In the current fast-paced corporate world, high-stakes projects create difficulties that can significantly affect an organization’s performance. The stakes frequently remain quite high, regardless of the endeavor – a multi-million-dollar software launch, a building project, or an event organizing campaign. Effective risk management becomes essential to recognize the potential risks and develop mitigation plans. This article explores risk management theory and presents practical solutions to ensure project success despite uncertainty.
The World Economic Forum’s 2024 Global Risks Report highlights the necessity for strong risk management frameworks in high-stakes projects and the growing complexity of global threats. Knowing how to manage risks entails more than simply avoiding problems; it also entails taking advantage of the possibilities that present themselves. Effective management enables teams to push limits and generate outstanding results while navigating through uncertainty. When the proper frameworks and methods are in place, high-stakes projects can achieve more success and innovation in addition to meeting their project goals.
Defining High-Stakes Projects
Project risk management refers to the systematic process that project managers use to detect, evaluate, and mitigate risks that might impede a project’s goals. By anticipating and mitigating these risks, project managers can prevent such setbacks from halting development. Project risk management helps teams to foresee possible problems and formulate tactical solutions that promote the project’s successful conclusion.
McKinsey’s analysis large-scale infrastructure projects and underscores the critical factors that categorize them as high-stakes, including significant capital investment and potential societal impact. Among the giants of the corporate world, big projects exhibit significant complexity and high risks.
Large-scale projects are fundamentally characterized by their complexity, magnitude, and the sometimes revolutionary change they bring about, in addition to their significant financial commitment and lengthy deadlines. These projects are distinguished by their scope and ambition, whether they include building a cross-country pipeline, implementing an across-the-nation IT system, or planning an international marketing campaign.
Why Risk Management is Essential in High-Stakes Projects
Deloitte’s Global Risk Management Survey indicates that 84% of organizations consider risk management is crucial for achieving strategic objectives in high-stakes environments. In order to foresee and control possible issues that can have a negative impact on project budgets, schedules, and results, project risk management is essential. Teams may identify project risks early and make sure they have backup plans in place by implementing a risk management approach. By being a project leader, keeping team members aware and ready for any risks, this not only protects project goals but also fosters teamwork.
Key reasons why risk management is critical in high-stakes projects:

Proactive risk management ensures success in complex, high-value projects by preventing disruptions and improving decision-making.
Reducing adverse impact
Potential risks are detected early, which enables project teams to develop proactive measures to prevent or mitigate them, this method aids in avoiding major disruptions and costly delays.
Informed decision-making
Risk analysis provides a good insight into the potential implications of different scenarios, thus better decision-making is ensured throughout the project lifecycle.
Strategic planning
The clear understanding of risks helps in preparing contingency plans and allocating appropriate resources to take care of vital issues.
Building stakeholder’s confidence
Developing a comprehensive risk management process provides stakeholders with confidence that a project is properly equipped to take on the adversities.
Safeguard reputation
Organizations can protect their reputations from drastic damage due to unanticipated incidents when they can manage risks actively.
Types of Risks in High-Stakes Projects
In order to prevent or reduce loss or company failure, a project risk analysis tracks a project’s performance from inception to conclusion. Depending on the project’s nature, level of complexity, and length, different risks have different origins. Understanding the typical project management risk types may aid in spotting potential risks, assessing their effects, and organizing the countermeasures.
Why is project risk analysis important?
Because it assists project managers in determining a project’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential opportunities during or after completion, so project risk analysis is crucial. It might be crucial to get knowledgeable about the possible issues or “high-risk” dangers that could jeopardize the successful completion of a planned project in order to conduct an effective risk analysis.
To prevent or reduce losses in an ongoing project, it is crucial to make a list of all the unforeseen circumstances that might interfere with the technology, resources, and procedures. A complete mitigation strategy requires a detailed readiness plan in order to handle losses efficiently.
Reducing the size of both internal and external risks is the goal of project risk analysis. The goal is to use a proactive approach to project management instead of a reactive one. It seeks to reassure the stakeholders that, in spite of the difficulties, the project’s goals will be achieved. Through risk analysis, a competent project manager and knowledgeable technical staff form a powerful team that management leads to close gaps and take advantage of opportunities within their respective areas of competence.
Common types of project risks

Understanding the types of project risks helps leaders build targeted mitigation strategies to improve project outcomes.
1. Risk associated with technology
The frequent turnover of new and sophisticated technologies makes project managers find the technology side of project management a challenging deliverable. A project’s technological component puts data security, organization services, compliance, and information security at risk. Managers find technology-related risks more difficult to manage since they often need to hire new staff and purchase software when introducing new IT systems. Other risks associated with technology include service outages, which might cause delays and project failure.
2. Risk of communication
When you control a project, closely adhering to the important work ethic of effective and timely communication might be helpful. You can monitor any changes, distribute work, and promote a cohesive team atmosphere by scheduling meetings with stakeholders, including project sponsors. With so many devices and communication channels at our disposal, team members occasionally overlook the essential elements of good communication, which can lead to data loss or disinformation and ultimately disrupt the project.
3. The possibility of scope creep
Unauthorized and uncontrolled changes to the project’s original scope might lead to additional expenses for features, goods, or services. Almost all projects face this risk, and while some stakeholders find the additional features important for the project’s success, that can occasionally create a permanent challenge.
4. Risk of cost
The project’s completion might be threatened by a lack of cash or poor financial management brought on by an overly ambitious budget or other limitations. The risk may move to other operations and labor segments if the project cost exceeds the allocated budget. A scope risk might also arise as a result of the funds being reduced.
5. The risk of operations
Inadequate execution of critical operations and fundamental processes, including manufacturing or procurement, can stagnate or end a project. Inadequate or unsuccessful qualitative and quantitative techniques might lead to a loss, either direct or indirect, due to these risks.
6. Risk to health and safety
One kind of risk that may undermine a business’s compliance policies is health and safety. Organizations must routinely review and monitor their health and safety policies to spot the risks that can cause losses or penalties. Management is responsible for establishing ongoing health and safety risk monitoring for the company’s facilities, goods, and services.
7. Risk to skills and resources
Because project operations might occasionally stagger in distinct waves at multiple sites, requiring in-house personnel attendance, using internal workers carries a potentially significant project risk. The overlap of the waves creates a possible cause of discomfort. Another risk that might increase the costs of staff transfers or retraining is staff ineptitude across different project divisions.
8. Risk to performance
There is a perceived performance risk when a project is unlikely to produce the desired outcomes. The risk inevitably affects the business’s overall performance. The performance of the competitors may be impacted, more funding may be needed, and nonperformance may result in a penalty.
9. Market Risk
Market risk is likely to arise when a project does not achieve the desired outcomes. The advantage might be used by rivals to hinder the company and drive it off the market. Commodity and international market patterns pose an additional market risk that might undermine the project’s early projections. Another possible market distraction to the project’s product sales is liquidity, credit, and interest rate fluctuations.
10. Risk of external hazards
A possible risk is a likely unfavorable event that is out of the project manager’s control. These risks can take many different forms, such as civil unrest, earthquakes, floods, vandalism, terrorism, and storms. In such cases, a project may stagnate or end. Organizations can avoid significant losses or damage brought on by unanticipated external hazards by using the proper monitoring plans.
Understanding Risk Management Framework (RMF)
Effective risk management is essential to any well-managed business’s drive for stability and expansion. Incorporating best practices into the company’s risk culture through the implementation of a risk management framework helps guarantee that it can endure future threats that are both predicted and unanticipated.
For instance, risk management is a key component of investment industry businesses, which enables them to weather significant market downturns.
Is Risk Mitigation is important in project management?
The process of reducing, managing, or eliminating risks or threats to a project’s goals is known as risk mitigation, and it is a crucial part of project planning. Risks that a project may encounter include scope creep, missing deadlines, higher than expected expenses, and project team turnover.
The project team evaluates the possible risks’ relevance by conducting a risk assessment after they have been discovered. The sorts of risks, their possible effects on the project, and their likelihood of occurring are all made clear by this evaluation. The choice of suitable risk reduction techniques is influenced by these elements as well as the cost of mitigation.
According to McKinsey’s research, companies with proactive risk mitigation strategies are 43% more likely to achieve project success in volatile markets.
Risk mitigation strategies
Project teams might pick from a variety of risk reduction techniques. Five of the most popular risk mitigation techniques that may be applied to address, control, or eradicate hazards are as follows:

Discover the five most effective risk mitigation strategies to address and manage project uncertainties for enhanced success and stability across all phases.
1. Risk acceptance
Determining if a project’s risks are acceptable is part of the acceptance risk mitigation method. This usually happens in situations where the risk’s effect or likelihood of happening are deemed minimal. When the cost of risk mitigation exceeds the cost of the risk happening, risk acceptance can also be put into practice.
When a risk is considered acceptable, no steps are made to reduce it, however there could be a strategy in place to deal with it should it materialize. This strategy entails accepting the risk’s potentiality and becoming ready to handle it if needed.
2. Risk avoidance
Any action will typically be performed to prevent a danger from happening when employing the risk avoidance technique. Since these steps can occasionally be expensive, this risk mitigation technique is frequently selected when a danger is thought to constitute a significant risk.
3. Risk control
A control plan can also be used by team members to reduce project risks. By addressing the risk through actions or regulations, this risk reduction technique works.
4. Risk transfer
Another effective risk reduction tactic is to shift the recognized risks to another party in order to lessen their effects. This tactic should be applied in a manner that all parties can agree with, however it may have disadvantages and extra expenses.
5. Watch and monitor risk
Employing this risk mitigation technique entails keeping an eye out for and recognizing any changes that could have an influence on a risk’s impact. Production teams may incorporate this tactic into their plan for project reviews. A project’s budget, timeline, and performance may all be tracked for emerging or shifting risks.
How do you pick the best mitigation plan?
Knowing which risks are most important to the company will help you select the best mitigation plan because different risk categories require different approaches. In order to guarantee the effective execution of a risk mitigation plan, you may also take into account the organization’s current resources. Additionally, you might examine past tactics employed by the business or its rivals in order to duplicate effective methods.
The Importance of Managing and Controlling Risks
Risk management is a crucial activity because it equips a company with the resources it needs to recognize and address any threats. Risk mitigation is simple once it has been identified. Furthermore, a firm may make wise decisions by using the foundation that risk management offers.
Assessing and managing risks is the greatest approach for a firm to be ready for any scenario that might impede its development and expansion. Businesses have a better chance of succeeding when they assess how they intend to handle possible challenges and then create mechanisms to deal with them.
Furthermore, progressive risk management guarantees that high-priority risks are addressed as forcefully as feasible. Additionally, the management will have access to the data they need to make wise choices and maintain the company’s profitability.
Risk Analysis Process
Risk analysis is a qualitative method to problem-solving that analyzes and determines risks in order to evaluate and address them using a variety of evaluation techniques. The risk analysis procedure is as follows:
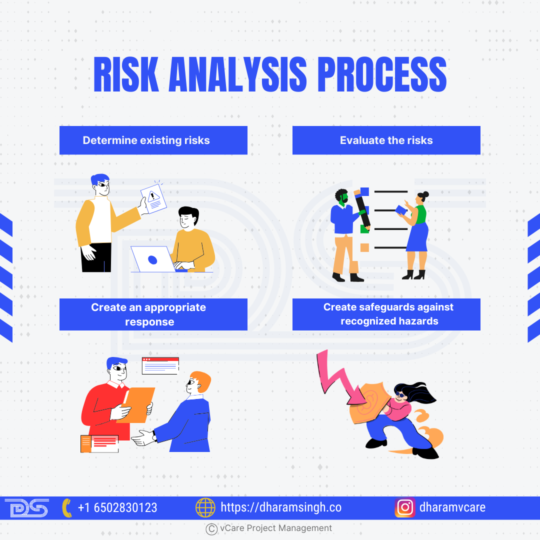
A well-structured risk analysis process empowers teams to detect, evaluate, and respond to risks with precision and foresight.
1. Determine existing risks
The primary method for identifying risks is brainstorming. To assess all the many sources of risk, a company brings its employees together. Sorting all of the risks that have been discovered according to priority is the next stage. Prioritization makes ensuring that risks that have the potential to have a major impact on an organization are addressed more quickly since it is impossible to minimize every risk that currently exists.
2. Evaluate the risks
Problem solving frequently entails first recognizing the issue and then coming up with a suitable fix. However, a company should identify the source of the risks by asking, “What caused such a risk and how could it influence the business?” before determining how to manage them.
3. Create an appropriate response
The following questions must be asked by a corporate entity after it has decided to evaluate potential solutions to reduce recognized risks and stop them from happening again:
· What steps can be made to stop the danger from happening again?
· What should be done in the event that it recurs?
4. Create safeguards against recognized hazards
In this case, the concepts that were determined to be helpful in risk mitigation are expanded into a variety of activities and subsequently into future-deployable strategies. Plans can be implemented in the event that risks materialize.
Risk Management Tools and Techniques
Tools for risk management are procedures, software programs, and methods created to recognize, assess, and rank risks. In order to reduce the potential consequences of any risk, they are executed through resource coordination. These risk management tools cover a range of features that assist firms in anticipating potential risks and putting effective mitigation plans into place, from risk assessment frameworks to financial and analytical tools. Maintaining the general health of the company, securing the organization’s assets, and guaranteeing project success are the ultimate objectives.
The Value of Risk Management Tools and Techniques in Risk Mitigation
It is necessary to discuss the importance of techniques for risk management and tools. Effective risk management has become crucial as a result of the world’s uncertainties and the speed at which technology is developing. These tools offer a number of significant advantages:
· Proactive Risk Identification: Rather than focusing on reactive solutions, risk management technologies assist firms in identifying potential risks and developing proactive solutions.
· Making Informed Decisions: By evaluating possible effects and weighing risks against benefits, risk management tools assist in making well-informed decisions.
· Resource Optimization: By giving priority to risks that pose a greater danger, risk management solutions help allocate resources more efficiently.
· Governance and Compliance: By ensuring that firms adhere to governance norms and legal laws, many risk management techniques help to lower legal liability.
· Improved Communication: By providing a consistent framework for talking about risks, risk management technologies help teams and stakeholders communicate more effectively.
Tools and Techniques
Here is an overview of the best risk management tools and techniques:

From qualitative tools like SWOT to advanced platforms like Riskonnect, the right mix of techniques strengthens your risk management strategy.
1. Probability and Impact Matrix
One essential tool for risk management is the Probability and Impact Matrix. It assesses and ranks risks according to their probability of happening and possible influence on project goals.
2. Evaluation of Risk Data Quality
In order to guarantee that risk management choices are founded on correct and superior information, risk data quality evaluation assesses the dependability and credibility of risk data.
3. Identification of Risks
An essential first step in the risk management process is risk identification. It accurately recognizes and records any risks to a project or company. To find possible risks and hazards, the business takes into account both internal and external elements. This makes it possible for enterprises to manage difficulties more effectively and lessen their effects.
4. A SWOT analysis
When it comes to project planning or company competitiveness, SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique that helps identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
5. Risk Register
Typically, a risk register is a document that includes all of the details concerning hazards that have been discovered, such as their status and strategies for mitigation.
6. Root Cause Analysis
A problem-solving technique called “root cause analysis” seeks to determine the primary source of danger or problems rather than just treating their symptoms.
7.Decision-making
Making decisions entails assessing possible risks and selecting the course of action that will have the least negative impact. Organizations may successfully reduce risks and handle uncertainties by including decision-making into risk management.
8. Risk Acceptance
A risk management technique known as “risk acceptance” involves choosing to accept the consequences of a risk without actively working to reduce it.
9. Risk Reassessment
By regularly reviewing the risk environment to find new risks and reassess old ones, risk reassessment makes ensuring that risk management plans are applicable and realistic.
10. Brainstorming
The innovative group problem-solving method known as brainstorming produces a large number of concepts for risk detection and mitigation plans.
11. Risk Monitoring
In order to identify risks, track lingering threats, and spot new ones, risk monitoring is a crucial step in risk management.
12. The Delphi Method
Developed as an interactive, methodical forecasting process with a panel of experts, the Delphi Technique is a structured communication strategy.
13. Checklists
To make sure the company takes into account all possible project risks and the required risk management procedures, checklists are straightforward yet powerful tools.
14. Reserve Analysis
Reserve analysis is the process of allocating contingency reserves (money, time, or resources) to deal with risks that could be more likely to materialize and have a greater impact.
15. The Riskonnect
Leading integrated risk management software provider Riskonnect provides a full range of tools to assist businesses in recognizing, controlling, and reducing risks throughout their operations.
Are Future Risks Predictable by Risk Management Tools?
Tools for risk management assist businesses in recognizing, evaluating, and reducing risks. Although they are essential for identifying possible risks based on data that is now available and past patterns, it is vital to understand their potential for risk prediction in the future.
Some of the Capabilities involved are:

Risk management tools can’t predict the future perfectly—but with AI, simulations, and predictive models, they help teams prepare for what might come.
1. Analyzing Data and Forecasting Trends
Data analytics is used by many risk management technologies to find trends and patterns in historical data. This might include external market dynamics, operational mishaps, and financial performance. The technologies can predict possible future threats by examining these tendencies. For this, predictive analysis may be useful.
2. Simulation Models
Numerous possibilities based on various assumptions and inputs may be explored with the use of tools such as Monte Carlo simulations. By offering a variety of possibilities together with probabilities, these simulations can assist firms in comprehending possible future risks under various circumstances.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
By examining enormous volumes of data, including unstructured data from news stories, social media, and other digital platforms, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are able to forecast possible future risks. These tools are able to identify new patterns and possible danger signs that conventional research can miss.
4. Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis-facilitating risk management tools allow firms to investigate the effects of different fictitious future scenarios. Even if it is impossible to forecast the precise kind or timing of a risk, this can assist prepare for potential outcomes.
Some of the Restrictions involved are:
1. Reliance on Past Information
Assuming that future occurrences would follow similar patterns, predictions are frequently based on previous data. This method might not be able to anticipate black swan occurrences or unusual risks with enough accuracy.
2. Changing Variables
Rapid changes in factors, such as advancements in technology, changes in geopolitics, and unforeseen worldwide occurrences like pandemics, can make prediction models less accurate.
3. Risks’ Complexity and Interconnectedness
Risks in the modern world are becoming more intricate and linked. The cascading impacts of a single risk on other facets of a company or the global economy may not be fully captured by traditional techniques.
4. Subjectivity and Prejudice
The results of risk assessments may be skewed by subjectivity and bias introduced by the input parameters and underlying assumptions of risk projections.
What Impacts Do Regulatory Changes Have on Risk Management Strategies?
Regulatory changes have a significant impact on risk management methods because they may provide new compliance requirements that firms must meet within tight deadlines. The operations, financial reports, and data management of a business may be impacted by such changes. In order to remain compliant, businesses must monitor and adapt their risk mitigation strategies. This lowers the risks associated with non-compliance, such as legal fines, monetary losses, or harm to the company’s reputation. Effective risk management in this context means discussing new laws and regulations, assessing their potential implications, and making the required adjustments to maintain the firm’s risk portfolio consistent with the current regulatory environment.
Direct Effects on Strategies for Risk Management

Understand how regulatory shifts impact risk management strategies directly through compliance and operations, and indirectly through technology, market dynamics, and stakeholder trust.
1. Compliance Risk Alteration: An organization’s compliance risk profile is directly impacted by new legislation or changes to current ones. To handle these developments, organizations must modify their risk management plans, making sure that any new compliance risks are recognized, evaluated, and successfully reduced.
2. Resource Allocation: Reallocating resources is frequently necessary when implementing modifications to comply with new laws. To handle compliance, this may entail making investments in new technology, educating employees, or recruiting more staff. The organization’s operational and financial risk management plans may be impacted by such modifications.
3. Process and Operational Adjustments: Organizational structures, operational procedures, and business processes may need to be altered in response to regulatory changes. In order to detect new risks brought about by these changes and minimize any possible effects on the organization’s goals, risk management systems must adjust to these operational alterations.
4. Strategic Reorientation: Regulatory changes may occasionally be so radical that a reassessment of the company’s business plan is necessary. This might entail expanding into new markets, phasing out particular products, or altering the company plan, all of which contain risks that need to be control.
Effects of Indirect Risk Management Strategies
1. The dynamics of the market: The competitive landscape can be changed by regulatory changes, which can impact market dynamics and, in turn, the market risk of a business.
2. Technological Innovation: In order to comply with new rules, organizations may need to embrace new technology more quickly than they had previously thought. As the company works to adopt and integrate new technologies, this creates technical risks including cybersecurity threats and strategic hazards. It could be useful to keep an eye on technical developments.
3. Reputation and Stakeholder Relations: An organization’s reputation and relationships with stakeholders, such as investors, consumers, and regulatory agencies, can be impacted by how it handles regulatory changes. Managing these connections and perceptions must be a part of any effective risk management strategy.
The Best Methods for Handling the Risks of Regulatory Change
1. Proactive Analysis and Monitoring: Organizations may anticipate changes and modify their risk management plans appropriately by conducting proactive analysis of potential effects and ongoing monitoring of the regulatory environment.
2. Frameworks for Adaptive and Flexible Risk Management: Organizations can react quickly and efficiently by creating adaptable risk management frameworks that can quickly adjust to changes in the regulatory environment.
3. Stakeholder Engagement: Talking with industry associations, regulators, and other stakeholders can help you understand possible changes to the law and provide you ways to influence its creation.
4. Integrated Compliance and Risk Management: A comprehensive strategy for handling the effects of regulatory changes is ensured by combining compliance management with more general risk management procedures.
Conclusion
Inherently, high-stakes projects include significant financial outlays, complex stakeholder relationships, and significant strategic implications. These programs cover critical industries including technology, healthcare, infrastructure, and aircraft; failures might lead to serious financial losses, harm to one’s reputation, and even fatalities. Because of these risks, the firm needs to create a strong and thorough risk management system to ensure success.
Stakeholders must recognize, evaluate, and mitigate the vast range of risks connected to high-stakes projects using a systematic approach to risk management. Some of these risks include regulatory non-compliance, technical disruptions, financial instability, operational inefficiencies, and geopolitical uncertainty. When a proactive risk management plan is not in place, teams face a far greater likelihood of project failure, which can have detrimental ripple effects both inside and beyond the company.
To minimize any interruptions and guarantee that projects stay on course, organizations must implement effective risk mitigation techniques. These initiatives include dynamic stakeholder interaction, well-defined contingency planning, comprehensive risk assessment procedures, and flexible project management approaches. By skillfully combining these components, organizations can strengthen their resilience and preserve operational integrity in unstable times.
Continuously monitoring and mitigating risks throughout the course of a project is equally important. To anticipate unanticipated difficulties, teams must implement strict risk monitoring, real-time reaction systems, and iterative modifications. Cutting-edge technology solutions, such as scenario-based modeling, real-time data monitoring, and AI-driven predictive analytics, enhance an organization’s capacity to successfully manage and reduce risks.
Airbus’s creation of the A380 is a noteworthy example of a risk management strategy that works well. After initially encountering significant technical difficulties, supply chain interruptions, and cost increases, Airbus used an integrated risk management approach. The company reorganized stakeholder alignment, developed strong cross-functional cooperation, and used advanced simulation models. These actions not only made it easier to finish the project, but they also demonstrated how crucial proactive risk reduction is in high-stakes project settings.
Looking ahead, risk management in high-stakes projects will gain greater importance from digital transformation, predictive analytics, and data-centric decision-making. If businesses adopt agile risk management frameworks and leverage emerging technology, they will be in a better position to manage uncertainty, allocate resources optimally, and achieve long-term, sustainable success. By fostering a culture of proactive risk management, businesses may improve project resilience, seize opportunities, and maintain a competitive advantage in a constantly changing global environment.
#RiskManagement #ProjectLeadership #HighStakesProjects #StrategicPlanning #ProjectSuccess #DeloitteInsights #McKinseyAnalysis #GlobalRisks2025 #ProjectManagement #RiskMitigation #CorporateStrategy #InfrastructureProjects #WEF2025 #ProjectDelivery #InnovationInProjects #ComplexProjects #RiskFrameworks #PMOLeadership #MitigationPlanning #vCareProjectManagement


Recent Comments