
by DharamCW | Aug 2, 2024 | Professional Development Webinars
Leading Successful Business Transformations – Best Practices and Lessons Learned | Cheryl Bowen | vCare PgMP Success Story
Join us for an insightful webinar hosted by vCare Project Management, featuring the distinguished Cheryl Bowen, a seasoned Program and Project Management professional with over 18 years of experience in the Reinsurance industry from Ocoee, Florida, United States. Cheryl, the Principal Project Manager at Hannover Re in Germany, is known for her exceptional skills in driving complex financial system conversions and overseeing large-scale program management initiatives.
Session discussion topics include the following:
+ Ensuring High Levels of Engagement and Buy-In from Stakeholders during Transformation Projects
+ Conducting Post-Mortem Reviews after Transformation Projects
+ Ensuring Sustainability of Transformation Initiatives
+ Rethinking Business Models for Successful Transformation
+ Ensuring Effective Leadership and Team Support during Transformational Changes
Attendees will benefit from Cheryl Bowen’s expertise, earn 1 PDU, and gain valuable industry, career, and certification insights. This knowledge will empower you to navigate the complexities of project management. Additionally, attendees will receive a special discount code on our upcoming PMP, PgMP, and PfMP programs.
🔗 Reserve your spot now: https://bit.ly/3Lpjifb
Session Date: Thursday, 29th August, 2024
Session Time: 10:00 AM – 11:00 AM (PDT) / 11:00 AM – 12:00 PM (MDT) / 12:00 PM – 01:00 PM (CDT) / 01:00 PM – 02:00 PM (EDT) / 02:00 PM – 03:00 PM (BRT) / 06:00 PM – 07:00 PM (BST) / 07:00 PM – 08:00 PM (CEST) / 08:00 PM – 09:00 PM (AST) / 09:00 PM – 10:00 PM (GST) / 10:30 PM – 11:30 PM (IST)
🚀 Elevate Your Project Management Career:
– Book an obligation-free consultation session on Project Management Career, training, and certifications: http://talktodharam.com
– Discover training offers and certification discounts: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
– Stay updated with our Q&A series and certification success stories by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube channel at https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
– Follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
#BusinessTransformation #ProjectLeadership #PgMPWebinar #Ocoee #Florida #USA #Germany #PMP #PgMP #PfMP #ProjectManagement #StakeholderEngagement #ProgramManagement #ChangeManagement #TransformationProjects #FinancialSystems #PostMortemReviews #SustainableChange #BusinessModels #TeamSupport #ProfessionalDevelopment #IndustryInsights #CareerGrowth #PgMPCertification #PgMPExam #PgMPCourse #PgMPTraining #AskDharam #DharamSingh #DharamSinghPgMP #DharamSinghPfMP #DharamSinghPMP #VCareProjectManagement #ProgramManagementProfessional #ProjectManagementProfessional

by DharamCW | Aug 1, 2024 | General
Today’s organizations are structured through many time-limited programs that transform organizational strategy into action. These programs necessitate a visionary mindset to align program goals with the organization’s strategic objectives. While project managers direct project work, they ensure individual projects align with program goals. Thus, program managers see their role as strategic and play an important role in managing the implementation of the organization’s strategic objectives by ensuring that the overall mission is met through the successful completion of planned programs.
Core Competencies of Program Managers
There are many similarities between a good program manager and a good project manager. However, a program manager must have broader organizational knowledge than a project manager. In addition, programs frequently necessitate strategic visioning and planning skills to align overall program goals and benefits with the organization’s long-term goals.
Here are the top ten core competencies of Program Managers:

Top 10 Core Competencies of Program Managers
1. Leadership and Teamwork
The program manager is the team’s leader and is accountable for the program’s overall success. As a result, it is critical to have a clear vision and the ability to communicate it effectively to all employees, whether charismatic, supportive, or inspiring. The program manager’s strong leadership provides direction, builds morale, and inspires the program and project teams.
As the team leader, the program manager is responsible for engaging all team members and fostering collaboration, individual commitment, and accountability. A program manager must decide which tasks can be assigned and who can delegate them. Understanding what to delegate and how to delegate is critical.
2. Planning and Organizing
Programs frequently necessitate strategic visioning and planning skills to align overall program goals and benefits with the organization’s long-term goals. Therefore, the program manager must be skilled at planning and organizing for the best outcomes. Aside from the program schedule, creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for the program at the summary level is critical. It also allows control accounts to manage cost, schedule, and scope. In addition, a well-designed Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) helps organize the team at the start of a program and makes change management easier.
3. Communication
A program manager must be a good communicator. Effectively moving information between project resources is critical to a program’s success. To ensure the success of the team and project, the program manager must be able to negotiate effectively and use persuasion when necessary.
Thus, effective communication entails breaking down barriers within and across projects and functional departments.
Communication “hard skills” include gathering and disseminating performance data, such as status reports, progress measurements, and forecasts. In addition, the program manager must communicate effectively with the program and project teams, top management, and stakeholders. For the project’s success, vertical and horizontal communication must be fluid and transparent.
4. Ethics and Ethical Values:
One of the key aspects of effective program management is ethics.
The Code of Ethics & Professional Conduct emphasizes ethical values such as trust, honesty, accountability, respect, and fairness—these five values foster team harmony and professionalism, which leads to project success. Building trusting relationships across cultures, time zones, teams, and departments aids in the smooth operation of projects.
Trust is the common thread that connects different cultural differences, disparate work cultures spanning multiple time zones, team members with different behaviors, and departments with distinct objectives. A project leader must grasp this and cultivate trustworthy relationships.
Treating people fairly and demonstrating responsible, ethical behavior toward subordinates creates a working environment where employees feel safe, protected, and confident that there is no room for injustice or discrimination.
5. Internal and External Stakeholder Engagement
The program manager must be able to focus on both internal and external stakeholders simultaneously. Identifying and documenting all individuals or organizations impacted by the program and its projects and pertinent information about their interests and involvement significantly impacts program and project success. This process enables dealing with internal stakeholders (other project managers, senior managers, and the like) and external stakeholders (other agencies and regulators).
6. Political Understanding
Another skill that the program manager must have is the ability to understand the organization’s political environment. This understanding includes the political aspects of networking and strategic thinking to make the best decisions. With a solid understanding of the political environment, the program manager must form positive relationships to realize the program’s full benefits when the activities are transitioned to gain leverage and buy-in for overall program success. According to PMI’s The Standard for Program Management, well-managed stakeholder expectations and established buy-in can ensure program success. Knowing the firm’s working dynamic and environment is critical to the program manager’s success.
7. Knowledge management
A successful program manager should have a solid understanding of the organization and its business practices and familiarity with the technologies used in the program’s projects. In addition, program managers must have “hard skills” such as technical expertise and detailed cross-functional knowledge. This knowledge keeps the PM from being unduly influenced by functional experts who either have a plan or make decisions based on limited information.
The program manager is responsible for interpreting, implementing, and reviewing program policies, procedures, and requirements and communicating these to all program team members and project managers.
8. Financial Management
In today’s environment of scarce and competitive resources, program managers must understand how to finance their programs with speed, economy, and efficiency. Program managers are in charge of budgeting and calculating the return on investment (ROI). Therefore, they must be familiar with the program’s financial aspects to keep the budget under control at all times. In addition, they will be required to make decisions that will directly impact the budget and ROI for all projects within the program; therefore, program managers must be knowledgeable about the financial issues involved.
9. Risk management
Program management works tirelessly to reduce business risk. However, a project with no risk has little potential for reward. Effective risk management necessitates identifying risks, assessing their potential for harm, and developing plans to address the threats. Program managers are in charge of gathering all risks from functional teams and leading the team through a risk analysis exercise to determine which risks are program-level and project-level.
The program risks are then classified and prioritized based on their potential impact on the program. Finally, a similar exercise is performed to mitigate project risks throughout the life cycle to reduce overall program risk.
10. Project and Process Management
Transitioning from project management to program management necessitates a greater emphasis on the horizontal domain and less on technical capabilities. This action requires the program manager to prioritize strategic efforts over tactical skills, which can be delegated. Therefore, the program manager must have excellent project and process management skills, ideally with prior project management experience.
Managing program complexity through efficient and effective project management is critical for program management. Program management imposes structure and provides a framework that breaks down the complexity of managing a group of dynamic, time-limited projects into more manageable and cost-effective elements. This framework is critical for planning, scheduling, budgeting, and quality control. In addition, a program manager with strong core project and process management competencies can successfully lead between and across multiple projects.
Leadership Styles for Future Project/Program Managers
One of the potential success factors for both program and project managers is leadership style. A project manager can become a great project leader by understanding leadership styles and their impact. As a result, the program and project managers must determine the best leadership style for each project team. Some of the most common project management leadership styles are:

Leadership Styles for Future Project/Program Managers
1. Coaching leadership style
The coach’s leadership style is one of the most advantageous to employers and employees. But unfortunately, because it takes more time than other types of leadership, it is also one of the most underutilized.
2. Visionary leadership style
A visionary leadership style is advantageous for small, rapidly growing, and larger organizations undergoing transformations or corporate restructuring.
3. Servant leadership style
Servant leadership is an excellent leadership style for organizations of any size or industry, but it is especially common in non-profits. These leaders excel at boosting employee morale and reinvigorating employees’ interest in their work.
4. Autocratic leadership style
Autocratic leadership can benefit organizations with strict guidelines or industries that rely heavily on compliance. It can also benefit employees who require extensive supervision, such as those who need more experience. However, this leadership style can stifle creativity and make employees feel confined.
5. Laissez-faire leadership style
Unlike autocratic leadership, laissez-faire leadership focuses on delegating many tasks to team members and providing little supervision. Furthermore, because a laissez-faire leader spends less time managing employees, they often have more time to devote to other projects.
6. Democratic leadership style
The democratic leadership style is a hybrid of autocratic and laissez-faire leadership styles. Before making a decision, a democratic leader solicits and considers feedback from their team. This style is frequently credited with increasing employee engagement and workplace satisfaction because team members believe their voices are heard, and their contributions are valued.
7. Pacesetter leadership style
One of the most effective ways to achieve quick results is to set the pace. Pacesetter leaders are mainly concerned with performance, frequently setting high expectations and holding their team members accountable for meeting them.
8. Transformational leadership style
Like the coaching style, the transformational style emphasizes clear communication, goal-setting, and employee motivation. However, the transformational leader is motivated by a commitment to organizational objectives rather than putting most of one’s energy into each employee’s goals.
9. Transactional leadership style
A transactional leader, similar to a pacesetter, is laser-focused on performance. Under this leadership style, the manager establishes predetermined incentives, usually monetary rewards for success and disciplinary action for failure. However, unlike pacesetter leaders, transactional leaders are equally focused on mentorship, instruction, and training to achieve goals and reap the rewards.
10. Bureaucratic leadership style
Bureaucratic leaders, like autocratic leaders, expect their team members to adhere strictly to the rules and procedures. The bureaucratic style focuses on fixed duties within a hierarchy. Each employee has a set list of responsibilities, and collaboration and creativity are not required.
Adapting Agility during Digital Transformation
Thriving in today’s competitive environment is a difficult task. Businesses must find ways to keep up with the trends as almost every industry is rapidly evolving, fueled by technological advances. As a result, many adopt an agile mindset to remain sustainable and efficient.
The ability of a company to change or adapt quickly to market changes is referred to as business agility. The idea is to manage operations and resources flexibly and responsively to maximize business value. Concurrently, digital transformation is upgrading business processes using modern technologies to improve performance and overall efficiency.
Based on the agile project management philosophy, the business approach is gaining traction among forward-thinking organizations. It enables them to recognize and capitalize on potential opportunities ahead of the competition. Companies concentrate on three key areas for improvement:
• Strategy
• Organization
• Operations
Business agility is no longer an option in the age of digital transformation. Instead, it is an essential component of any successful business. As technology changes the world at breakneck speed, the program manager must be adaptable and develop alongside it.
Are Program Managers adapting to the agile environment?
Traditional project management entailed following a pre-defined plan to achieve pre-defined goals. However, in an agile environment, the concept of “done” is rapidly becoming obsolete. So, what does it take to manage projects effectively with constantly shifting requirements?
• Managers must first understand their organization’s goals when implementing agile workflows.
• Following that, they must reconsider their success metrics: rather than meeting a predetermined budget, timeline, or scope of work, project managers should focus on metrics such as development cycle time and the proportion of decisions made based on objective data.
• Finally, agile project managers must continuously examine their processes and seek to adapt and improve themselves to meet the evolving needs of their customers and coworkers.
Skills for a Hybrid Working Environment
Flexibility takes many forms as the world enters the “new normal” of business. However, the new flexible work models present some difficulties. To be successful in hybrid work, specific skills are required. Here is a list of five skills to concentrate on as you prepare for the new work environment.

Skills for a Hybrid Working Environment
1. Technology and Processes
2. Online Security
3. Communication
4. Team-Building
5. Leadership
Every organization’s flexible work patterns look different. Additionally, there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach to implementing a hybrid work model. But, regardless of the circumstances, one thing is certain: training will be critical to your success.
Relevant information is critical. The right delivery methods are also important if you want them to stick. Finally, reaching and engaging your employees is critical to providing meaningful training. Use the best digital solutions to level the playing field for both in-office and remote employees. No matter where your employees are, the right approach will set them up for success.
Significance of Upskilling Project/Program Managers
Project/Program managers are valuable professionals who can work in various industries. It is frequently a highly sought-after position with numerous responsibilities. According to a study by PricewaterhouseCoopers, project management is critical to business performance and organizational success for 97% of organizations.
To ensure that a project management career takes off, one must have a mix of technical and soft skills. The top eight skills are listed below.
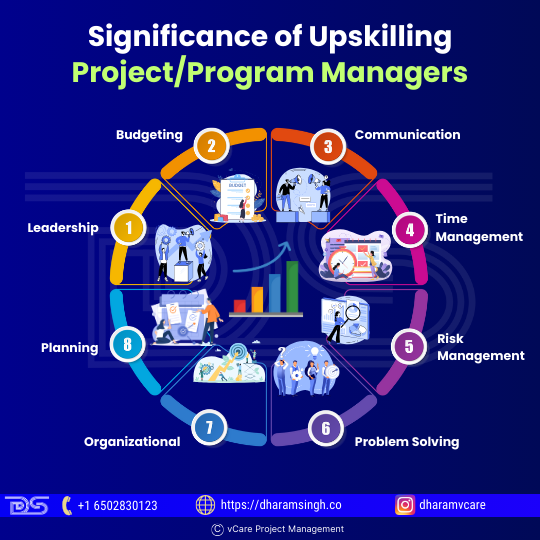
Significance of Upskilling Project/Program Managers
• Leadership
• Budgeting
• Communication
• Time Management
• Risk Management
• Problem Solving
• Organizational
• Planning
The world of project and program managers has changed significantly in the last few decades, with increased competition and the drive for efficiencies forcing companies to work differently. As project managers advance in their careers, they gain experience managing multiple related projects and making decisions that advance strategic and business objectives. As employers seek program managers to support the organization’s strategic goals, PgMP® credential holders will have a distinct advantage in employment and promotion opportunities over their peers.
How PgMP aids in gaining program managers’ knowledge
The Program Management Professional (PgMP®) certification is a visible indication of advanced experience and skill. As a result, it gives one distinct advantage in employment and promotion. As on 6th June 2024, there are 6,358 PgMP® that exist worldwide. The PgMP® is intended for professionals who have advanced in their careers and can manage multiple projects to ensure the success of a program. Furthermore, PgMP® holders are expected to manage complex tasks across multiple organizations, geographic locations, and cultures.
PgMP® Certification Benefits

PgMP Certification Benefits
Enhanced Strategic Decision-Making:
The PgMP® certification equips program managers with the skills to make strategic decisions that align with organizational goals, ensuring the successful integration and delivery of multiple projects.
Improved Stakeholder Engagement and Communication:
Certified PgMPs are trained to effectively engage and communicate with stakeholders at all levels, fostering trust and ensuring stakeholder needs are met throughout the program lifecycle.
Mastery in Benefits Management:
Gain expertise in identifying, planning, and realizing program benefits, ensuring that the program delivers measurable value to the organization and its stakeholders.
Robust Governance Frameworks:
Learn to develop and implement robust governance frameworks that ensure program alignment with strategic objectives, risk management, and compliance with organizational standards.
Also, while preparing for PgMP® Certification, you will learn the best practices for conducting your programs more efficiently and achieving great results for your organization. This aspect might assist you in securing better pay and a higher position. In addition, you will be recognized as a certified program manager.
Final Thoughts
Program management will only be effective if the anticipated benefits are realized and effective leadership is at the top. Often, programs fail to achieve the organizational goal due to a lack of management skills in dealing with the program’s complexity and demand. Competence and skills are entirely different concepts, with skills acquired through training and competence referring to the level of proficiency in applying the acquired skills. The skills and competencies of a program manager and a project manager are similar. Still, those of a program manager are expected to be deeper and much more strategic in aligning a series of projects.
When program managers use their unique perspectives and insight to guide programs in the most strategically advantageous way, they can provide long-term value for the company’s vision and direction. Any organization that manages more than one project at a time will benefit from the assistance of a program manager.

by Dharam CW2 | Jul 11, 2024 | General
Many PMOs recognize digitalization as an essential step in their organizations’ journey toward project management maturity. As a result, the Project Management Office (PMO) must shift its focus from project governance and delivery to supporting digital transformation.
To keep up with the evolving demands and needs of an increasingly digitized world, digital transformation has to be drifted through organizations of all shapes and sizes. However, many realize that successful digital transformation entails changing foundational cultures, structures, and methodologies and implementing digital tools. As organizations expand to accommodate this change, the PMO’s role within those organizations must change to do the same.
Digitalizing PMOs
Digital transformation is a familiar idea. Businesses constantly look for new ways to adapt and leverage emerging technologies to improve their business processes. Before the pandemic, PTC research found that 70% of organizations had or were working on a digital transformation strategy.
The PMO is crucial to achieving an organization’s strategic goals. If PMOs are to be an organization’s strategic drivers, they must expand their role beyond its traditional boundaries. They must assume their strategic role by leading change and capitalizing on opportunities in the digital space. PMOs must be at the forefront of emerging technologies, constantly evaluating opportunities and implementing new strategies. The recent pandemic and sudden shift to remote work have highlighted the challenges of developing community and culture through digital spaces. Here are some ways that PMOs can help the organization drive into digital transformation.
Five ways the PMO drives digital transformation
- PMOs can inspire and encourage change.
- PMOs act as the strategic arm
- PMOs provide support and insight.
- PMOs properly manage transformations.
- PMOs enable successful digital adoption.

Five ways the PMO drives digital transformation
How PMOs can aid an organization’s digital transformation
The nature, ownership, and stakeholders of IT strategy, governance, and management activities are changing dramatically due to digitization. According to Gartner research, 87% of organizations prioritize digitization. Furthermore, technology is now responsible for 77% of an executive’s top priorities.

Advantages of PMOs
As a result, PMOs are under intense pressure to transform. Unfortunately, their project, program, and portfolio management processes are designed for predictability and consistency rather than the speed and flexibility required to meet digital demand. Most PMOs have three significant advantages, which are either inherent due to the PMO’s role or location or have been developed through previous experience:
- A neutral enterprise perspective: As capital allocation and portfolio prioritization approaches change to enable the funding flexibility required for digital work, the PMO’s impartial, enterprise-wide perspective on demand, investment, and resource utilization is hugely valuable.
- The ability to operate via influence: As organizational boundaries become more fluid and who “owns” project management becomes less certain, influencing and enabling others, rather than direct ownership, becomes even more critical.
- Stakeholder insight: As digitization spreads throughout the business and accounts for an increasing proportion of work, there are more first-time stakeholders and greater stakeholder complexity for each piece of work. Understanding the preferences of these various stakeholders and experiencing synthesizing their feedback becomes critical in delivering results from digital work.
Elements Driving Digitalization
Traditional businesses worldwide have long recognized that digital transformation is the key to thriving in a fast-paced world. Digital transformation involves integrating digital technology into all aspects of a business. It fundamentally alters how businesses operate and provide value to customers. It increases efficiency, transparency, customer experience, employee engagement, and culture and saves time and money. Modern digital tools have elevated the project management process to new heights.
The following are the seven critical elements of a successful strategic digital transformation framework:
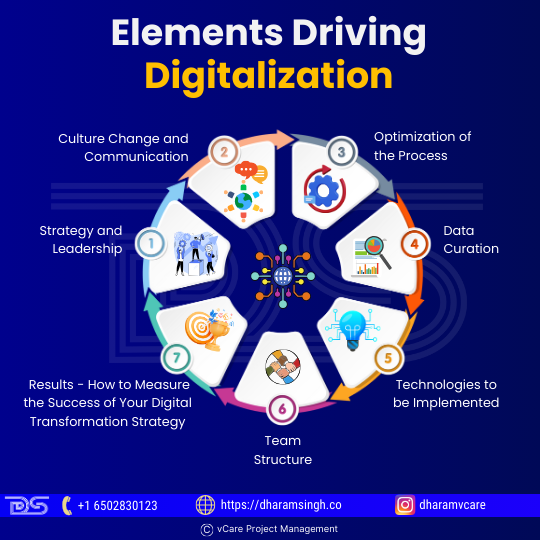
Elements Driving Digitalization
- Strategy and Leadership
An effective game plan is an obvious but frequently overlooked component of a digital transformation strategy. Instead, what matters is “how and who” formulates the strategy. A basic strategy and the appropriate technologies can help you digitize or digitalize your business, but transformation requires the right mindset and guidance. As a result, strategy combined with the right leadership is the first and most important component of an effective digital transformation strategy.
Visionary leadership combined with the appropriate digital transformation strategy can achieve a better, smoother, more cost-effective, and time-effective plan for your business’s transformation.
- Culture Change and Communication
Prepare for a massive cultural shift. A company’s clients and employees are typically resistant to significant changes, making implementing any transformation challenging. However, any successful digital transformation program must include culture. Therefore, giving your employees advanced training in good communication will be advantageous.
- Discuss the digital transformation strategy with your employees and how it will benefit all stakeholders.
- Conduct training sessions with your employees ahead of time to prepare them.
- You can prepare your employees by demonstrating the importance of aligning culture with new initiatives.
- Optimization of the Process
Every business has various processes and operations that can be improved to make workflows more efficient and effective. As a result, when developing a digital transformation strategy, consider business process optimization.
The strategy must optimize the business process while meeting customer and internal team goals. The digital transformation strategy must cover all interconnected business processes to achieve maximum output.
- Data Curation
One of the primary reasons for implementing digital transformation is to eliminate your business’s pain points for your team and your customers. But how will you know what these aches and pains are?
Data analysis and integration can assist you in locating them. People frequently choose their preferred technologies when developing transformation strategies before analyzing their data. Data analysis and the dissemination of its results can assist the team in identifying the best solutions to problems, leading to developing a better digital transformation strategy and making the most of the transformation process.
- Technologies to be Implemented
Finding the right technologies for your business is one of the most crucial steps in creating a digital transformation strategy. Introducing new technologies into your business will necessitate a significant financial investment, so it must be done correctly to avoid the need for additional funds. Any impactful strategy for digital transformation will always include options and budget constraints to help you make the best decision possible. Whether dealing with legacy system updates, application modernization, or implementing entirely new digital systems, you must find the best technology.
Some cutting-edge technologies that must be incorporated into your digital transformation strategy are:
- Cloud and Distributed Platforms
- Data Analytics & Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Experience and Digital Reality
- Team Structure
Harvard Business Review says digital transformation is about people, not tools. As a result, team structure is a determining factor in delivering results by the Digital Transformation Strategy.
The scope of the project should determine the team structure. The following components should be included in the digital transformation initiative:
- Pack of Leaders
- Business Experts
- The cast of Coders and Designers
- Results – How to Measure the Success of Your Digital Transformation Strategy
Your company’s digital transformation outcomes will greatly influence how you lay out your strategy. The outcomes will always vary depending on the practices and technologies used. Your digital transformation strategy’s success is dependent on its agility. First, of course, you must stick to your detailed strategy, but you must also be open to changes if things don’t go as planned.
By developing an effective, clear, and robust digital transformation strategy, you can ensure your company’s digital transformation goes as smoothly as possible. A digital transformation strategy is similar to a personalized road map for significant changes in your business operations. However, it requires significant financial investment, time, and technical expertise.
From Traditional PMO to Agile
Traditionally, PMOs have focused on maintaining project control to complete projects on time and within budget. However, in today’s increasingly complex and changing competitive environments, agile management is gradually displacing more traditional management methods; PMOs that remain anchored in this “classic” management model risk disappearing if they do not set the following objectives:
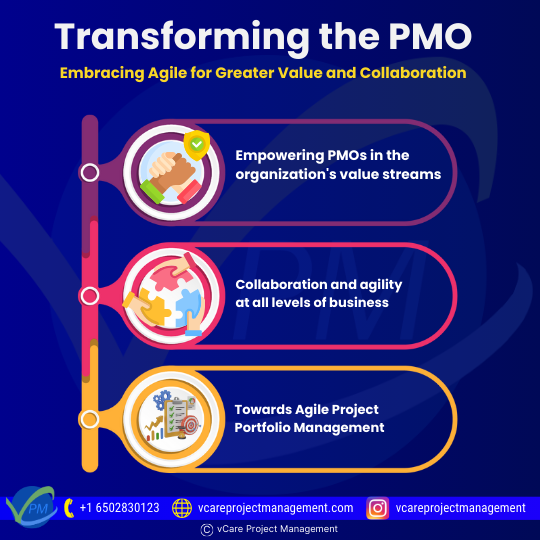
Transforming the PMO
- Empowering PMOs in the organization’s value streams
Organizations are now focusing on the value they provide to their customers and how different areas and departments contribute to that value creation. Suppose PMOs stick to their command and control model to ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget. Their contribution to the organization’s value streams will be marginal, and senior management will view them as an unnecessary expense for the company.
- Collaboration and agility at all levels of business
Silo-based organizational models need to gain ground in agile and collaborative environments. As a result, PMOs must evolve beyond simply providing Project Managers with the tools they need to complete the organization’s projects.
On the one hand, PMOs must maintain open lines of communication with senior management to align the Project Portfolio with the organization’s goals. On the other hand, it serves as a reference point for stakeholders and project work teams, providing real-time information on project status and support at all levels for proper project implementation.
- Towards Agile Project Portfolio Management
Change is the norm in this new competitive environment, with highly volatile markets demanding businesses to bring products and services to market as quickly as possible. As a result, company objectives can shift dramatically quickly, necessitating a rethinking of project portfolio prioritization. This phase is where PMOs must adapt to this new environment and manage key project management issues like prioritization, resource management, budgets, or delivery dates in an agile manner, as well as learn to react to changes in their project portfolios in an agile and efficient way without losing sight of the organization’s objectives.
Post-pandemic challenges for PMO
If PMOs establish these three goals, they might avoid extinction because senior management will no longer recognize their value to the organization.
It will be challenging, and the Project Management Office will face several challenges as it adjusts to the new reality. In particular, the PMO will face some challenges for its role to be perceived as critical to the organization’s value streams:
- Coincide the project portfolio with the overall strategy of the organization.
- Resource management is a real challenge for PMOs.
- Responsiveness to changes in the project portfolio.
- Fluent in communication with the organization’s senior management.
- Embrace Agile Leadership.
- Standardization of processes and workflows.
- Renewal of project portfolio management tools.
Mitigating mediocre implementation of Programs
There are always equal chances of success and failure in programs/projects. As a result, it is critical to understand how to avoid and overcome project failure. There are numerous reasons why a PMO succeeds or fails. Still, the most common reasons for failure are often not related to process or technology issues but to “people issues” in an organization.

How to avoid PMO Failures
Here are the most common reasons why PMOs fail:
- Adopt the Proactive Approach
After many years, project managers gain the skills and knowledge needed for the current project from their experience. As a result, an experienced and highly skilled project manager is equipped to deal with customers and avoid project failure. If you are new to project management, consult a professional mentor to discuss your concerns and receive appropriate advice based on their experience. If you have project management experience, you should apply your skills and knowledge to the project and be aware of the common causes of project failure.
- Plan the Project’s Strategy and Project Implementation
The most important stage of any project is planning. Most of the time, proper attention is not given during the planning stage. If you plan properly, you will increase the project’s chances of success. After scheduling your project, use the Project Management Life Cycle to begin project execution.
- Manage the Project Goals
It would be best to document the project’s decisions, actions, and outcomes before beginning, during, and after completion. To avoid project failure, it is always necessary to ensure project deliverables and work appropriately with customer requirements. Never rely on understanding, verbal agreements, or memory for project implementation decisions.
- Avoid Unrealistic Expectations
Always set realistic expectations and time frames with stakeholders, team members, or customers to meet your project’s deadline. This move is related to the proper project start but goes deeper until completion. To avoid project failure, realistic expectations for team members must be set based on their capabilities. It would help if you encouraged them to work enthusiastically and push themselves beyond their comfort zone to meet the project’s objectives.
- Track Project’s Progress
Project planning will assist you in determining where your project should be now. In addition, you should know how much of the work has been completed, whether your work is on schedule, proceeding as planned, and so on. These three parameters govern any project and are critical in preventing project failure.
- Identify Risk Factors
The best way to avoid risk is to identify, analyze, and respond to risk factors. So, if you identify the risks and potential issues early on in the project, your project team can avoid them with appropriate actions. In addition, identifying and resolving risk factors will assist the project manager in lowering the likelihood of project failure. As a result, you can perform proper risk management and avoid project failure.
- Use Correct Methodology
One of the most important decisions a project manager must make is the methodology to use for project management. What you choose will have a significant impact on teamwork. However, each methodology has advantages and disadvantages depending on the project type and scope. Here are some top project management methodologies to consider.
- Waterfall method
- Agile/Scrum
- Hybrid approach
- Critical Chain Project Management
- Integrated Project Management Technique
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
All project management methodologies cannot be regarded as the best for all projects, so one can understand the project requirements and select the best option. The correct methodology will assist you in achieving the project goal within the specified time frame, thereby avoiding project failure.
- Focus on Stakeholder’s Requirements
As we all know, a project will only succeed if it meets its objectives and exceeds the expectations of its stakeholders. Therefore, to be successful in project management, all team members must be actively involved in the project and committed to its success. Devoting entails writing down the following stages:
- The competent initiative assists the team in implementing various tasks throughout the project life cycle.
- Adequate funding ensures the organization’s cost-generating department has enough money to fund the projects.
Final Thoughts
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment, agile working methods might provide significant added value that should be noticed.
Digitalization is making projects more complex. As a result, the use of technology to manage projects is growing, and project teams must be cross-functional to achieve project goals. Agile project management provides an opportunity to respond quickly to new requirements and be more visible in the market. For organizations that use a traditional approach to project management, the transition to an agile PMO is part of their digital and agile transformation.
It should be noted that this is not an evaluation of “better” or “worse” methods. When used correctly, each project management method can reveal its strengths. It is critical to think about, use, and improve them.

by DharamCW | Jun 11, 2024 | General
People in the Project Economy have all the skills and capabilities required to turn ideas into reality, regardless of the type of project they are working on. It is the process by which organizations provide value to stakeholders by completing projects, delivering products, and aligning with value streams.
Project-based work has well-defined goals, milestones, deliverables, and a start and end date. Projects can last hours, months, or years, depending on the project and business needs. However, the work is focused on business needs and objectives rather than specific roles.
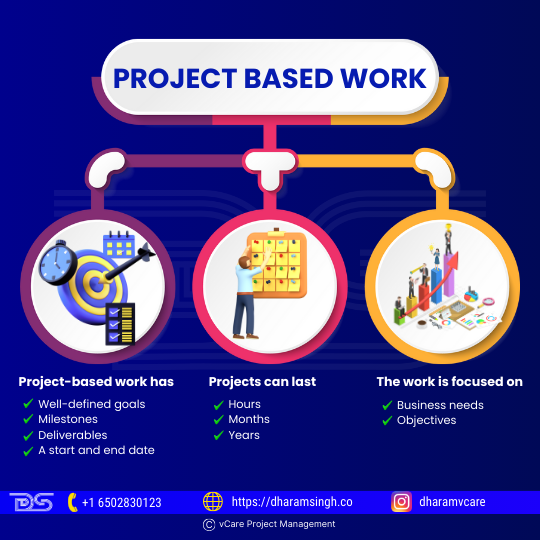
Project Based Work
Business leaders always want their teams to be agile and nimble. Adopting a project-based work mindset can help them achieve their goals. In addition, according to a recent MIT and Deloitte report, executives are increasingly viewing their workforce as an ecosystem, drawing on the diverse skill sets of their full-time employees and freelancers to meet business challenges.

Business Leaders Need
The Project Economy Has Arrived
The Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook (2021) by Antonio Nieto-Rodriguez states that:
- By 2027, nearly 88 million people worldwide are expected to be employed in project management, and the value of project-oriented economic activity is expected to reach $20 trillion.
- However, research shows that only 35% of global projects are successful, implying that project professionals waste time, money, and opportunity.
- To capitalize on the new project economy, businesses must adopt a project-driven organizational structure to ensure executives can sponsor projects and train managers in modern project management.
The Rise of the Project Economy
Berkley’s guide states that the rise of the Project Economy will play an essential role in the Future of Work. The following statistics from the below-mentioned survey make this statement more accurate:
- Almost 80% of executives believe the future of work will be project-based rather than role-based.
- More than 85% of all highly skilled independent contractors work in the Project Economy.
- According to the PMI, project-based economic activity will increase by 68 percent, from $12 trillion in 2013 to $20.2 trillion in 2027. Employers will require 87.7 million PM-related specialists by 2027.

PMI Report
- 89% have at least one project management office (PMO), and 50% have multiple.
- Project work is expected to increase by 68% in the future, according to The State of Project Management report by Wellingtone.
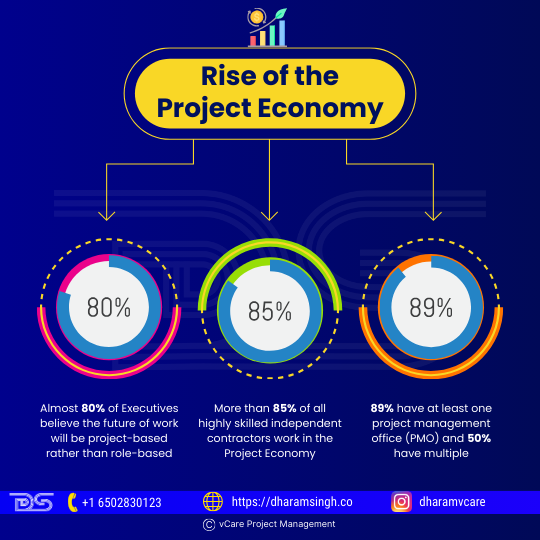
Rise of the Project Economy
Challenges for the whole organization
The world is changing faster than ever, and businesses need help keeping up. However, savvy companies understand that the solution lies in developing and leveraging their people’s most valuable asset.
According to Global Talent Trends 2022 studies, workers are more stressed than ever. Eighty-one percent report being at risk of burnout, and one in five blame working for a company whose values do not align with theirs.
Human resource and project managers face many challenges in the whole organization.
- Close Skill Gap
Planning and managing long-term skill development will become more important as people lead longer, more diverse careers. Digital skills are now expected, and knowledge of business processes and related concepts is considered a core competency in every worker’s skill set.
Analytical and critical thinking skills have progressed from the exception to the norm, while interpersonal and leadership abilities are more valued than ever. Yet, many businesses face crucial skill shortages, particularly in retail, construction, real estate, manufacturing, education, medical and health services. According to McKinsey, 87 percent of executives report or expect skills gap challenges in the next few years.
- Initiatives to improve hiring
Hiring talented, qualified people has become critical to business success in a world of labor shortages and job-hopping. But it takes work.
- According to Josh Bersin’s study, 74 percent of businesses in the United States underperform when hiring, and only 60 percent of newly created jobs are filled.
- Businesses are attempting to attract not only talented but also diverse employees: The State of DEI Efforts report states that Finding various candidates with appropriate qualifications is the most difficult challenge for 43 percent of respondents.
- Also, Glassdoor’s Diversity and Inclusion Workplace Survey states that 76 percent of job seekers and employees value a diverse workforce when evaluating companies and job offers.
- Leadership development
Living in a volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) world has become the norm. Influential leaders must be agile, constantly reevaluate and iterate their leadership practices, and strongly desire to build resilience for the future.
Organizations must adapt to new levels of complexity and ambiguity due to the COVID-19 pandemic’s disruption of the global economy and traditional modes of operation. The recovery from COVID-19 and the long-term impact of its disruption remain unknown. However, many organizations plan to meet their strategic goals and objectives as things begin normalizing. They must be especially cautious in the VUCA world.
VUCA: Companies and managers must embrace versatility, agility, and discomfort to progress. Covid-19 was the year of the phygital revolution – the physical, digital, and online-offline workplace convergence. In such a VUCA environment, managers and companies must be versatile, uncomfortable, collaborative, and agile to progress in a Phygital world. Therefore, every company and leader must be skilled in being versatile, uncomfortable, collaborative, and agile.
- Workforce retention
The ‘Great Resignation’ has resulted in historic numbers of people quitting their jobs, with the following industries suffering the most:
- Leisure and hospitality
- Trade, transportation, and utilities
- Professional and business services
- Education and health services
- Manufacturing
- Construction
Businesses are grappling with the issue of how to retain employees. One solution is to provide employees with opportunities for learning and skill-based career growth. However, employees see professional development opportunities as the most important way to improve and change the company culture.
- The Workplace Learning 2022 Report states that 46% of L&D leaders said upskilling or reskilling was a top focus area this year; internal mobility, career pathing, and employee retention fell toward the bottom.
- According to The American Upskilling Study 2021 study, 66 percent of workers aged 18-24 ranked upskilling opportunities as the third-most important benefit in evaluating a new job, and 48 percent of workers in the United States would relocate for such opportunities.
- Enterprise agility
To thrive in a highly dynamic world, organizations must quickly adapt to changing technology, markets, and customer needs. Enterprise agility denotes a shift away from traditional hierarchical structures and disconnected teams toward an operating model that optimizes strategy, structures, processes, people, and technology.
Rather than being hindered by the relentless pace of change, agile enterprises are more likely to capitalize on emerging technologies and business trends to differentiate themselves from the competition. However, as per a McKinsey report, two-thirds of businesses say they need to prepare for workforce disruptions brought on by technological and market trends.
- The transformational potential of learning
Employees and organizations are moving together as they navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing world. Workers must embrace a culture of lifelong learning to remain relevant. The benefits for businesses are evident, with skilled workers becoming more agile and motivated. In addition, Upskilling and reskilling can transform society as a whole, allowing under-represented groups to participate in the economy and be more involved.
- Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies continue to influence how we live, work, and interact in a world driven by digital solutions. Many technological advancements are beneficial: they increase productivity, make necessary services more accessible, and generally make our lives easier.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, cybersecurity, and big data can make products and services more widely available, particularly to those currently unable to use them.
Several significant benefits for business processes should also be considered. Businesses already use a variety of digital solutions to attract customers, such as applications and websites. By 2030, approximately 70% of companies worldwide will have adopted at least one type of AI technology, with other emerging technologies being implemented quickly. Thus, technological solutions will continue to automate and innovate our work.

Future Challenges for the Whole Organization
Perspective Competency and Strategic Envisioning
A better approach would be to stop thinking about today’s challenges in terms of ‘project management.’ Instead, we must reframe the question to how we can do our work most efficiently. This also entails abandoning the notion of project management as a technical discipline in favor of viewing it as a collection of skills and disciplines required to complete work today. Christoffer Ellehuus, in the article Succeeding in the Project Economy, outlines four significant components for this phase.
- Strategy
Executing a strategy must be rooted deeply in the organization and must be understood by all. The biggest challenge is selecting the right work and eliminating unnecessary tasks. In addition, identifying opportunities for innovation, growth, and value creation are critical areas for improvement.
- Work
Work completion necessitates action in three areas: process expertise, workflow management, and innovation. The most challenging priority is managing multiple priorities and interrelated work streams. Project management is a skill that should be developed in every sector.
- People
80% of managers see the need to create conditions for leading in an environment of ambiguity. 79% know the challenge of leading through change or transformation as a priority. A significant shift in how leaders approach people management is required to nurture team members and build the capacity to deal with challenges.
- Self
A well-developed ability to manage and improve your capacity is immensely valuable. Therefore, the most urgent focus areas are to build creative, problem-solving, and critical-thinking skills.
Understanding Generation Z in the workplace
A new generation brings a new outlook on work. Generation Z is already an undeniable force in shifting corporate culture. By 2025, Gen Z employees will account for 27% of the workforce, bringing their expectations and values. There may be an area where an existing employee’s opinions, ideas, and working patterns vary. So, there should be an area to bridge the gap between the experienced and Gen Z employees.
Bridging the Gap – Experienced vs. Generation Z
Today, younger generations are entering the workforce. At the same time, older employees remain in the workforce for longer due to economic necessity. In the workplace, the experienced and Generation Z employees may have noticed a few challenges and questions to the management while allocating them a task together:
- Do these coworkers have difficulty conversing with one another?
- Do they appear to have opposing processes and preferences for completing their work?
- Have their differences hampered their ability to generate complementary ideas and collaborate on projects from start to finish?
- Do they find it difficult to relate to customers of different generations and adapt to their expectations?
- Are they having trouble identifying common motivators for their team?

Challenging Questions For Experienced & Generation Z
But it might be better if the experienced employee tries to learn about Gen Z’s as they are thoroughly updated on technologies and adapted to hybrid working culture. Some aspects that may build the bond between experienced and Gen Z employees:
- Gather inputs from each other
- Live the culture
- Create opportunities for face-to-face interaction
- Facilitate frequent peer-to-peer recognition
- Form cross-generational teams
- Implement social technology for building relationships at work

Building Bonds Between Experienced & Gen Z Employees
The Skills Challenges of the Future Workforce
Technology, globalization, demographics, social values, and changing personal expectations of workforce participants are causing a dramatic change in the future of work and the workforce. As per The Future of the Workforce study, there are four significant workforce causes of disruption:
- Demographic upheaval
- Ever-present and changing digital technology
- An accelerated rate of change and business-model innovation
- The rise of a new social contract
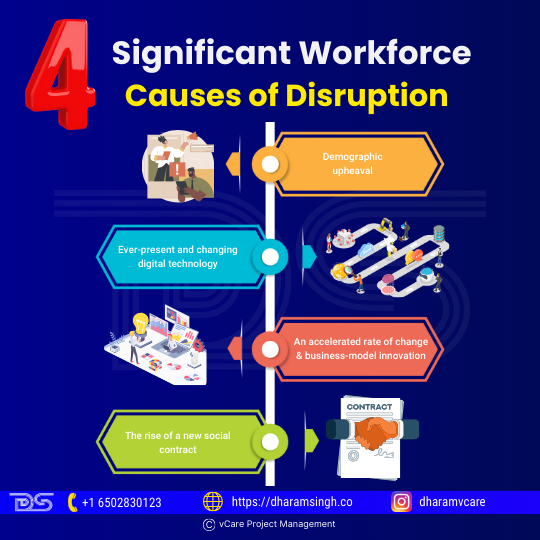
Significant Workforce Causes of Disruption
To survive the hypercompetitive, fast-paced future of work, an organization must be laced with strong interpersonal connections across a diverse workforce. In the aspect of a better workforce in the future, the employees need to necessitate the combination of four key work skills:
- Digital tools and technological abilities
- Good understanding of analytics and data
- Business management abilities
- Design and creative abilities

Key Work Skills to Survive
Get adapted to change
The projectification of work has rapidly shifted the nature of most professionals’ work, moving away from routine operations and decisively toward project leadership. In this new world, executives must answer three critical questions.
- Is your organization prepared to thrive in the project-based economy?
- Do professionals in your organization have the necessary adaptive mindset to carry out critical projects?
- Do your project managers have the business skills to prioritize competing workstreams and align with shifting business priorities?
The way forward
Great projects don’t just improve work; they improve the world. Key characteristics that leaders must possess to excel in a project-driven world:
- Project management skills
- Product development and subject matter expertise
- Strategy and business acumen
- Leadership and change management skills
- Agility and adaptability
- Ethics and values
Managers and organizations must become comfortable devising strategies driven by change rather than efficiency to transform themselves and thrive in the new project economy. They must delegate more resources, budgets, and decision-making authority to projects and project teams rather than the traditional departmental hierarchy. They will need to develop project management skills and adopt new technologies. Finally, they must encourage a shift in emphasis away from inputs and outputs and toward outcomes and value.

by DharamCW | May 29, 2024 | Program Management
Implication Of Organizational Capacity On Project Delivery | Justin Buckwalter | Dharam | Episode 17
Exploring the critical link between organizational capacity and project success, Episode 17 features insightful discussions on key aspects:
1. How does the scalability of organizational capacity influence project adaptability in dynamic business environments?
2. How can organizational capacity influence project risk assessment and mitigation plans?
3. What strategies enhance an organization’s capacity for handling simultaneous or complex projects, and what unique challenges differentiate managing these projects from others?
4. What challenges arise when scaling project delivery capabilities to meet increasing organizational demands?
5. Discuss the influence of stakeholder engagement and communication on leveraging organizational capacity for project success.
6. How does organizational capacity affect adaptability and responsiveness to changing project requirements or unexpected obstacles?
7. How can organizational capacity be measured and improved to optimize project delivery outcomes?
Stay informed and enhance your project management skills by delving into these crucial insights.
🚀 Seize the opportunity to Elevate Your Project Management Career:
– Register for my upcoming PMI Certification Success Story Webinars: https://bit.ly/4aVhrd6 / https://bit.ly/3QeVhKF
– Book an obligation-free consultation session on Project management Career, training, and certifications: http://talktodharam.com
– Discover training offers and certification discounts: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
– Stay updated with our Q&A series and certification success stories by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube channel at https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
– Follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd



























Recent Comments