
by DharamCW | Jan 15, 2023 | General
A project can be a complex, nonroutine, one-time effort constrained by time, budget, schedule, satisfaction, quality, and scope to meet the customer’s needs. Today, many businesses prioritize project management because it focuses on meeting project objectives and achieving them successfully. Moreover, it got significant because it employs managerial processes and tools that give managers a good chance of achieving their project’s goal.
Project Management Today
Project management has become an essential part of various industrial segments because it crosses corporate and geographic boundaries, adapting to the unique characteristics of various businesses and teams. Here are some of the project trends on the project’s success/ failures.

Key Project Management Trends
The Most Important Project Management Trends for 2022
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
- Hybrid project management approaches are getting increased.
- The significance of emotional intelligence (EQ)
- A greater emphasis on data analytics and numbers
- Tools and solutions for advanced project management
- Increased use of remote working
Key Project Management Statistics 2022 (Success and Failures)
Project Success Statistics
- Project management software is used by 77% of high-performing projects. (Hive, 2020)
- 35% of organizations are somewhat satisfied with their project management maturity level. (Wellingtone, 2020)
- 29% of projects are completed on time (Wellingtone, 2020).
- Surprisingly, 54% of organizations lack access to real-time KPIs (Wellingtone, 2020).
- Around 51% of organizations complete projects that meet the business objective or original goal. Meanwhile, 52% of organizations complete projects that meet the needs of stakeholders (KPMG, 2020).
Project Failure Statistics
- COVID-19 had a moderate or significant impact on 58% of organizations, causing project delays and cancellations (KPMG, 2020).
- Organizations with low-value delivery maturity have a project failure rate of 21%, which is significantly higher than the failure rate of organizations with high-value delivery maturity, which is 11% (PMI, 2020).
- 25% of organizations do not use technology suitable for team collaborations on informal projects, despite consuming 20% of their productive time at work (Wellingtone, 2020).
- The most challenging obstacles to implementing agile techniques in an organization are resistance to change (48%), a lack of leadership participation (46%), and inconsistent practices across teams (45%). (Digital.ai, 2020).
- 47% of agile projects are late, have budget overruns, or have dissatisfied customers (Scrum, 2021).
- Understanding these statistics allows project professionals to prepare better for what comes next and make more informed decisions.
Success and Failure of Projects
The business environment is constantly changing, and meeting the customer’s ever-changing needs has become challenging. In addition, customers’ expectations increase as competition in the global market increases. This is sometimes reflected in the pressure that Project Managers face when attempting to provide the best possible value to their customers.
While project management is constantly improving, there are some challenges for which solutions have yet to be found. Global projects are typically getting complex, and as a result, a similar project may be successful in one part of the world while failing in another. Let’s look at the factors for successes and failures on similar projects, as well as how leadership style can help to improve project performance as a contributing factor to the project’s outcome.
Causes of project failure
A project is considered a failure if it fails to deliver on time within the estimated budget. Most project managers have felt the agony of a failed project. In fact, according to a Pulse of the Profession® survey 2021, 12% of projects in an organization failed in the previous year.
When a project is considered a failure?
- First, the project did not meet the expectations.
- The client did not receive the desired deliverable.
- The work was not finished on time.

Reasons of Project Failure
So here’s to planning ahead of time and avoiding these common project pitfalls.
- Unclear Goals And Objectives
Businesses that fail to set clear employee goals and objectives waste significant time and effort. The following are the consequences of ambiguous project goals and objectives.
- Unclear objectives lead to ambiguous operational methods.
- Individually, the level of performance can be justified.
- It’s not always obvious when a project deviates from its original path.
- People involved in a project cannot work to their full potential.
- Lack Of Resource Planning
In project management, resources refer to people, money, and materials. Human resources are likely underutilized or overworked if you do not use a good task management tool.
Another critical aspect of project resource planning is financial planning. Projects with poor cost estimation and inconsistent tracking will almost certainly go over budget. In addition, project managers who do not understand how to track and manage finances are more likely to fail the project.
- Poor Communication
Poor communication in the workplace can have disastrous consequences for the project, including poor collaboration and decreased productivity, resulting in stressed employees, dissatisfied customers, and workplace mistrust.
Whether it’s delayed communication, a lack of communication, or no communication at all, the fact is that the project is likely to fall through the cracks if the project professionals don’t have an effective communication strategy in place.
- Stakeholder Management Is Inadequate
Stakeholders have an inherent interest in the project, for better or worse. Project managers are responsible for identifying and communicating with all stakeholders promptly and without delays. Unfortunately, there are numerous reasons for poor stakeholder management, some of which are listed below.
- Stakeholders are too narrowly defined.
- Failure to strike a balance between compliance and strategic opportunities
- Stakeholders are prematurely removing resources.
- Stakeholders’ disinterest
- Stakeholders are unaware of the project’s progress.
Engaged stakeholders provide support and insights to help a project succeed, whereas disengaged stakeholders can become barriers to success.
- Poorly Defined Project Scope
The project scope details everything you intend to do (and not going to do). In project management, scope creep refers to uncontrolled, continuous changes in the scope of a project. Conversely, a poorly defined project scope leads to scope creep, where the former is vaguely defined, documented, or controlled.
A project with an unclear project scope is more likely to fail and encounter a variety of issues, including:
- Failure to meet customer expectations
- Continual changes are being requested throughout the project’s life cycle.
- The budget exceeds the allocated budget.
- Failure to meet deadlines
- Inaccurate Cost And Time Estimates
Inaccurate cost and time estimate frequently result in team members making accurate predictions about the expected duration of tasks and the project’s cost based on an average duration of time and cost for previous projects.
Inaccurate estimates are frequently the result of two underlying causes:
- Upfront planning
- Poor estimation practices
- Inadequate Risk management
Risk management enables project managers to identify and analyze issues that may arise during the project and impede its progress. If risks are not effectively managed, they will likely emerge during the project’s later stages, causing significant scope creep. Conversely, poor risk management can lead to project delays, low user adoption, late assignments, overspent budgets, and project failure.
- Monitoring And Controlling
Monitoring and controlling the project is one of the lesser-known facts that project managers and their teams often overlook. However, a project manager needs to “track, review, and regulate the project’s progress; identify areas that require changes in the planning, and initiate the corresponding changes.”
Every effort should be made to keep the project on track, and if it falls behind budget or schedule, the plan should be adjusted to get the project back on track.
How to Recover a Failing Project?
Three key questions you can ask to quickly and clearly understand the project.
- Are the problems internal or external?
You can determine whether the source of the problem is internal (and thus correctable) or external (outside of your control).
Review project documents such as the charter, plan, and schedule for:
- Requirements from relevant stakeholders.
- A reasonable timetable with attainable goals.
- Allocation of resources
- A method of collecting and managing change requests.
- Unexpected expenses (internal and external).
- Success metrics.
- A procedure for upholding quality standards.
- Why are we behind schedule?
Next, determine why the project is running late.
- Were tasks properly prioritized?
- Were tasks clearly explained?
- Was the timetable overly ambitious?
- How frequently did the project manager provide status updates?
- Who made important project decisions?
- Is there a record of decisions and change requests?
- How were risks communicated and addressed?
- Was the initial budget adequate?
- Is the team working effectively?
Finally, consider how well the team worked together.
- Did the team understand the project’s goal and its roles and responsibilities?
- Was the team using the same procedures and tools?
- Did the team meet regularly to share updates and challenges?
- Was a clear communication strategy in place?
- Were the right people assigned to the project?
- Were there any issues with suppliers or vendors?

Techniques for Recovering Failing Projects
Techniques for recovering failing projects
While failures are unavoidable in project management, project professionals can always learn from the failures to succeed in the future. So, let’s look at how project managers can ensure that their next project runs smoothly and that any potential problems are identified and resolved before they become too large to cause project failure.
- Plan diligently and identify any gaps.
- Communicate effectively and frequently.
- Examine your Resources
- Set realistic goals for yourself.
- Use the Proper Methodology
- Monitor Project Development
Strategic alignment in project management
Strategic alignment in project management refers to aligning project goals with your organization’s long-term vision and mission.
Contrary to popular belief, strategic alignment in project management does not only refer to establishing and maintaining key financial metrics. Instead, it’s a broad concept that encompasses everything from key financial and quality indicators to customer satisfaction, brand recognition, and value proposition.
Every project has a goal. While some may seek to provide a service or product, others may seek intangible benefits such as positive customer relationships or company goodwill. These strategic goals guide a project professional’s day-to-day business operations and help them turn their ideas into desired results.
Importance of Strategic Alignment in Project Management
- Focus the energy in the right place
- Allow for productive team collaboration
- Describe the organization’s competitive advantages
- Manage priorities that conflict
- Avoid duplication.
- Accept market manoeuvrability
Leadership performance is significant to project success
Effective leadership in project management is the ability to persuade people of the need for change, stimulate new ways of thinking and problem solving, and encourage them to achieve project objectives. Leadership also guides team members to grow as professionals while completing their project responsibilities.
Today’s evidence-based theories of leadership can be characterized into six major classes, which include:
- Attributes
- Behavior
- Contingency
- Visionary
- Emotional intelligence
- Competency

PMI’s Talent Triangle
PMI’s Talent Triangle – How to Stand Out as a Successful Project Manager
Project managers must be more agile and resourceful than ever to keep up with and make an impact in a fast-changing world. PMI has always been dedicated to assisting project professionals in developing strong skills. Nonetheless, project managers now require a skill set that includes a variety of disciplines and practices, as well as other in-demand skills.
To assist project professionals in navigating this changing world of work and embracing smarter ways of working, project professionals need to focus on:
- Ways of Working: Formerly Technical Project Management
- Power Skills: Formerly Leadership
- Business Acumen: Formerly Strategic and Business Management
Factors of project success
Project success has been defined as a project that meets its objectives on time and within budget. A development project’s success extends beyond meeting schedule and budget objectives. It also includes meeting the expectations of beneficiaries, stakeholders, donors, and funding agencies. However, defining these dimensions of success is more complicated and can only be assessed years after the project is completed.
Measuring project success after the fact is important because it aids in determining future strategies when planning new projects. Continuous improvement based on data from past projects enables project managers to identify problems before they occur. Using past data allows new processes to be implemented with fewer errors and greater management success.

Factors of Project Success
Here are some of the factors for the project’s success:
- Goals and objectives
The project’s overall goal is specified and recognized by all stakeholders; it is not at odds with subsidiary objectives, and project leaders have a clear vision of the project’s outcomes.
- Capable sponsors
Sponsors play an active role in the project’s life cycle; they bear ultimate responsibility and accountability for the project’s outcomes.
- Secure funding
The project has a secure funding base; contingency funding is recognized from the start, and budgets are strictly regulated to ensure maximum value is realized.
- Project planning and review
Pre-project planning is thorough and considered; progress is monitored regularly and carefully; the project has realistic time schedules, active risk management, and a post-project review.
- End users and operators
End users or operators are involved in the project’s design; the project team works with users who can effectively and efficiently implement what the project has produced.
- Aligned supply chain
All direct and indirect suppliers know the project’s requirements, timelines, and quality standards. As a result, the supply chain’s higher and lower tiers are coordinated.
- Proven methods and tools
Good project management tools, methods, and techniques are used to maintain an effective balance of flexibility and robustness.
- Appropriate standards
Quality standards are actively used to drive output quality. In addition, other standards are regularly monitored to ensure delivery at the best practice levels.
Knowing what success factors are important at the end of a project is critical for assessing how that project went and making changes for the next one. It is critical to understand what distinguishes success from failure.
By investing time in learning about the future of project management, project professionals will be better prepared to capitalize on new opportunities and develop their skill set accordingly. So many opportunities for growth and success are on the horizon; use these trends and factors to propel your company, projects, and team to new heights!
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Dec 18, 2022 | General
Artificial Intelligence, the most common and vibrant technical term in the 21st century, has begun to rule the world stage with its intelligent functionalities. There is no doubt that AI is transforming the productivity and workflow of various industries around the world. However, there may be a constant concern about human job opportunities in the coming years. Organizations have gradually realized that Artificial Intelligence requires collaboration with human employees, and ample job opportunities are emerging.
Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Project Management
Project management has evolved significantly in the last decades. According to an IPMA & PwC report, 56% of organizations has already digital transformation projects, including AI adoption. The current adoption of AI among project professionals is expected to move from 27% to 35% in the next three years.
The organization must consider that successfully implementing projects in the digital age necessitates new skills and different focus areas for project managers. There is a growing demand for digital literacy, critical thinking, and creativity skills, replacing traditional project management skills such as teamwork, communication, and the ability to build effective relationships.
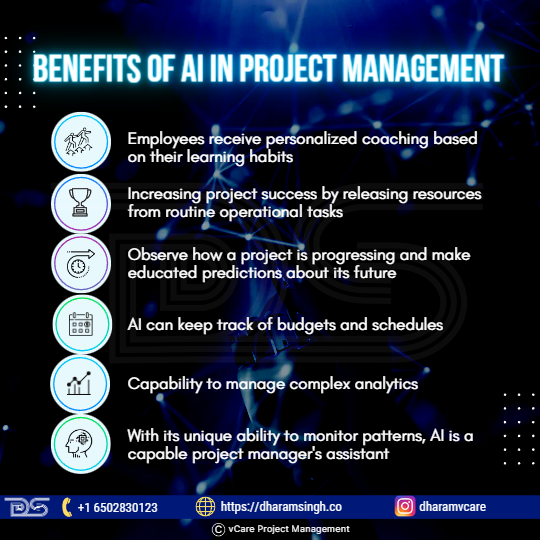
Benefits of AI in Project Management
Benefits of AI in Project Management
Aggregating task statuses to generate weekly status reports, calculating the budget implications of increasing scope and timeline, and performing risk modeling are all functions that an AI technique in your project management software can provide. Here are a few more advantages of AI-enhanced project management:
- Employees receive personalized coaching based on their learning habits.
- Increasing project success by releasing resources from routine operational tasks.
- Observe how a project is progressing and make educated predictions about its future.
- AI can keep track of budgets and schedules.
- Capability to manage complex analytics.
- With its unique ability to monitor patterns, AI is a capable project manager’s assistant.
Digital Skills for Project Managers
Businesses are creating better products and stronger customer relationships at an unprecedented rate. They rely on a workforce with the necessary skills and experience to deal with the effects of disruptive technologies. Organizations combine those experts with data and digital tools such as artificial intelligence and machine learning that allow for agility and speed.

Digital Skills for Project Managers
Top Six digital-age skills for Project Delivery
1. Data Science Skills
Data science is the umbrella term for data management, analytics, and big data. It focuses on Project Managers’ ability to extract meaningful knowledge from available data to improve project outcomes. Data science is expected to play an increasingly important role in all stages of project development, from planning to completion.
2. Innovative Mindset
Today’s project teams are being asked to do more with less. That means that Project Managers who can think creatively and find new ways to achieve great results will be in high demand in the job market. Skills and experience are no longer sufficient. It is now critical to provide examples of one innovative mindset in the workplace.
3. Security and Privacy Knowledge
Today, most businesses and individuals are concerned about data security. In addition to the legal requirements, there is a general expectation that all personal and project data is handled securely. This skill is becoming increasingly important as more projects rely on digital information systems.
The best Project Managers contribute to the security of the projects they manage. They are aware of the requirements and collaborate closely with their IT and legal teams to ensure that data security guidelines are incorporated into each step of project delivery.
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance Knowledge
Ensuring the project is legal and regulatory compliant is not new. Leading Project Managers are always aware of this. The difference that the digital age brings is the growing need to act as a bridge between project teams and the IT, Legal, and Data Protection teams, all of which are critical to the process but need little understanding of each other’s areas of expertise.
5. Ability to Make Data Driven Decisions
Using data to make sound business decisions is core to the best practice of project management. Today’s challenge is synthesizing the massive amount of data available to gain useful insights that propel a project forward. Data is only useful if it is appropriately interpreted. The best project managers use cutting-edge tools to make informed decisions and gain an advantage.
6. Collaborative Leadership Skills
Because of remote working, outsourcing, and cross-functional teams spread across multiple locations, Project Managers today require collaborative solid leadership skills more than ever. Their ability to establish standards and bring team members together (even if only virtually) for the sake of the project is becoming increasingly important. Project managers who can implement collaborative platforms and work management tools to improve their team’s work will outperform their competitors.
An Emotionally Intelligent Project Manager
Emotional intelligence can be referred to as our ability to recognize, control, and communicate emotions. People with high emotional intelligence understand how they feel, what their feelings imply, and how their feelings affect others. In interpersonal situations, it is also the ability to empathize with others. Emotional intelligence is about creating a positive work environment, which is critical to the success of any project.
According to a LiquidPlanner study, most project managers commit approximately 10% of their time to people-related activities. Top project managers dedicate 70% of their time to these activities. As a result, emotional intelligence is critical to project success.

EI skills that a Project Managers require
Some EI skills that project managers require are:
- Intra – Personal – Ability to know and manage yourself
- Inter–Personal – Your ability to interact and get along with others
- Adaptability – Ability to be flexible and to solve a wide range of problems
- Stress Management – – Ability to manage stress
- General Mood – Ability to be positive and in a good mood

Project Managers with Emotional Intelligence
Emotionally Intelligent Project Managers
Project managers with high emotional intelligence have a better chance of success, better physical and mental health, good work relationships, and lower stress levels. Project managers with emotional intelligence can also:
- Successfully manage difficult situations
- Express themselves clearly
- More flexible
- Solution-oriented
- Keep cool under pressure
- Motivate themselves to get things done
- Have a growth mindset
Project Leadership in “DIGITAL AGE”
Over the last decade, the project management practice has evolved from a simple guide for project managers to a deeper understanding of organizational maturity and business agility. However, to capture the true essence of organizational maturity and business agility, the project management practice needed to evolve again, this time by adapting to the needs of the digital world.
According to a PMI’s report, The Project Manager of the Future, which surveyed over 450 HR professionals, over three-quarters of these organizations recognized the importance of project managers understanding disruptive technologies. They were actively recruiting project professionals with specialized skill sets required to manage the impact of disruptive technologies. But what are these skill sets?

Skills to manage the impact of disruptive technologies
- Technology
- Mindset
- Operating Model
- Business Agility
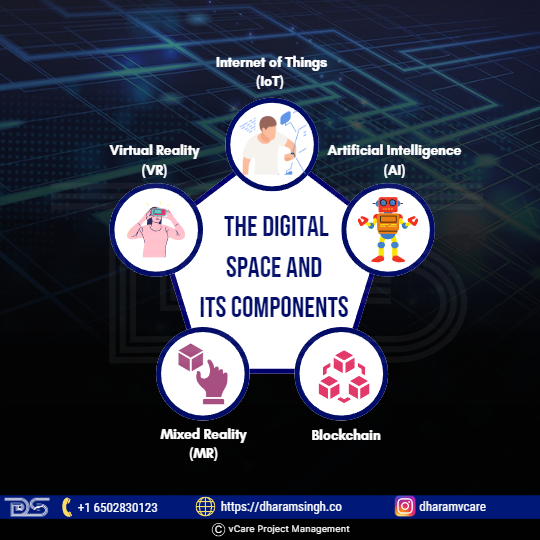
The Digital Space and its Components
Beyond using digital transformation as a token, project managers must gain a thorough understanding of the digital space and its various components, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain, Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR).

Qualities of a Project Leader in Digital Age
Along with that, the project leader must have these qualities in the digital age:
- A human with a “Magical wand”
- Continuous learning & fail fast attitude
- Strong affinity for novelty
- Work smarter than harder
- Breaking industry boundaries for a shared future
- Better Understanding of Innovation & Creativity
- Never consider digital as the only outcome
Digital transformation in project management is more of a collective mindset than a task that can be checked off as completed. It describes a vision that needs constant improvement and encourages future innovation and growth.

3C’s need to be followed by project leadership in the digital age
Here are the 3C’s need to be followed by project leadership in the digital age:
- Calm – Inspire more trust and better performance.
- Connect – People will forget what you said, People will forget what you did, and People will never forget how you made them feel that moment.
- Communicate – The biggest problem in communication is the illusion that it has occurred.
Challenges faced by Project leadership Teams
1. Disconnected & disengaged remote workforce
HR leaders and project managers nowadays, regardless of industry or size of business, assume that connecting with people within the organization is becoming increasingly difficult. Remote working, prompted by the pandemic, has only exacerbated the situation. But why is having a connected workforce important?
A well-connected workforce means employees and the company’s vision, mission, and values are connected. Employees who might feel isolated and disconnected from the business and its goals and objectives, regardless of where they work, are likely to feel disengaged and demotivated, which may affect productivity and efficiency at work. Here are some ideas for how businesses can manage disengagement and create a more connected workforce.
- Use technology to stay connected
- Recognize the good work
- Implement Open Culture
2. Uncertainty in decision making
Project managers strive to conform to all elements and avoid uncertainty in project management to ensure the success of their endeavor. However, no one can predict the future. Working on large, complex projects, such as those in technology, frequently entails high uncertainty in terms of time, cost, and scope, as well as uncontrollable external forces such as inflation, regulation, and financing constraints. These factors can impact a project management system’s ability to assist managers in leading and monitoring projects. Therefore, the project management must comprehend the process of applying decision analysis techniques to the practice of project management, like:
- A process that can assist project managers in improving their ability to make decisions under uncertain conditions.
- A process that can assist project managers in confronting
- Resolving the realities of the project management—uncertainty, external influences, and risk.

Challenges faced by Project Leadership Teams
3. Loss of company culture
Employee attitudes, values, beliefs, behaviors, and underlying assumptions comprise organizational culture. Furthermore, culture is important because it forms the foundation of the business logic applied to any specific decision or problem; there is a minimal chance that something will be done that violates the culture because it would mean contradicting fundamental beliefs.
An organization’s culture, which is not supportive of project management, may be perceived as an additional burden and an impediment to daily work.
4. Lack of alignment
Project success begins with good project management practices and a good team. But how do you make sure they’re in sync? Especially when alignment requirements can take many forms, such as alignment to the overall strategy, stakeholder expectations, mandated processes or policy, or delivering the right things at the right time and in the right way.
Moreover, business organizations may require precise alignment of project strategy to prevent projects from duplicating work or producing useless deliverables to reduce waste and manage costs. Strategic thinking is one way to foster the game-changing power of aligned organizational strategy to project outcomes.
5. Low morale
Employee morale is employees’ attitude, contentment, loyalty, and willingness to give their all and actively contribute to their employer’s success. It’s also about how they feel about their job and workplace.

Strategies to improve Employee Morale at your workplace
If the employee morale is low, it may reduce motivation and efficiency. Employees with low morale produce only the bare minimum of work. As a capable leader, improving workplace morale should be one of your top priorities. According to an SHRM survey, 67 percent of employers find it challenging to maintain employee morale. However, the good news is that the following strategies can help immediately improve employee morale at your workplace.
- Be prepared to manage change
- Challenge your employees
- Conduct team-building activities
- Pay attention to your employees’ physical and mental health
- Spend money on training and development

Tips to improve project performance at your organization
Revamp Project Team Performance
A combination of managerial skills and software tools are used to improve project performance. Ensure that the team understands the goal of every project, has access to open communication channels, and understands the importance of tasks. In addition, project management software can create consistent project plans and automate time tracking and billing to improve project performance. Here are some tips to improve project performance at your organization.
- Process Orientated to People Orientated
- Reactive Approach to Proactive Approach
- Binary Metrics to Holistic Analysis
- Scheduled Retros to Real-Time Pulse
- Individual Evaluation to Team Evaluation
The Five Dysfunctions of a Team
Patrick Lencioni, the author of “The Five Dysfunctions of a Team” examines why effective teams are so rare and offer specific recommendations for removing barriers that lead to dysfunctional teams. The work of Lencioni outlines the causes of team dysfunction and what can be done to overcome each one.

5 Dysfunctions of a Team
The five dysfunctions which have been compared with project management are:
- Absence of Trust – Teams that lack trust conceals flaws and mistakes, are hesitant to seek assistance, make assumptions about the intentions of others, harbor grudges, and dread meetings.
- Fear of Conflict – Fear of conflict results from a lack of trust. Most companies’ employees are more concerned with politics and personal risk management than problem-solving. As a result, meetings are frequently boring because contentious issues are avoided.
- Lack of Commitment – When teams avoid conflict, they fear failure. These teams struggle to make decisions and constantly second-guess themselves.
- Avoidance of Accountability – Second-guessing and a lack of common objectives lead to an inability to develop performance standards. Team members miss deadlines and produce mediocre results.
- Inattention to results – When teams lack focus and clear objectives, team members become stagnant, distracted, and self-centered.
High-performance teams
High-performance work teams are critical to how most organizations perform and carry out their work, resulting in superior performance and a significant competitive advantage. A high-performance team also requires the following to function effectively:
- Uplift the quality of work.
- Mentor guidance to increase productivity.
- Peer-to-Peer monitoring & building a competitive environment.
- Facilitating & enriching the team to handle emerging project delivery practices.
Nurturing the Right Culture
Building an organization’s strong project management culture opens the door to numerous benefits and improves customer service. Organizations with solid project cultures operate under a unique value system that aligns each team member with objectives and goals on a budget, time, and target. Professionals today are expected to demonstrate a wide range of skills and juggle multiple organizational tasks.

Steps to create High-Performance Culture
5 Steps Involved in Creating High-Performance Culture
- Fostering an environment to encourage innovation.
- Adapting to new and disruptive technology shifts.
- Creating a culture that views disruptive technologies as an opportunity to evolve the best practices.
- Encouraging project managers to take advantage of flexible practices that allow them to evolve project scope/requirements due to rapid technological changes.
- Expecting project managers to adapt to new opportunities and challenges to succeed in the age of digital disruption.
Conclusion
To capitalize on all opportunities created by technological disruption, the most forward-thinking organizations rely on the power of project leaders. One significant competitive advantage is where project leaders are prepared, willing, and able to assist their organizations in surviving and truly thriving in the face of massive change.
However, innovative organizations recognize that project leaders with the necessary digital-era skill sets do not appear by chance. As a result, innovators understand the importance of investing in three key areas:
- Skills, training, and development
- Tools and approaches
- Culture
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
You can subscribe and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
You can subscribe to vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our certification Q&A series and student success stories using the link https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
For any questions related to Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com























Recent Comments