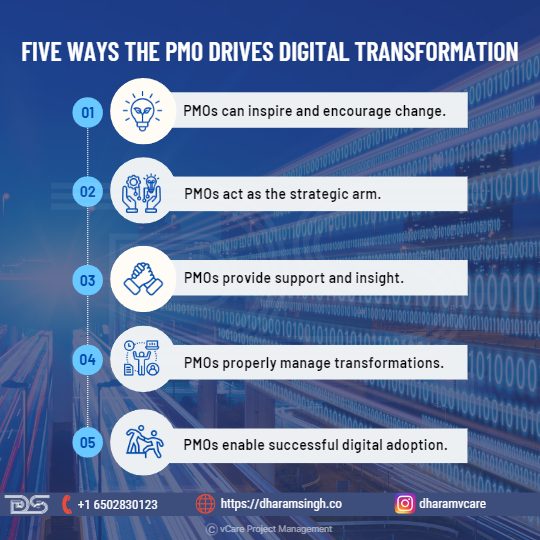
Five ways the PMO drives digital transformation
Five ways the PMO drives digital transformation
1. PMOs can inspire and encourage change
The PMO’s role is to assist organizations in gaining the support of all key stakeholders for a digital transformation. Teams are more inclined to invest in digital projects if the transformation’s advantages are personal. PMOs may implement explicit feedback mechanisms to ensure that all important input is easily supplied, reviewed, and acted upon.
2. PMOs act as the strategic arm
PMOs must ensure that their digital transformation plan is consistent with the organization’s overall strategy. For example, investing in high-end software is pointless if your company is attempting to save money and merely needs essential project management tools. PMOs must also comprehend the strategic benefit of digital technology investments and be able to quantify, justify, and carry out plans.
3. PMOs provide support and insight
Digital transformation programs are frequently large-scale enterprise-wide undertakings that need ongoing support and higher-level knowledge to influence their development. For example, PMOs may assist employees via virtual portals with the help of a PPM solution while also gathering Big Data to help evaluate the new technologies’ success and efficiency.
4. PMOs properly manage transformations
Introducing new technology frequently entails forming new teams and learning new skills to ensure a successful adoption process. Managing digital transformation entails guaranteeing the availability of relevant resources, skills, feedback mechanisms, and data collection procedures. PMOs can monitor the full effect of digital transformation activities, manage possible bottlenecks or pressure spots, and optimize ongoing operations.
5. PMOs enable successful digital adoption
PMOs are essential in getting people excited about digital initiatives and driving further use of the tools or processes. PMOs may assist employees in understanding the value of digital technologies by delivering interactive demos and holding learning sessions. When more individuals utilize the application, there is more data to accurately analyze the overall performance of digital activities.
Project Governance and its components
Project governance is an oversight position that includes the project life cycle. It is tied to the governance model of the organization. It provides the project manager and team with structure, processes, decision-making models, and tools for effectively managing and controlling the project. Project governance is critical, especially for complex and risky enterprises. It defines, documents, and communicates consistent project processes to give a whole way of project control and success. It includes a framework for making project choices, defines roles, obligations, and liabilities for project completion, and controls the project manager’s performance.
Components of Project Governance
Components of Project Governance
According to PMI, eight project governance components offer real-world value:
1. Governance Models
The organization should develop a baseline of important aspects required for project governance based on the project’s scale, duration, complexity, risk, stakeholders, and relevance to the company.
2. Accountability and Responsibilities
The project manager’s primary responsibility is to define accountability and obligations. An organization’s operations will only be successful if accountability and obligations are adequately distributed. Therefore, the project manager must specify who is accountable, responsible, consulted, and alerted for each project’s deliverables.
3. Stakeholder Engagement
It is essential to thoroughly understand the project environment while setting the groundwork for your governance plan. The first stage is to identify all of the stakeholders. If even one stakeholder is excluded, it can disrupt the entire project and have a negative impact. One must identify stakeholders from various sources, including sponsors, suppliers, the project team, government boards, company owners, etc. The project manager must identify the stakeholders, their interests and prospects, and, most critically, how to interact with them.
4. Stakeholder Communication
The project manager must design a communication plan after identifying all stakeholders and describing their interests and expectations. A well-planned communication strategy provides all stakeholders with concise, efficient, and timely information.
5. Meeting and Reporting
Once the communication strategy has been properly designed, the project manager ensures that the optimal mix of meetings and reporting is in place. It is critical to design the communication strategy so that each stakeholder knows the mode and content of the communication and the owner, receiver, communication milestones, and decision gates. Furthermore, communication must be concise, accurate, and to the point.
6. Risk and Issue Management
Projects and programs are riddled with hazards and difficulties due to their uncertainty and unpredictability. It is challenging to forecast what will happen. Still, it is vital since a lack of preparation will throw the project team well behind schedule. Any project or program must begin with an agreement on identifying, categorizing, and prioritizing risks and concerns. How the danger or issue is handled is far more significant than the issue itself.
7. Assurance
Project assurance ensures that risks and concerns are addressed effectively and provides the indicators that provide delivery confidence. One of the most important aspects of assurance is developing metrics to provide a view of project success.
8. Project Management Control Process
It is the simplest component yet the most complicated to implement. Process control activities, metrics relevant to the project, and measurements are monitored and controlled. Also, this is a collaborative review; the management must monitor performance regularly and address any variances on time.
Creating project governance is more complex than it sounds. First, a significant investment is required when embarking on a new project. What’s more challenging is determining what advantages are linked with it. The following are four major advantages of project governance:
- Single point of contact
- Problem management and resolution
- Information dissemination and clear communication
- Outlines the roles, connections, and responsibilities of project stakeholders
Reinvent the PMO’s role in the digital age
The structure, provenance, and stakeholders of IT strategy, regulation, and management operations are changing dramatically due to digitization. As a result, the project management office, or PMO, must move its focus from project governance and delivery to digital transformation. According to a Gartner study, 87% of firms prioritize digitalization. Furthermore, today, 77% of an executive’s top priorities depend on technology.
As a result, PMOs are under enormous pressure to transform. But unfortunately, the project, program, and portfolio management processes they build and monitor are geared toward predictability and consistency rather than the speed and flexibility necessary to satisfy digital demand.
More flexible job descriptions and growing ownership of project management activities by business partners and other delivery professionals put traditional hierarchies and established PMO positions to the challenge. As a result, the PMO’s future role in digitization initiatives is established rather than for it since it usually needs to be considered in discussions about digitally driven changes to the IT operating model.
The traditional role of the PMO: Three advantages
Organizations are altering the function of the PMO in response to better support the enterprise’s digital aspirations. To accomplish so, they must examine possible activities critically through the prism of the PMO’s comparative advantages. The majority of PMOs have three main benefits, which are either inherent because of the PMO’s function or location or were developed as a result of experience:
1. A neutral enterprise perspective:
As capital allocation and portfolio priority approaches alter to give the financial flexibility necessary for digital work, the PMO’s objective, enterprise-wide perspective on demand, investment, and resource consumption, is more valuable.
2. The ability to operate via influence:
As organizational boundaries grow more flexible and who “owns” project management becomes less definite, influencing and empowering others, rather than direct ownership, becomes even more crucial.
3. Stakeholder insight:
As digitalization expands throughout the business and accounts for an increasing quantity of work, the number of first-time stakeholders and stakeholder complexity for each work item increases. Therefore, understanding the preferences of these many stakeholders and experiencing synthesizing their feedback becomes critical in producing results from digital work.
The PMO’s new role: Advancing digital ambitions
Leading PMOs are leveraging these advantages to shift the focus of their mission away from governance and delivery activities, embracing a strategy-over-governance and management-over-operations stance. Here are three approaches to altering the PMO’s role in the digital age:

Altering the PMOs role in the Digital age
1. Orchestrating delivery and team workflows
The PMO is well-suited to develop and promote interactions across increasingly different types of work and stakeholders due to its enterprise perspective and stakeholder insight. PMOs can play significant roles in driving the adoption of new delivery practices (e.g., Agile, DevOps) and will need to build systems for team collaboration across methodologies. This move entails identifying and managing interdependencies that might derail existing activity and lowering the effort necessary for interaction across teams, other governance roles, and third parties.
2. Developing and enabling digital talent
PMOs have expanded their roles in creating and fostering digital talent, adjusting career paths, and equipping project management professionals with the skills and techniques required to handle increasingly dynamic digital work. This initiative includes fostering new competencies such as product ownership, cultivating an enlarged network of project management practitioners, and providing targeted assistance for increasing business-managed projects.
3. Supporting digital transformation
Digitization is driving change in the IT operating model, with 52% of IT businesses utilizing or planning to use a new model centered on product lines. The PMO’s role in facilitating this transformation will be essential in the future. For example, the PMO may assist with enterprise-level capital allocation, design, and management of product line investment roadmaps, assess product line success, and manage the organizational transformation required when IT transitions to product lines. Aside from IT, the PMO will be asked to help implement digital business activities.
Final Thoughts
The future PMO will be more strategic and intricate than traditional approaches, emphasizing driving decision-making, execution, and outcomes while becoming more decentralized to interact with each workstream to achieve one common goal efficiently. Finally, PMOs will be more crucial than ever in addressing the challenges that organizations are now confronting. An effective transformation will need PMOs to act as the organization’s voice and face.
As the pace of digitalization increases, the PMO role will be put under increased pressure. As a result, PMOs are looking for methods to cut back on their time and effort on operational and governance tasks. Thus, PMO leaders must leverage their unique assets to change their focus from governance and delivery assistance to strategy and management activities that support digital projects.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting https://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Aug 25, 2023 | General
The modern workplace is undergoing a significant transformation. As a result, project professionals in both the public and private sectors worldwide have started to recognize the full range of benefits that successful project management can bring to their businesses and are prepared to make the required adjustments, particularly on cultural changes.
The success of each project is dependent on an effective project management strategy. Considering the next generation of project professionals, it is critical to have an efficient leader who can direct this process since it is methodically planning, organizing, and executing a pre-determined series of procedures to maximize resource utilization and achieve objectives. Project goals will likely be met with a manager monitoring adequate planning and checking off milestones.
To compete in the upcoming competitive market, a project manager must have the technical, digital, and other essential project management skills to comprehend future project challenges. On the other hand, a project leader with an effective skill set can tackle all the challenges in a project in the right way. So here are some of the challenges and skill sets to manage a project for the next generation of project managers.
Challenges of Project Management
According to data provided in the PMI’s Pulse of the Profession 2020, 11.4 percent of corporate investment is lost owing to poor project performance.
What variables might contribute to poor project performance? There are examples of a need for more precise planning, inconsistent procedures and techniques, incorrectly managing or accounting for all project stakeholders, budget overruns, and other causes.
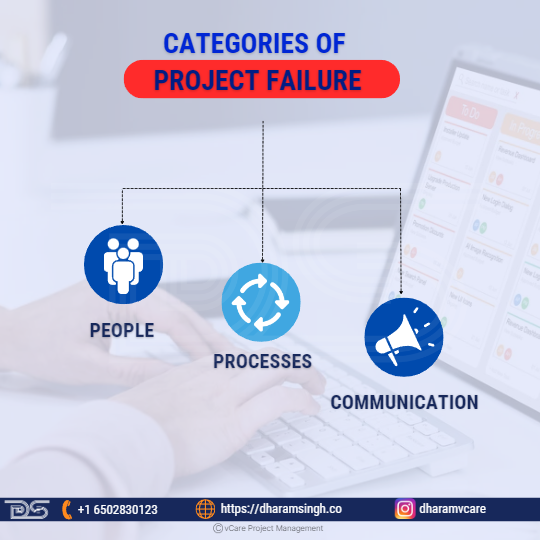
Categories of Project Failure
However, if we take a step further, the causes of project failure fall into three major categories:
- People
- Processes
- Communication
Let’s look at the most common challenges for project managers and some tips on how to overcome them.

Challenges of Project Management
- Undefined Goals
Identifying project goals is one of the most common challenges in project management. The entire project and team might suffer when objectives need to be clearly defined. When top management cannot agree on or support undefined goals, the project has a limited likelihood of success. To define and convey clear goals, the project manager must ask the right questions and make the right decisions.
- Scope Creep
“Scope creep” occurs when incorrect project management permits the scope of a project to expand beyond its initial objectives. Clients and supervisors may request modifications to a project, requiring the project manager to examine each request and determine how and whether to accept it meanwhile also conveying the implications to all stakeholders regarding budget and timelines.
- Inadequate Skills for the Project
A project may necessitate the use of talents that the project’s contributors may need to have. Project management may assist a project manager in determining the required competencies, assessing existing personnel, and recommending training, outsourcing, or recruiting extra people.
- Lack of Accountability
When each team member accepts responsibility for their role in project success, the project manager’s leadership characteristics may come through. A lack of responsibility, on the other hand, might bring a project to an end. Learning to lead groups toward a shared objective is an essential part of project management.
- Improper Risk Management
Another key aspect of project management is learning to cope with and plan for risk. Because projects rarely go as planned, risk management is a desired project manager trait. To do their work effectively, project managers must solicit input, build trust, and understand which aspects of a project are most likely to deviate from the original plan.
- Ambiguous Contingency Plans
Project managers must understand which path to pursue in pre-defined “what-if” situations. The entire project may become entangled in unexpected problems if contingencies are not recognized. On the other hand, requesting that people identify possible problem areas can result in a smooth and successful project.
- Poor Communication
Poor communication can cause major project management issues. Project managers must offer direction at all project stages so that each team member understands what is expected from them. Therefore, effective communication with all people involved in the project is critical to its success.
- Resource Deprivation
Management must offer adequate resources for a project to function smoothly and successfully. The project management process aids project managers in establishing demands and securing approval up front, as well as how to assign and prioritize resources during a project.
- Lack of Stakeholder Engagement
A project can be ruined by an uninterested team member, customer, CEO, or vendor. A skilled project manager communicates openly and invites input at every stage to increase participant participation.
- Digital Transformation
Adapting to the correct tools, systems, and procedures becomes even more crucial as more firms board the digital transformation train. This difficulty stems from adapting to the appropriate project management system, enabling teams to construct, change, and improve existing procedures to expand and scale.
Overall, project management is in great demand and isn’t going away anytime soon. Indeed, project management is anticipated to expand by 33% by 2027. However, to keep up with the ever-changing business landscape, project managers must be updated on proper project management methods and trends.
Major Challenges for the Next Generation Project Managers

Major Challenges for the Next Generation Project Managers
- The first major challenge project managers must confront is technology globalization and the disruption of traditional corporate culture and model. This aspect includes eliminating the requirement to do business or manage projects from a single place. The adaptation of the “virtual team” has become a must, and a company’s agility might mean the difference between success and failure. What used to take months may now be accomplished instantly, emphasizing the necessity of a company’s ability to fast and naturally adapt to the fluctuating nature of today’s technology culture.
- The second major concern is worker involvement, a project manager’s capacity to grasp various roles and responsibilities and use agility to wear numerous “hats” depending on the project. Knowing generational drives, establishing moral leadership, and understanding how the team performs are all part of this.
- Finally, project managers will be impacted by innovation and risk. The problem is figuring out how to strike a balance between innovation and risk—as managing risk is an important project management skill—but without it, it’s hard to realize the entire project’s potential.
Future Trends of Project Management
Consider project management ten years ago: fewer tools, smaller teams, and more straightforward tasks. Since then, the project landscape has changed dramatically, with important developments such as:
- Blockchain
- Artificial intelligence
- Sustainability
- Remote teams

Future Trends of Project Management
Trend 1 – Blockchain
More businesses use blockchain technologies for management, such as when conducting dispute investigations. The capacity of blockchain to automatically update data makes it ideal for reconciling records and transactions. One of the most significant contributions of blockchain to project management will be smart contracts, which are effectively self-executing contracts powered by computer code.
Smart contracts reduce the number of key functions within the project manager’s scope, such as checking on project milestones and assigning new ones, which speeds up management processes. As a result, quicker workflow assures project completion on time and improves a company’s overall performance.
Trend 2 – Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is increasingly finding its way into project management systems, managing anything from predictive analysis to risk management. Because of its efficacy, as per the PwC report, by 2030, AI is expected to contribute:
- $42.7 B (7.7%) to Egypt’s economy
- $135.2 B (12.4%) to Saudi Arabia’s economy
- $96.3 B (13.6%) to the UAE economy
The primary capacity of AI is to provide data insights for decision-making, which increases the agility of any given project.
Trend 3 – Sustainability
Project sustainability is more critical than ever now. Governments and societies worldwide are demanding greener alternatives throughout the life cycle of a project.
Green initiatives are cost-cutting solutions for businesses. For example, energy is required for project completion, and shifting to renewable sources reduces costs. In addition, this frees up resources that may be directed toward other essential areas like innovation and research. Meanwhile, sustainable practices improve a company’s reputation and encourage consumer loyalty.
Trend 4 – Remote Teams
Remote teams have been the norm since the advent of communication technology. As a result, businesses gain from a more diverse and borderless talent pool easily available through contracts. In addition, they spend less on office space, travel, and other administrative expenses.
Data from Upwork’s Future Workforce Report 2021 revealed that more than half of the US population was working remotely to some level. Furthermore, 40.7 million Americans will likely be fully remote during the next five years.
Furthermore, in its 2022 State of Remote Work Report, Buffer discovered that 97% would promote remote work to others and continue to work remotely, at least for some time or for the rest of their lives. On the other hand, just 26% of businesses are prepared to offer a remote work environment.
As a result, it’s not unexpected that more workers anticipate that workplaces will become entirely virtual over the next several years. In general, remote working arrangements enable businesses to extend their resources while increasing operational efficiency. As such, they are crucial in developing lean, competitive firms.
Key Skills needed for Next-Generation Project Managers
Because of rising trends such as remote teams, digitalization, and automation, project management has changed dramatically in recent years. More companies rely significantly on technology to plan, execute, and monitor work.
As an example:
- Big data and artificial intelligence for better risk forecasting
- Remote progress tracking using digitization technologies
- Automation software for more efficient execution
These solutions have improved firms’ management capabilities and altered project management’s future.
According to Gartner research, 80% of management duties will be automated by 2030, and future managers will need more technical skills. They must be knowledgeable about cybersecurity, blockchains, machine learning, and robots, all of which are expected to play larger roles in management.
To stay up with trends in modern project management, a fundamental understanding of topics such as data science, conflict resolution, and entrepreneurship is required. For example, data science skills may assist a manager in incorporating AI into more elements of the project life cycle. Here’s a closer look at what these skills include and how they’ll stay up with future innovations in project management.

Key Skills Needed For Next Generation Project Managers
Skill 1 – Data Science
Big data insights are essential management tools in the future, especially for large projects with extensive life cycles. In terms of planning, insights from previous projects indicate inefficiencies that can guide the current project, such as the number of idle hours and their causes. In terms of execution, data analytics assess progress and spot deviations early, such as changes in material prices and exchange rates that exceed estimates.
Skill 2 – Conflict Resolution
Today’s projects are extremely complicated, with constantly changing deliverables. As a result, conflicts are never far away.
These conflicts, if left unaddressed, can undermine your team’s performance, resulting in delays and missed deliverables. Managers must thus understand the aspects of conflict resolution, such as:
- Behavioral and organizational aspects of a positive workplace
- Effective communication
- Effective contingency planning
Skill 3 – Entrepreneurship
Project managers are essentially CEOs. On the one hand, they are in charge of project deliverables, while on the other, they are negotiating with shareholders and setting targets based on estimates. As a result, being productive requires more than technical and administrative skills. Project managers must also have entrepreneurship skills, such as strategic thinking and market insight. This skill is beneficial for modifying deliverables, which is typical in agile projects like software development.
Skill 4 – Resource Management
Budgets and timeframes became tighter as projects got more significant and more complicated. Today’s project managers must balance budget constraints, deliver quality, and achieve deadlines with limited resources. They are entrusted with creating a lean organization.
For optimal efficacy, a delicate balance of resource allocation is required, as over-allocation to one activity inhibits the others. So, managers must understand resource management principles such as equilibrium shifts and flexibility.
Skill 5 – Digital Skill
Digital skills are essential for future project managers. According to the CBI’s report on developing a world-leading innovation economy, upskilling employees with digital skills is critical. However, the digital skills pipeline could be improved. They believe more should be done to foster more ambition in that field.
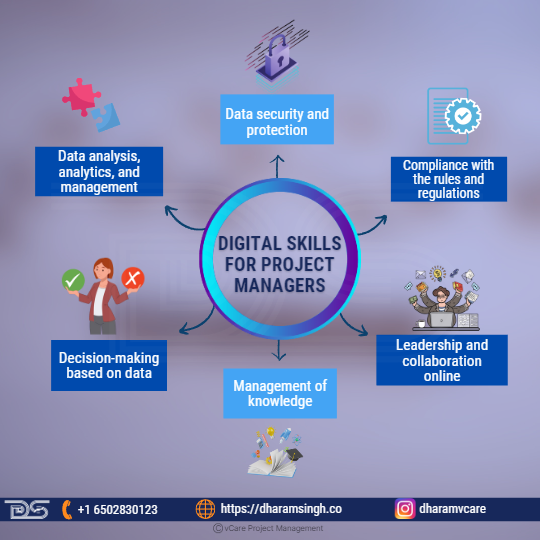
Digital Skills For Project Managers
Project managers need to have the following digital skills:
- Data analysis, analytics, and management
- Data security and protection
- Compliance with the rules and regulations
- Leadership and collaboration online
- Management of knowledge
- Decision-making based on data.
Considering the vital significance of the project manager’s role and how it changes, here is a list of additional skills for project leaders to follow in the present and future to enhance their careers and succeed.

Skills For Future Project Leaders
- Emotional Intelligence: The capacity to detect and interpret events and interactions (both verbal and nonverbal) in the context of the project plan.
- Adaptive Communication:The ability to explain one’s views to various individuals, groups, and cultures, whether orally or in writing, utilizing the most successful communication approaches for each group.
- People Skills: The ability to rapidly establish and maintain strong connections with team members and stakeholders.
- Management skills: The capacity to serve, encourage and concentrate a team, and create team member collaboration.
- Flexibility:The willingness and capacity to modify one’s project management style and course of action in response to business needs.
- Business Skills:Understanding the organization’s business, strategy, and industry. Understanding of a plan and ability to coordinate tactical work around that strategy.
- Analytical abilities:The capacity to think through circumstances and make judgments.
- Customer Focus:The ability to comprehend the end user’s or end customer’s demands and the drive to guarantee that projects meet those needs.
- Results-Orientation:The capacity to do tasks efficiently and successfully.
- Character:The project manager should have a pleasant demeanor and a solid moral and ethical foundation.
Final Thoughts
With a focus on the future generation, we’ve entered a project management world where we need to be aware of the key challenges we’ll encounter as project managers and the skills we’ll need to improve to succeed: technology globalization, worker engagement, and the battle between innovation and risk. There are, however, a few crucial insights to remember as you continue your journey through the strange and ever-changing world of project management.
- Be agile or be gone:Business constantly needs greater flexibility, strategy, and adaptability than ever before. No one strategy will work every time; knowing how to adjust to change with agility and rapidity is essential.
- Expect all teams to act differently:Teams will always be more diverse than those who make them up. However, you can lead more successfully if you genuinely grasp your team and each member’s unique imperatives. Because project teams determine project success, one of the most crucial skills of a competent project manager is the ability to construct an effective, high-performing team.
- Help team members understand the big picture:This will assist them in preparing for obstacles. When attempting to resolve an issue or manage change, keep the immediate consequences in mind to prevent losing sight of the forest for the trees.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting https://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Aug 11, 2023 | General
A project manager or leader is much more than someone who develops a strategy and controls all operations within a project. These experts, for example, must be skilled in communication and connection-building because the work requires them to do it frequently. The capacity to develop long-term, trusted relationships with stakeholders is a critical component of project managers’ and leaders’ success. Whether they like it or not, diverse stakeholders directly impact the business. As a result, companies with managers who can foster a deep connection with their stakeholders have a substantial competitive edge in today’s interconnected business environment.

Stakeholders
Why Stakeholders are Important to a Project
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization whose interests are affected by the success of a business venture or project. As the name suggests, stakeholders are interested in a project’s success. They might be internal or external to the entity funding the initiative. Stakeholder relationships may positively or negatively impact the project’s life cycle. Therefore you’ll need to identify your key stakeholders and develop a stakeholder management plan to fulfill the requirements.
Every project you manage has stakeholders, whether internal or external. One of the most common reasons for project failure is that the deliverables differ from what the customer requested or did not meet the customer’s demands. To guarantee project success, one should be familiar with the project’s main stakeholders, how they communicate their needs, and what acceptable results are.
Engaging stakeholders throughout the project, especially at the start, will assist, reduce and discover hazards and boost overall “buy-in.” When stakeholders are fully engaged, their impact is amplified. Stakeholders are vital to a project in the following ways.

Importance Of Stakeholders In Project
- Providing Expertise
Stakeholders are a source of information about current processes, historical data, and industry expertise. When gathering and documenting requirements, it is critical to include all essential stakeholders. Project managers and those in charge of deliverables may be experts on only a few projects. Key stakeholders can contribute to industry-specific needs or limitations that can be useful in identifying project constraints and risks.
- Reducing and Uncovering Risk
The more one engages and involves stakeholders in the project, the more they will decrease and identify risks. For example, during discussions, stakeholders may raise concerns regarding satisfying original specifications, project demands, and limits. Identifying risks and developing a plan to manage them before issues arise will significantly improve your initiatives’ success.
- Increasing Project Success
Stakeholders should be aware of the project scope, significant milestones, and when they will be asked to evaluate deliverables before final acceptance. Set expectations early in the project life cycle if the business must satisfy stakeholders’ demands due to competing needs or priorities. This move will assist in maintaining the relationship throughout the process.
- Granting Project Acceptance
The more frequently you interact and include stakeholders from the beginning, the more likely you will have a successful project outcome. By the end of the project, team members should be aware of delivery expectations and risks and how to reduce those risks. The final acceptance is their last stamp of approval at the project completion phase.
Stakeholder Relationships are key
Building relationships with stakeholders leads to improved trust. People collaborate more readily and successfully when there is trust. Investing time and effort in discovering and cultivating stakeholder connections may boost project confidence, reduce uncertainty, and accelerate issue resolution and decision-making. This concept recommends making a deliberate decision to devote time, attention, and effort to stakeholder relationships. In addition, personal qualities such as self-awareness, mindfulness, respect for others, and courage may be essential to developing trustworthy, open, and honest relationships.

Ways To Approach Stakeholder Relationships
How could we approach it?
- Determine the stakeholder hierarchy.
- Create profiles for individual and group stakeholders.
- Create relationship maps.
- Determine who should interact with whom and when.
- Always maintain a professional and genuine demeanor.
- Build trust and confidence through controlling and satisfying expectations, acting with integrity, honoring commitments, and being trustworthy.
- Consider how you can assist your stakeholders rather than just how they can assist your project.
Risks of overlooking this concept include:

Risks Of Overlooking Into Stakeholders Relationship Concept
- Increased project risk in terms of time, cost, and quality.
- Greater known and unknown project opposition.
- Project management is shattered.
- Reduced team motivation.
- Low cohesiveness within the project community.
- Personal and corporate reputational damage, as well as recrimination.
The benefits of applying this concept include the following:
Benefits Of Building Stakeholder Relationship
- Mutual trust and confidence have grown.
- Stress reduction and a more pleasant working atmosphere.
- Improved problem-solving and decision-making.
- Increased bid value and increased possibilities of keeping clients and employees.
- Opportunities for personal development, maturity, and career progress.
- Sufficiently prepared to deal with challenging circumstances.
- Legacy to carry on with future endeavors.
Ways to build good relationships with Project Stakeholders
Stakeholders must be effectively taken care of for any firm to succeed. These include the customers, suppliers, partners, investors, workers, and the general public interested in your company. When a stakeholder is neglected, the organization can feel the consequences. Building great connections with stakeholders requires work, time, and a well-thought-out action plan.
Building trusted relationships with key stakeholders and maintaining communication throughout your project is essential. Through active engagement and speedy resolution, engaged stakeholders motivate individuals and keep the project on track.
Project managers establish trust and interact with important stakeholders at the outset. However, as the project progresses and the team size rises, we need to catch up on the importance of maintaining those connections. If unengaged, it usually results in communication failures, a mismatch of expectations, delayed decision-making, and, in extreme cases, misaligned project goals with company strategic objectives.
Here are six suggestions for developing and maintaining effective stakeholder relationships.
Ways To Build Good Relationships With Project Stakeholders
- Identify the key stakeholders.
In every project or program, the project manager oversees the initiative and identifies all stakeholders involved in planning, status reporting, or managing the dependencies. However, the focus here is on how you engage your important stakeholders. Who are the most important stakeholders? It is determined by project type, organizational structure, industry, and internal and external relationships.
Key stakeholders in project engagement are:
- Persons who have decision-making authority.
- Influence.
- A vested interest in the project’s result.
They might be part of your project’s organizational structure (such as a project sponsor or business sponsor) or an extended stakeholder (like external customers or funding partners).
Identifying these important stakeholders early in the project allows the PM and team to build trusted relationships and understand their expectations of project deliverables, their role, and their level of engagement on an ongoing basis.
- Analyze the individual stakeholders
Analyze the individual stakeholders identified at the previous stage to determine the amount of involvement and time required to create the connection. Historical data, team brainstorming sessions, focus groups, and interviews might provide the necessary knowledge for analysis. Next, each important stakeholder is examined to determine their attitude toward the initiative, level of support, influence, and acceptance of the change.
The project manager would decide on the amount of engagement based on their interest in the project and their ability to affect change. When there is more ambiguity about the program’s scope, objectives, and expected outcome, the PM’s role in managing expectations and relationships is more significant.
- Plan on how to keep your stakeholders engaged in your project
Consider organizational culture and attitudes toward the project while developing an engagement plan. For example, understand the stakeholder’s level of support or resistance to team talks.
Define how you will assess when a stakeholder becomes disengaged as part of your strategy; the metric may be anything like the number of mandatory meetings missed by the stakeholder in a month. When a significant stakeholder consistently skips a needed meeting or fails to make timely decisions, it is a source of contention. If not handled, this disengagement will begin to undermine the project.
- Keep all key stakeholders informed and updated
The project manager is responsible for keeping all key stakeholders informed and updated as frequently and as early as feasible during the project. Therefore, maintain a proactive approach in your discussions with them.
To build a standardized onboarding process, new stakeholders should become acquainted with a collection of standard artifacts (like the charter, communication plan, business case, and risk register). Also, take the chance to hear from current stakeholders. Feedback from stakeholders who no longer have a vested interest in your endeavor may help you adjust your path.
- Maintain involvement
It is critical to maintain your involvement, especially in long-term initiatives. At the end of a project, we’ve seen project teams wear out, with stakeholders eager to move on to the next big thing. The project manager must keep the engagement going. The connections and reputation you build via this involvement can help you succeed in future efforts in large businesses. Maintain contact with your key stakeholders long after the project has been completed and delivered.
Project Management Trends That Will Shape the Future
Project management is crucial in deciding how businesses and organizations will fare in the marketplace. Projects might include implementing a corporate plan, running marketing efforts, or organizing business events. Teams work to interact, manage, and communicate as effectively as possible to complete tasks and meet deadlines.
Organizations flexibly responded to the pandemic’s disruption by developing new methods of operation. However, they were thrust into the era of digitization and had to reconsider their methods of operation. These top 6 project management trends in the future demonstrate the ongoing need for technical innovation and digital transformation regarding the function of project management software in the future by building great stakeholder relationships.

Future Project Management Trends
- AI Automation and Implementation
The use and usage of artificial intelligence are the most obvious of the new current trends in project management. Knowing which initiatives are more successful enables teams to precisely determine which aspects are vital if the firm is to reduce costs and risks. As a result, organizations may increase transparency and productivity. The main factor driving the current increase in the adoption of such software is this characteristic of project management systems.
Let’s look at a few instances:
- A few businesses currently use automated and machine learning technologies to get alerts about potential issues the company could run into. For instance, suppliers might now get notifications about possible obstacles like bad weather and traffic.
- Building machine learning algorithms to support a project manager’s decision-making capabilities by evaluating data from several projects in the project portfolio is a promising study area.
- Globalized Project Management
As working circumstances got more flexible due to the forced work from home caused by the worldwide pandemic, businesses and teams became even more globalized. It has long since established roots. Mercer estimates that 70% of businesses want to use the hybrid work model.
Although the remote work and hybrid model trend allows for the employment of creative and inventive individuals worldwide, project management has to keep up with it. Collaboration, for example, is challenging when team members are unavailable due to competing schedules created by different time zones.
Software for project management provides a tool that could address this issue. The platform enables all brainstorming sessions and discussions to take place in a single setting, allowing businesses to access talent worldwide.
- Hybrid Project Management
The third new development in project management is the rising use of the hybrid approach, which refers to how project teams combine the Waterfall methodology, the systematic approach, with the Agile methodology, which is the quick-moving methodology. A hybrid approach aims to elevate teams to become aware of the specific project lifecycle while providing the ability to support them in changing the plan as necessary.
How do you know what will work for you, and how can you prepare for this trend?
PMs must learn about the most recent techniques, examine some of the fundamentals, and analyze how to use them correctly to obtain a greater understanding of the project situation and its aspects, such as the clients, the corporate objectives, and the purpose of the project, and the team’s attitude.
There is an increasing requirement to adapt your strategy and develop a project plan that enables you to lead projects unconventionally and comprehend different components of multiple techniques that cater to the demands of your team, perceived timeline, environment, end goals, etc.
- Stakeholder-Centered design
The fourth most recent trend in project management is an emphasis on delivering transparency for the benefit of the company’s stakeholders and developing products centered on the human perspective. Project managers may communicate with, collaborate with, and inform stakeholders. This design makes it easy for investors and customers to support any project launched as part of a company’s business plan.
- Soft Skills
Soft skills have become an essential component of project management. Project managers must interact with stakeholders, clients, and project teams. They will mitigate risks, resolve internal disagreements, and keep the project team engaged. Having a high level of emotional intelligence will also be useful in project management. Therefore, organizations should begin investing in tools and programs that assist employees in acquiring soft skills.
- Predictive Data and Simulation-Based Analyses
The most difficult and demotivating aspect of managing several projects is when unanticipated repercussions jeopardize their success. Project managers seek a solution to give them the knowledge to account for the unexpected. Project teams with predictive and data analytics skills may fully use KPIs and benchmarks and execute them proactively by developing data-backed best practices.
Companies cannot afford to bear the repercussions of project failure, given the competitive environments of most markets. Therefore, projects must be started successfully to stand out from the competition. The most recent advancements in project management software demonstrate that technology will play a role in this element of corporate operations in the future. Suppose you want projects to succeed and businesses to thrive. In that case, you should consider introducing project management solutions to simplify your, your teams, and your stakeholders’ lives.
Final Thoughts
Stakeholder involvement will become essential to optimize success as knowing stakeholders becomes increasingly critical for firms. For example, stakeholder engagement may assess reactions, track public impressions of a company’s operations, and assure collaboration and partnership with all stakeholders. In addition, an organization’s long-term performance may be determined by its connections with stakeholders, which provide commitment and buy-in to future initiatives and difficulties. As a result, the company becomes more aware and responsive to the demands of all its users and stakeholders.
Stakeholder management must place a greater emphasis on involvement to move projects from installation to execution. Stakeholder management must be less hierarchically centered while considering companies’ changing political nature. Projects should begin by identifying diverse stakeholders, engaging with them consistently, and coordinating continuously to increase project success.
As a project proceeds, Stakeholder management processes need to account for the dynamic nature of stakeholders’ commitment to a project and the interactions between various stakeholders. As a result, project teams will get the competitive advantage they want by focusing not just on their stakeholder position but also on the other major stakeholders in a project and how they interact. To achieve more effective stakeholder involvement, follow these three steps:
- Create a stakeholder map and keep it updated as the project progresses.
- Prioritize essential stakeholders and regularly evaluate assumptions about commitment levels and impact.
- Create essential stakeholders and increase their commitment to the change.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Jul 24, 2023 | General
Delivering a successful project is challenging, especially when there are multiple stakeholders. However, even if a project is performed on time, on budget, and to the expected scope, it can still be regarded as a success only if the stakeholder expectations are managed appropriately.
Each project stakeholder has certain expectations. Project managers are at the forefront of potentially disastrous situations when such expectations conflict. They must address and resolve the issue or risk jeopardizing the project and their position. Because the fundamental cause of problems is only sometimes apparent, project leaders and teams must analyze links between issues and stakeholder motives using interpersonal skills such as resolving conflict, resistance to change, and trust building.

Project Stakeholders
Project Stakeholders
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization that is affected by the result of a business venture or project.
Stakeholder interactions may positively or negatively impact the project’s life cycle. Thus, a project leader must identify important stakeholders and develop a stakeholder management plan to satisfy their demands. Using project management tools and strategies to keep track of the key stakeholders is an excellent method to remain on top of things and ensure that project stakeholders remain satisfied and productive.

Types of Stakeholders
Internal Stakeholders
An internal stakeholder is somebody whose interest in the project is directly linked to their affiliation with the entity in charge. Internal stakeholders want the strategic and commercial goals of the project to be realized. They might be project managers, team members, sponsors, owners, or investors.
External Stakeholders
External stakeholders are not directly linked with the company but are important to the business or are influenced by the project in some way. Those are frequently supply chain participants, creditors, or public groups.
Stakeholder Management
The stakeholder management process includes communicating project status, expenses, and barriers to stakeholders to increase visibility, navigate changes in project direction, and manage expectations. Project stakeholders are those involved in the project or whose interests may be influenced by the project’s execution or completion.
Stakeholder management helps project managers keep change at the forefront of their thoughts while making it less intimidating. Furthermore, the stakeholder management plan is a reminder for every interaction the project managers have with direct or indirect stakeholders, helping them maintain a genuine link between the project and day-to-day operations.
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Means
An effective stakeholder management process ensures that timely and relevant feedback is provided, and that the stakeholder management strategy directs the change effort. The project manager maintains stakeholder expectations, resolves conflicts, and identifies and fixes any problems that develop throughout the project. In general, the following are the fundamental parts form the stakeholder management process:

The Necessary Elements For Successful Stakeholder Management
- Managing stakeholder expectations: The project is more likely to succeed when stakeholders’ expectations are actively managed. As a result, to ensure perfect conformance with project goals and expectations and to continue the project management effort, the project manager must continually negotiate and influence the demands of stakeholders.
- Managing stakeholder perception: It is critical for project success to ensure that stakeholders are involved in the project regularly and are kept up to date on the project’s progress. High-level stakeholder perception increases the likelihood that stakeholders will provide the necessary support and the project will be completed as intended.
- Keeping track of stakeholder activity: The project manager is primarily responsible for recording and tracking all stakeholders’ activity. As a result, to secure stakeholder acceptance and project communications plan adherence, the project manager should formally document all contacts with stakeholders and keep records of the project’s outcomes.
- Solving problems and resolving conflicts: To avoid challenges and conflicts, the project manager should address stakeholders’ concerns and identify risks and threats in collaboration with conflict management. By referring to change requests, the project manager can generate solutions.
Understanding the components of the managing stakeholder’s process enables the project manager to engage with stakeholder expectations and demands and build action plans to be used when disputes and challenges emerge. The project manager can utilize the following tools to assess conflicts and challenges, as well as manage stakeholders on an individual and group level:

Tools To Assess Conflicts And Challenges In Managing Stakeholder’s Process
- Issue logs: An issue log is a tool for assessing issues and documenting resolutions. It is a document with a rigid categories structure that allows each issue to be placed in the appropriate category (issue group). The project manager uses problem logs to ensure that each stakeholder understands the project and maintains positive working interactions among all stakeholders, including project team members.
- Change Logs: It is a tool for documenting any changes that occur throughout a project. The project manager uses change logs to track changes and their impact on project goals and deliverables. A change log should be provided to project stakeholders and should include data on changes to risks, uncertainties, costs, and budgets.
A change request for project deliverables may result from the technique for managing and engaging stakeholders. Changes to the stakeholder management approach and registry are also feasible. The method of managing stakeholders allows for evaluating and modifying stakeholder benefits created earlier in the project’s life cycle.
Five pitfalls to address while dealing with the expectations of stakeholders
5 Pitfalls To Address While Dealing With The Expectations Of Stakeholders
- Identify the stakeholders
A project often involves many stakeholders, and it can take time to identify all of them. A stakeholder is a person, a group, an organization, or a set of organizations that are actively involved in or may be affected by the project. Stakeholders can have an impact on a project in a variety of ways.
For example, if a stakeholder is top management in an organization and is not completely committed to a project, it may drastically limit buy-in throughout the business. Founders and C-suites are also stakeholders who can positively or negatively impact a project. Therefore, the identification of stakeholders is a critical step in managing expectations.
- Classifying stakeholders
Effective stakeholder management necessitates a project manager categorizing stakeholders based on their role in project completion. A project manager must determine which stakeholders are supporters and which may be obstacles to the project. It might be challenging to define the types of risks, where and when each risk exists, the impact on the project, or how to build strategies to handle possible risks if stakeholders cannot be classified.
- Mapping expectations
Project managers must resolve possible concerns, keep stakeholders involved and motivated, and finish the project on time. A project manager must have a good understanding of all stakeholders’ expectations. Stakeholder analysis and adequate documentation can be useful in mapping expectations. Stakeholders may have different priorities when completing tasks, milestones, or the full project. Their interests may be interpreted differently and have different definitions of success.
For example, one stakeholder may prioritize project completion on time, while another defines success as keeping it under budget. Mapping expectations and obtaining clarity among all stakeholders enhances the possibility that a project manager and their team can effectively complete a project.
- Using appropriate communication methods
Stakeholder management requires determining and implementing appropriate communication methods. To successfully manage stakeholder expectations, a project manager must establish the available and preferred communication mechanisms for stakeholders. A poor or incorrect communication approach can lead to distrust and dissatisfaction between stakeholders and a project manager. It is also essential to adjust communication tactics and frequency based on elements such as time, message, purpose, secrecy, or changes based on stakeholder contexts.
- Engaging stakeholders
Stakeholder engagement during the project with frequent updates boosts stakeholder confidence, which is essential for project success. In addition, efficient stakeholder management necessitates the involvement of stakeholders in decision-making by the project manager.
Although a project manager may believe they have already determined the optimal course of action, they should incorporate stakeholders in procedures and pertinent talks to ensure all options have been examined; otherwise, key possibilities and expectations may be missed.
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Methods
Before beginning a new project, start by identifying all stakeholders. First, identify those impacted by the project and the organizations that will influence the project. Then, using the strategy outlined below, begin developing strong relationships with each stakeholder.
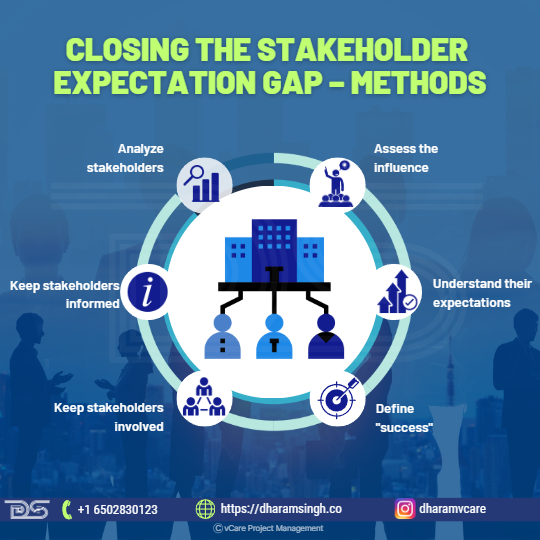
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Methods
- Analyze stakeholders
Conduct a stakeholder analysis or an evaluation of the key participants in a project and how the initiative will affect their issues and requirements. Determine their unique qualities and interests. Find out what motivates them and what frustrates them. Define responsibilities and levels of engagement, and assess whether there are any disputes among stakeholders.
- Assess the influence
Determine the extent to which stakeholders can have an impact on the project. The more powerful a stakeholder is, the more a project manager will require assistance. When evaluating stakeholders, consider the question, “What’s in it for them?” Knowing what each stakeholder needs or desires from the project allows the project manager to measure their degree of support. Remember to weigh support against influence, like Is it more necessary to have strong support from a low-level stakeholder or moderate support from a high-level stakeholder?
- Understand their expectations
Determine the exact expectations of stakeholders. Then, when necessary, seek clarification to ensure they are thoroughly understood.
- Define “success”
Every stakeholder may have a distinct definition of project success. Discovering this towards the end of the project is a potential disaster. Instead, gather definitions and integrate them into the objectives to guarantee that all stakeholders support the final results.
- Keep stakeholders involved
- Don’t just provide updates to stakeholders.
- Solicit their opinions.
- Schedule time for brief meetings to get to know them better.
- Determine each stakeholder’s ability to engage while keeping time restrictions in mind.
- Keep stakeholders informed
- Send regular status updates.
- One update each week is generally adequate.
- Hold project meetings as appropriate, but allow enough time between them.
- Respond to stakeholders’ inquiries and emails as soon as possible.
- Regular contact is usually valued – and may help ease the impact when you have unpleasant news to deliver.
These are some of the fundamentals of developing effective stakeholder connections. However, like with any relationship, there are subtleties that every effective project manager knows, such as understanding the distinctions and responding successfully to various types of stakeholders.
Final Thoughts
There is a link between resolving conflicts in stakeholder expectations and project success. Similarly, the faster project teams defuse a potentially dangerous situation by recognizing the source of conflicts, the link between issues, and the motivations of stakeholders, the simpler it is to develop trust, settle conflicts, and overcome resistance to change.
Using diverse modes of communication between the project team, senior management, and stakeholders improves prospects for mutual understanding. These methods may help the project managers to meet the stakeholder expectations and reduce the risk of project disaster.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd




























































































Recent Comments