
by admin | Mar 11, 2024 | Program Management
Join Precious Chikwata PMP®,MBA,PgMP®PgCert Cybersecurity and me for an insightful Q&A session as we explore the dynamics of cross-functional teams. Dive deep into the reality beyond the statistic that “75% of cross-functional teams are dysfunctional.” As seasoned Project/Program Managers, let’s discuss this figure, exchange experiences, and examine the essence of effective teamwork.
In this episode, we’ll also discuss how to navigate crises by building resilient networks of teams and the pivotal skills required for managing cross-functional teams and stakeholder expectations.
🔑 Highlights of the session include:
– Precious Chikwata’s personal PgMP journey
– Strategies to construct resilient teams during crises
– Debunking the myths of cross-functional team dysfunction
– Navigating stakeholder expectations within complex team structures
– Tactics to dismantle silos and enhance inter-team collaboration
– Resolving tough conflicts and extracting valuable lessons
– Essential skills for leading cross-functional teams as a Program Manager
– Managing expectations when program deadlines are at risk
– Utilizing PDUs effectively
– Tips for passing the exam
– Insights on rebounding from market challenges to secure your next role
Unlock these insights and enrich your knowledge by watching the full episode now: https://youtu.be/D3rzic6MbSg
🚀 Elevate Your Project Management Career:
– Register for my upcoming PgMP/PfMP Success Story Webinar: https://bit.ly/3ON2Ibl
– Book an obligation-free consultation session on Project management Career, training, and certifications: http://talktodharam.com
– Discover training offers and certification discounts: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
– Stay updated with our Q&A series and certification success stories by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube channel at https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
– Follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Feb 7, 2024 | Leadership in Project Management
Maximizing Success – Benefits of Building Stakeholder Relationships
In the realm of project, program, and portfolio management, forging robust stakeholder relationships is a cornerstone of success. I want to highlight why nurturing these connections is pivotal for organizational growth and individual career trajectories.
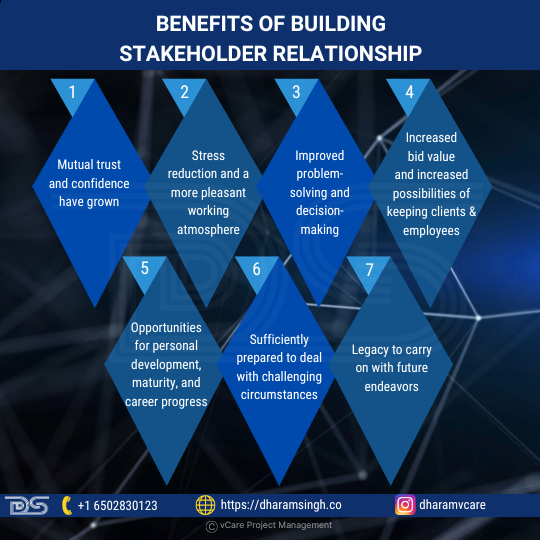
A strong stakeholder rapport yields:
– Enhanced trust and reciprocal confidence
– A harmonious work environment with less stress
– Sharpened problem-solving acumen
– Informed and agile decision-making processes
– Elevated bid values and client/employee retention rates
– Ample personal growth, paving the way for career advancement
– A resilient foundation for navigating complex challenges
– An enduring legacy that underpins future projects
Benefits of Building Stakeholder Relationships
Investing in stakeholder relationships is more than a strategy; it’s a commitment to cultivating a thriving ecosystem that benefits all parties involved.
Let’s embrace the journey of building stakeholder relationships that stand the test of time and change.
🚀 Elevate Your Project Management Career:
– Register for my upcoming PgMP/PfMP Success Story Webinar: https://bit.ly/3S53K3a
– Book an obligation-free consultation session on Project management Career, training, and certifications: http://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
– Discover training offers and certification discounts: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
– Stay updated with our Q&A series and certification success stories by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube channel at https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
– Follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Jul 24, 2023 | General
Delivering a successful project is challenging, especially when there are multiple stakeholders. However, even if a project is performed on time, on budget, and to the expected scope, it can still be regarded as a success only if the stakeholder expectations are managed appropriately.
Each project stakeholder has certain expectations. Project managers are at the forefront of potentially disastrous situations when such expectations conflict. They must address and resolve the issue or risk jeopardizing the project and their position. Because the fundamental cause of problems is only sometimes apparent, project leaders and teams must analyze links between issues and stakeholder motives using interpersonal skills such as resolving conflict, resistance to change, and trust building.

Project Stakeholders
Project Stakeholders
A stakeholder is an individual, group, or organization that is affected by the result of a business venture or project.
Stakeholder interactions may positively or negatively impact the project’s life cycle. Thus, a project leader must identify important stakeholders and develop a stakeholder management plan to satisfy their demands. Using project management tools and strategies to keep track of the key stakeholders is an excellent method to remain on top of things and ensure that project stakeholders remain satisfied and productive.

Types of Stakeholders
Internal Stakeholders
An internal stakeholder is somebody whose interest in the project is directly linked to their affiliation with the entity in charge. Internal stakeholders want the strategic and commercial goals of the project to be realized. They might be project managers, team members, sponsors, owners, or investors.
External Stakeholders
External stakeholders are not directly linked with the company but are important to the business or are influenced by the project in some way. Those are frequently supply chain participants, creditors, or public groups.
Stakeholder Management
The stakeholder management process includes communicating project status, expenses, and barriers to stakeholders to increase visibility, navigate changes in project direction, and manage expectations. Project stakeholders are those involved in the project or whose interests may be influenced by the project’s execution or completion.
Stakeholder management helps project managers keep change at the forefront of their thoughts while making it less intimidating. Furthermore, the stakeholder management plan is a reminder for every interaction the project managers have with direct or indirect stakeholders, helping them maintain a genuine link between the project and day-to-day operations.
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Means
An effective stakeholder management process ensures that timely and relevant feedback is provided, and that the stakeholder management strategy directs the change effort. The project manager maintains stakeholder expectations, resolves conflicts, and identifies and fixes any problems that develop throughout the project. In general, the following are the fundamental parts form the stakeholder management process:

The Necessary Elements For Successful Stakeholder Management
- Managing stakeholder expectations: The project is more likely to succeed when stakeholders’ expectations are actively managed. As a result, to ensure perfect conformance with project goals and expectations and to continue the project management effort, the project manager must continually negotiate and influence the demands of stakeholders.
- Managing stakeholder perception: It is critical for project success to ensure that stakeholders are involved in the project regularly and are kept up to date on the project’s progress. High-level stakeholder perception increases the likelihood that stakeholders will provide the necessary support and the project will be completed as intended.
- Keeping track of stakeholder activity: The project manager is primarily responsible for recording and tracking all stakeholders’ activity. As a result, to secure stakeholder acceptance and project communications plan adherence, the project manager should formally document all contacts with stakeholders and keep records of the project’s outcomes.
- Solving problems and resolving conflicts: To avoid challenges and conflicts, the project manager should address stakeholders’ concerns and identify risks and threats in collaboration with conflict management. By referring to change requests, the project manager can generate solutions.
Understanding the components of the managing stakeholder’s process enables the project manager to engage with stakeholder expectations and demands and build action plans to be used when disputes and challenges emerge. The project manager can utilize the following tools to assess conflicts and challenges, as well as manage stakeholders on an individual and group level:

Tools To Assess Conflicts And Challenges In Managing Stakeholder’s Process
- Issue logs: An issue log is a tool for assessing issues and documenting resolutions. It is a document with a rigid categories structure that allows each issue to be placed in the appropriate category (issue group). The project manager uses problem logs to ensure that each stakeholder understands the project and maintains positive working interactions among all stakeholders, including project team members.
- Change Logs: It is a tool for documenting any changes that occur throughout a project. The project manager uses change logs to track changes and their impact on project goals and deliverables. A change log should be provided to project stakeholders and should include data on changes to risks, uncertainties, costs, and budgets.
A change request for project deliverables may result from the technique for managing and engaging stakeholders. Changes to the stakeholder management approach and registry are also feasible. The method of managing stakeholders allows for evaluating and modifying stakeholder benefits created earlier in the project’s life cycle.
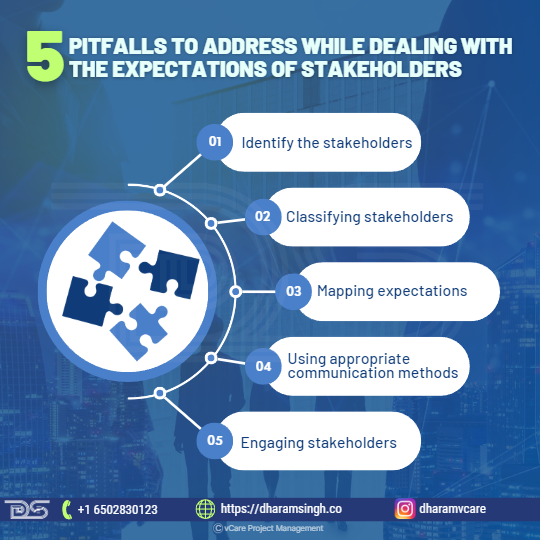
Five pitfalls to address while dealing with the expectations of stakeholders
5 Pitfalls To Address While Dealing With The Expectations Of Stakeholders
- Identify the stakeholders
A project often involves many stakeholders, and it can take time to identify all of them. A stakeholder is a person, a group, an organization, or a set of organizations that are actively involved in or may be affected by the project. Stakeholders can have an impact on a project in a variety of ways.
For example, if a stakeholder is top management in an organization and is not completely committed to a project, it may drastically limit buy-in throughout the business. Founders and C-suites are also stakeholders who can positively or negatively impact a project. Therefore, the identification of stakeholders is a critical step in managing expectations.
- Classifying stakeholders
Effective stakeholder management necessitates a project manager categorizing stakeholders based on their role in project completion. A project manager must determine which stakeholders are supporters and which may be obstacles to the project. It might be challenging to define the types of risks, where and when each risk exists, the impact on the project, or how to build strategies to handle possible risks if stakeholders cannot be classified.
- Mapping expectations
Project managers must resolve possible concerns, keep stakeholders involved and motivated, and finish the project on time. A project manager must have a good understanding of all stakeholders’ expectations. Stakeholder analysis and adequate documentation can be useful in mapping expectations. Stakeholders may have different priorities when completing tasks, milestones, or the full project. Their interests may be interpreted differently and have different definitions of success.
For example, one stakeholder may prioritize project completion on time, while another defines success as keeping it under budget. Mapping expectations and obtaining clarity among all stakeholders enhances the possibility that a project manager and their team can effectively complete a project.
- Using appropriate communication methods
Stakeholder management requires determining and implementing appropriate communication methods. To successfully manage stakeholder expectations, a project manager must establish the available and preferred communication mechanisms for stakeholders. A poor or incorrect communication approach can lead to distrust and dissatisfaction between stakeholders and a project manager. It is also essential to adjust communication tactics and frequency based on elements such as time, message, purpose, secrecy, or changes based on stakeholder contexts.
- Engaging stakeholders
Stakeholder engagement during the project with frequent updates boosts stakeholder confidence, which is essential for project success. In addition, efficient stakeholder management necessitates the involvement of stakeholders in decision-making by the project manager.
Although a project manager may believe they have already determined the optimal course of action, they should incorporate stakeholders in procedures and pertinent talks to ensure all options have been examined; otherwise, key possibilities and expectations may be missed.
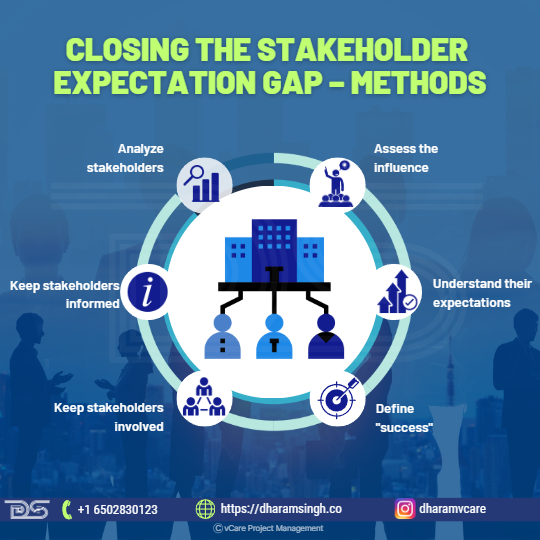
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Methods
Before beginning a new project, start by identifying all stakeholders. First, identify those impacted by the project and the organizations that will influence the project. Then, using the strategy outlined below, begin developing strong relationships with each stakeholder.
Closing the Stakeholder Expectation Gap – Methods
- Analyze stakeholders
Conduct a stakeholder analysis or an evaluation of the key participants in a project and how the initiative will affect their issues and requirements. Determine their unique qualities and interests. Find out what motivates them and what frustrates them. Define responsibilities and levels of engagement, and assess whether there are any disputes among stakeholders.
- Assess the influence
Determine the extent to which stakeholders can have an impact on the project. The more powerful a stakeholder is, the more a project manager will require assistance. When evaluating stakeholders, consider the question, “What’s in it for them?” Knowing what each stakeholder needs or desires from the project allows the project manager to measure their degree of support. Remember to weigh support against influence, like Is it more necessary to have strong support from a low-level stakeholder or moderate support from a high-level stakeholder?
- Understand their expectations
Determine the exact expectations of stakeholders. Then, when necessary, seek clarification to ensure they are thoroughly understood.
- Define “success”
Every stakeholder may have a distinct definition of project success. Discovering this towards the end of the project is a potential disaster. Instead, gather definitions and integrate them into the objectives to guarantee that all stakeholders support the final results.
- Keep stakeholders involved
- Don’t just provide updates to stakeholders.
- Solicit their opinions.
- Schedule time for brief meetings to get to know them better.
- Determine each stakeholder’s ability to engage while keeping time restrictions in mind.
- Keep stakeholders informed
- Send regular status updates.
- One update each week is generally adequate.
- Hold project meetings as appropriate, but allow enough time between them.
- Respond to stakeholders’ inquiries and emails as soon as possible.
- Regular contact is usually valued – and may help ease the impact when you have unpleasant news to deliver.
These are some of the fundamentals of developing effective stakeholder connections. However, like with any relationship, there are subtleties that every effective project manager knows, such as understanding the distinctions and responding successfully to various types of stakeholders.
Final Thoughts
There is a link between resolving conflicts in stakeholder expectations and project success. Similarly, the faster project teams defuse a potentially dangerous situation by recognizing the source of conflicts, the link between issues, and the motivations of stakeholders, the simpler it is to develop trust, settle conflicts, and overcome resistance to change.
Using diverse modes of communication between the project team, senior management, and stakeholders improves prospects for mutual understanding. These methods may help the project managers to meet the stakeholder expectations and reduce the risk of project disaster.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by admin | Jul 19, 2023 | General
Project management is a fulfilling career choice that may offer competitive pay and a wide range of job opportunities. As a result, project managers are constantly in demand: Qualified individuals are always needed to plan and provide work in every business.
Over the next ten years, demand for project managers is one of the roles which will expand faster than the need for workers in other roles. But on the other hand, organizations may face risks due to the talent gap.
Understanding PMOE
Projects are becoming an increasingly important component of business completion. The acceleration of business evolution, increasing emphasis on digital transformation, and ever-changing consumer expectations and competitor offers are here to stay. As a result, project management skills and talents are becoming increasingly important in organizations.
Organizations will not invest in training the people in those positions to accomplish that work if those roles are not recognized as contributing to project management. As a result, they will not foster an environment where employees may develop experience, and they will eventually find themselves unable to sustain the number of projects that must be delivered.
One of the reasons that technical roles are considered part of PMOE is the growing adoption of agile ways to deliver work. However, many organizations still see agile as a ‘project management free’ delivery method, where the self-organized nature of agile teams eliminates the need for project management. But, again, this thinking must change if there is any hope of closing the skills gap.
Organizations must assess their skill profiles for all roles and determine if project management competencies should be included. Even roles that do not entail daily project delivery or where employees are more frequent contributors than leaders are likely to benefit from project management skills and experience. Unless that is ‘built in’ to job profiles, hiring and development methods will remain the same, and the shortage will remain unaddressed.
Talent Gap Report 2021
Successful projects are a significant contributor to global economic growth. As more industries become projectized, the demand for qualified project managers will likely rise over the next decade.

The Talent Gap Report 2021
The Talent Gap Report 2021 has been released by the Project Management Institute. The headline is the scarcity of qualified candidates for project management-oriented employment (PMOE). As a result, around 25 million more employees will be required by 2030 than in 2019. To put this in context, there were 90 million workers in those positions in 2019, implying a 30% increase.
Simultaneously, 13 million existing project management-oriented employees will retire, with the vast majority nearing the top of the experience curve. This phenomenon implies that enterprises will lose significant knowledge and skill. And this will happen when they increase the need for that experience by introducing a large number of new project-related staff who must progress quickly. In developed economies, on the other hand, retirement is the primary source of job possibilities for younger workers.
The report’s most critical statement comes near the end: “Global demand for project management expertise is unlikely to be addressed by 2030 unless firms encourage a culture of continuous learning.” As a result, firms confront a huge growth in PMOE roles and an inability to address that requirement based on current business processes.
Addressing challenges of this magnitude demands a strategic approach backed by financial commitments and constant responsibility for performance. In some circumstances, it may also necessitate a transformation in how leaders understand their companies and roles.

3 Reasons For The Project management Talent Gap
Why and where is the Talent Gap?
There are three reasons for the project management talent gap:
- The number of positions requiring project management skills is increasing.
- Project managers are in high demand in emerging and developing companies.
- Project managers are retiring faster than young talent can replace them.
Upskill the people
Unless firms foster a culture of continuous learning, the worldwide need for project management skills is unlikely to be met by 2030. The most resilient firms will prioritize reimagined employee capability-building.
According to a McKinsey report, over 80% of business leaders consider skill building to be “very” or “very” vital to their organization’s growth, up from 59% before the pandemic. As a result, organizations will need to support new learning initiatives and seek partnerships to equip employees with the appropriate project management skills to develop their talent. These talents include power skills like teamwork and leadership; business acumen to develop well-rounded employees; and mastering new methods of working, such as growing use of tech-enhanced problem-solving tools.
Gaining a Competitive Advantage in the Talent Acquisition Race: The Front-Runners
According to PMI and PwC study, a cohort of 250 organizations face fewer challenges in attracting and retaining talent than their counterparts. Their project management offices (PMOs) are better connected with corporate strategy—three quarters have a C-suite presence, and 90% are seen as strategic partners by their executive leaders. As a result, they have an easier time recruiting people with important project skills. They are more successful at developing project managers. They are also twice as likely to have outperformed in revenue growth, customer acquisition, customer happiness, and environmental, sustainability, and governance (ESG) indicators.
Facilitating project-based organizations
The concept of stable operations is unlikely to exist at any scale by 2030, which is one of the most important factors driving the demand for more individuals in PMOE roles. The rapid growth of technology has resulted in much shorter lifecycles for both customer-facing and internal solutions. This trend is expected to continue as digital transformations drive organizations to the point where technology is vital in managing every business area.
Future of project management
Project management is being massively disrupted by management technology. As a result, forward-thinking professionals are questioning how to effectively prepare for the upcoming tidal wave of change caused by technological innovation.
Here are four skills that project managers of the future might need:
- Data Science
- Conflict resolution
- Entrepreneurship
- Resource management
Project Management’s Future in the Age of Advanced Technology
Because of emerging trends such as remote teams, digitalization, and automation, project management has changed dramatically in recent years. As a result, companies now rely significantly on technology to plan, execute, and monitor work. As an example:
- Big data and artificial intelligence for better risk forecasting
- Remote progress tracking using digitization technologies
- Automation software for more efficient execution
These innovations have improved firms’ management capacities and altered project management’s future. According to Gartner research, 80% of management duties will be automated by 2030, and future managers will need more technological abilities. They must be knowledgeable about cybersecurity, blockchains, machine learning, and robots, all of which are expected to play larger roles in management.
Future Trends of Project Management
Consider project management ten years ago: fewer tools, smaller teams, and more straightforward tasks. Since then, the project landscape has changed dramatically, with major trends such as:
- Blockchain
- Artificial intelligence
- Sustainability
- Remote teams

Future Trends of Project Management
Trend 1 – Blockchain
More companies use blockchain technologies for management, such as when conducting dispute investigations. The capacity of blockchain to automatically update data makes it ideal for reconciling records and transactions. One of the most significant contributions of blockchain to project management will be smart contracts, which are effectively self-executing contracts powered by computer code.
Smart contracts reduce the number of key functions within the project manager’s scope, such as checking on project milestones and assigning new ones, which speeds up management processes. As a result, quicker workflow assures project completion on time and improves a company’s overall performance.
Trend 2 – Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence quickly infiltrates project management systems, handling anything from predictive analysis to risk management. Because of its efficacy, AI is expected to contribute:
- $42.7 B (7.7%) to Egypt’s economy
- $135.2 B (12.4%) to Saudi Arabia’s economy
- $96.3 B (13.6%) to the UAE economy
The primary capacity of AI is to provide data insights for decision-making, which increases the agility of any given project. For example, assume a manager considers which product features to include; AI finds correlations and patterns in consumer data and then recommends which product features are more likely to sell. Such insights improve an organization’s competitiveness by avoiding commitment to poorly planned, hazardous ventures.
Trend 3 – Sustainability
Today, project sustainability is more crucial than ever. Governments and societies all around the world are demanding greener approaches throughout the life cycle of a project.
Green initiatives are cost-cutting methods from a business standpoint. For example, energy is required for project execution, and shifting to renewable sources reduces costs. In addition, this frees up resources for other essential areas, such as innovation and research. Meanwhile, sustainable practices improve a company’s brand and foster consumer loyalty.
Trend 4 – Remote Teams
Remote teams have been the norm since the advent of communication technology. As a result, businesses gain from a more diverse and borderless talent pool easily available through contracts. In addition, they spend less on office space, travel, and other administrative expenses.
As a result, it’s not unexpected that 65% of workers anticipate that workplaces will become entirely virtual over the next several years. In general, remote working arrangements enable businesses to extend their resources while increasing operational efficiency. As such, they are crucial in developing lean, competitive firms.
Skills Future Project Professionals Need
To stay up with modern project management trends, a fundamental understanding of ideas such as data science, conflict resolution, and entrepreneurship is required. For example, understanding data science may assist a manager in incorporating AI into more elements of the project life cycle.
Here’s a closer look at what these talents comprise and how they’ll stay up with future project management improvements.

4 Skills Future Project Professionals Need
Skill 1 – Data Science
Big data insights are essential management tools, particularly for large projects with extensive life cycles. Insights from previous projects show inefficiencies that guide the current project, such as the number of slack hours and their causes. Data analysis assesses progress and uncovers deviations early, such as changes in material costs and currency rates that exceed expectations. As a result, project managers must comprehend topics such as statistical inference and regression analysis.
Skill 2 – Conflict Resolution
Today’s projects are extremely complicated, with constantly changing deliverables. As a result, conflicts are never far away. These issues, if left unaddressed, can undermine the team’s performance, resulting in delays and missed deliverables. Managers must thus grasp the various aspects of conflict resolution, such as:
- A conducive work environment’s behavioral and organizational components
- Effective communication
- Effective contingency planning
Skill 3 – Entrepreneurship
Project managers are, in essence, CEOs. On the one hand, they manage project deliverables. Yet, simultaneously, they negotiate with shareholders and set goals based on estimates. As a result, being effective requires more than technical and administrative skills.
Entrepreneurial skills, such as strategic thinking and market insight, are also required of project leaders. Such skills are especially important when modifying deliverables, typical in agile projects like software development.
Skill 4 – Resource Management
Budgets and timeframes became tighter as projects became larger and more complicated. Today’s project managers must balance budgetary constraints, quality delivery, and achieving deadlines with limited resources. They are entrusted with creating a lean organization.
For optimal efficacy, a precise balance of resource allocation is required, as over-allocation to one activity inhibits the others. As a result, managers must understand resource management principles such as equilibrium shifts and flexibility.
Bridging the talent gap
The PMI Talent Gap report delves into a decade’s worth of project management-related job trends, costs, and global implications. PMI has completed its most recent study of the “projectized” businesses that leverage these talents better to understand talent and employment trends in project management. Using data from selected areas, the PMI Talent Gap report provides a birds-eye perspective of the most in-demand talents and the magnitude of the talent shortfall.
PMI data shows a continuing gap between the global demand for project management skills and talent availability. This data translates into many new career prospects in PMOE for job-seeking project professionals. However, the skill shortage is a significant issue for firms that rely on project leaders and changemakers. For example, by 2030, this skill gap is anticipated to affect every area, resulting in a potential global GDP loss of up to US$345.5 billion.
Here is a summary of the top three reasons for the skill gap, as identified by PMI research and explained in the report:
- An increase in the number of professions that need project management expertise.
- Economic growth drives demand for project managers in emerging and developing countries.
- The rate of labor-force retirement
Final Thoughts
Project management has a bright future. There is still a high demand for change agents. PM will transition from being viewed as an administrative function by some executives to the strategic partnership that it has the potential to be in every organization, not just those enlightened businesses with high levels of program management maturity.
For many years, the skills of project managers have migrated toward “soft” skills. However, given how the future of work is shaping, this will become much more important. Project managers will need to be team players. As a result, we’ll need to interact with people who have the skills that the technical companion lacks:

Skills That The Technical Companion Lacks
- Empathy
- Strategic thinking
- Fun
- Creativity
- Motivation and persuasion
- Thoughtful customer service
- Listening
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Apr 21, 2023 | General
What makes a successful Project/Program/Portfolio Manager? Is it the number of years of experience? Technical know-how? Or the one who is good at managing people?
Creating objectives, critical path analysis, work breakdown structures, resource scheduling, and risk management are just a few of the technical areas of project management that project managers usually get training in. However, understanding pertinent people and management issues is important to a project’s success. In addition, a project manager must also continually deal with clients and other stakeholders. As a result, project managers’ people skills, also known as soft skills, are becoming increasingly important.

People Skills
People skills
People skills are linked with behavioral patterns or behavioral interactions that assist one in communicating effectively with people. Project leaders with strong people skills may favorably influence others, socialize effortlessly, and overcome public anxiety.

Project Leaders With Strong People Skills
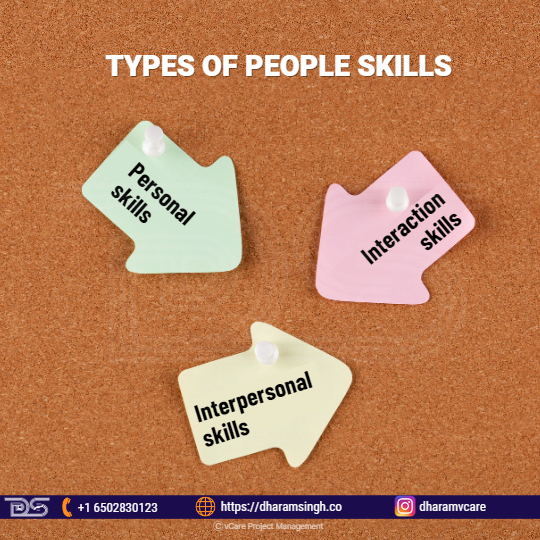
They are transferrable social abilities that allow one to collaborate well with others. The three main types are personal, interaction, and interpersonal skills. These categories achieve the same overall objective: making the working connections with others mutually satisfying, pleasant, and productive.
Types Of People Skills
Types of People Skills
- Personal skills: These include the capacity to communicate your skills and exhibit yourself to others successfully. It comprises characteristics such as self-assurance, honesty, and aggressiveness. Furthermore, one must be able to recognize their limitations and make sound judgments based on logic rather than emotion.

Personal Skills
- Interaction skills: It is essential for understanding the behavior and ideas of others while preserving limits and creating connections. A project manager, for example, should have social etiquettes that need empathy and listening skills to know that you have listened to them and given respect for their limits and requirements to connect with co-workers and clients productively.

Interaction Skills
- Interpersonal skills: These are related to intercession skills, but they apply mainly to situations in which the persons involved have opposing interests or viewpoints.
Contrary to popular belief, people skills are not subjective concepts. On the contrary, these skills are critical, particularly in the project management role, which is largely concerned with people.

Interpersonal Skills
Project management is more than just completing the project; it is also about how you lead and assist your team. Leading others and leading them through the whole project lifecycle entails a certain amount of responsibility and necessitates certain abilities.
Furthermore, as work evolves, businesses embrace a varied workforce. As a result, people skills are essential for embracing tolerance and diversity. In short, good project management is based on human communication and connection.
Essential People Skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers
A successful project professional must possess a wide range of skills. Those that come to mind first are the technical skills required to create a project plan, schedule, budget, and all relevant paperwork. One must also have the conceptual skills to “see” the project as it develops.
However, such talents will only assure project success if the project manager can supplement their technical skills with a wide range of interpersonal skills or people skills. Here are some of the essential people skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers:
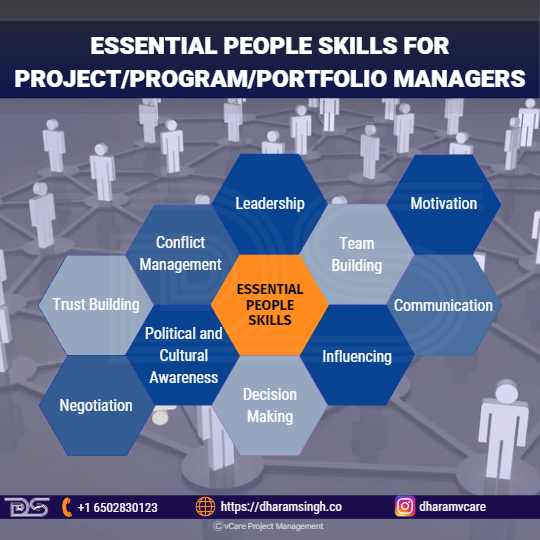
Essential People Skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers
- Leadership
One of the crucial skills a successful project manager has to have is leadership. This skill is essential because the project manager frequently has little control over the team members involved. This aspect calls for leadership on their part to handle the project. Although managing via leadership rather than authority might be more challenging, it is typically more effective since it is based on respect and trust.
At the start of a project, a leader must establish their vision and express it to the team. It makes supporting the project’s objectives easier for everyone on the team. Effective leadership will also keep the team members inspired and motivated to perform at their highest level.
- Team Building
Another vital skill for a competent project manager is team building. Because of the nature of projects, personnel from diverse departments are engaged. Most employees might have never worked together and may not even be familiar with one other’s departments. If the project manager can unite these individuals into a cohesive team with the same goal, the project may stay within its objectives.
Although some of the project’s individuals or sub-teams may execute their jobs individually, they must feel like they are part of the overall team. When choosing their part of the project, they must consider what is best for the project, not simply what is best for them and their departmental problem. A sense of belonging to a team that solves an issue for the entire company (rather than playing departmental favoritism) may go a long way.
Creating a team in which each member feels comfortable reaching out to the others will also guarantee that minor problems do not escalate into major concerns later in the project. It is consequently critical that project managers not only understand the duties and procedures involved in team building but also have the skill and finesse to apply them correctly.
- Motivation
If you want your project to succeed, you should concentrate on improving your motivating skills. Having these qualities will assist your project team members to stay interested in the project, strive for excellence, and work toward a common objective.
Good motivating skills will enable a project leader to create an environment where team members can fulfill project objectives while being satisfied with their work.
- Communication
Most professions require excellent communication skills. Some project managers believe the communication part of project management to be their primary job obligation.
Excellent communication skills are essential for building relationships among project team members, establishing trust, and keeping everyone motivated and on track.
A project involves several stakeholders informed of its status, timeframes, progress, risks, and concerns. A skilled project leader must convey all of these facts to project stakeholders on time and in the manner they anticipate. Project managers must also interact effectively with top management within their business.
Giving the interested stakeholders too much or not enough information might prevent the project from reaching its full potential.
- Influencing
It is critical to be able to influence people if you want to be a successful project manager. But what is important is understanding when and how to utilize such skills and avoid becoming a manipulator. There is a narrow path to follow.
A project manager’s responsibility is to bring employees from disparate departments together and get them to work together toward a similar objective. Sometimes, getting these diverse people to comprehend and agree on the specifics of achieving that goal might not be easy. A skilled project leader will utilize their skills to persuade others and assist them in reaching an agreement.
So, think about your relationship and influence over people not just for the time of the project but also for how things will proceed long after the project is complete. After the project, customers and end-users will utilize the goods, deliverables, and outcomes developed by the project. A powerful and positive effect creates a trusting atmosphere among all team members during and even after the project.
- Decision Making
A successful project manager must acquire various talents, one of which is decision-making skills. There are four primary decision-making styles: Directive, Analytical, Conceptual, and Behavioral. Project managers should be conversant with all four since either has to be leveraged at some time. In addition, consultation, consensus, command, and random styles are provided.
Having a decision-making model will facilitate this process. In addition, since so many people who may disagree with a decision are involved in the project, having a process to follow can be very helpful in gaining consensus with the group.
- Political and Cultural Awareness
In today’s world, project managers work in a more globalized context than in the past. As a result, cultural diversity is another critical component of effectively navigating the corporate world as a project leader. A successful project manager must be able to notice and comprehend cultural differences and incorporate them into the project plan.
Cultural differences can impact decision-making and the pace with which work is performed. It can also lead to members acting without sufficient forethought. Recognizing cultural differences can lead to conflict and stress within the project, further delaying it.
Furthermore, it is critical to understand the politics at work in the project environment. The use of political skills can greatly aid a project manager’s success. More significantly, failing to recognize the politics involved can lead to substantial challenges and impediments that can cause a project to be delayed or even destroyed.
- Negotiation
The nature of a project manager’s work necessitates being skilled negotiators. Typically, several stakeholders are involved in the project, and most projects include team members from many departments. This aspect frequently leads to a variety of points of view, which can make it challenging to keep the project on track and within the intended scope.
Negotiation skills can assist a project manager in obtaining an agreement or making a compromise on an issue that may be causing difficulty or delay.
There are several negotiation skills that the project leader should be able to employ. These include assessing each scenario, being an engaged listener, and communicating coherently throughout the dialogue. It can be important to distinguish between the wants and requirements of the people concerned. Another critical focus is recognizing the distinction between people’s perspectives and their interests and concerns directly relevant to the project.
- Trust Building
When collaborating on a project, trust is really valuable. A trusting environment promotes effective relationships and communication among team members and stakeholders. Therefore, a project leader wants to foster an atmosphere of mutual trust. This trust helps to maintain morale, keep conflict at a minimum, and keep everyone working effectively together.
If you were working on a project, you would want everyone participating and working hard to see it through to completion. When you work hard, you expect that others are also working hard to achieve the project objectives. The team leader wants to trust a team member who suggests they can execute a task properly and on time. If someone in the team wants assistance, they want a team that will support and collaborate to achieve the work. So don’t waste time second-guessing someone who isn’t telling the truth or has bad motives.
There are several approaches for a project manager to establish trust. First, a project leader must be a great and open communicator to reduce misunderstandings and build confidence among team members. Often, one may have to put their self-interests aside for the team’s sake and must model and display the behavior they demand from others.
- Conflict Management
On a project, conflict is almost unavoidable. Members of the project team and stakeholders may have differing perspectives, areas of expertise, interests, personalities, work styles, and so on. When one adds additional factors to the mix, such as tight deadlines, resource limits, and communication challenges, it’s easy to understand how conflict might arise.
Conflict often leads to a better solution to a problem. For example, if a team member would prefer to agree or accept the status quo, then risk causing conflict by pointing out a problem, asking a question, or suggesting an improvement. In that case, it is simpler to accept a suboptimal solution. However, disagreement frequently stops the team from working successfully together and diverts attention away from the duties at hand.
The goal is to prevent conflict or its escalation or to know how to regulate or lessen it when it arises if they cannot avoid it. For example, a project manager may use several tactics or methods when dealing with a dispute. They can be aggressive, accommodating, avoiding, or compromising. Some approaches work better in particular situations than others.
The project manager and team members involved in the conflict influence the team’s efficacy. A project manager can also utilize many approaches; if one fails, they may have to try another to see if it is more successful.
Why are people skills important?
People skills are crucial because it is much more difficult for people in an organization to work together to achieve common goals if they fail to express themselves or understand how their co-workers feel about a certain project, task, or difficulty.
As a result, the organization’s production and profitability suffer while creativity and innovation endure. People skills, in particular, may assist us in the following:

Why Are People Skills Important?
- Avoid misunderstandings: People are less likely to misinterpret what you’re saying if you communicate ideas and instructions.
- Win support: If you can communicate effectively and understand what your team wants to hear, it will be much simpler to persuade them and get them “on board.”
- Improve customer support: You’ll be better positioned to fix their difficulties if you can get inside their minds and comprehend their key problems.
- Solve conflicts: Conflict isn’t always unpleasant, but if it goes unresolved, it can harm morale and productivity. Strong people skills allow us to see things from a new perspective and identify similarities, which reduces the likelihood of significant conflicts.
How to develop people skills?
Even while people skills are critical, they are frequently undervalued by employers when it comes to job advancement. Internal training sessions are frequently centered on teaching hard skills, such as completing a given activity or utilizing a specific piece of software. These methods make it more difficult for professionals to build their interpersonal skills.
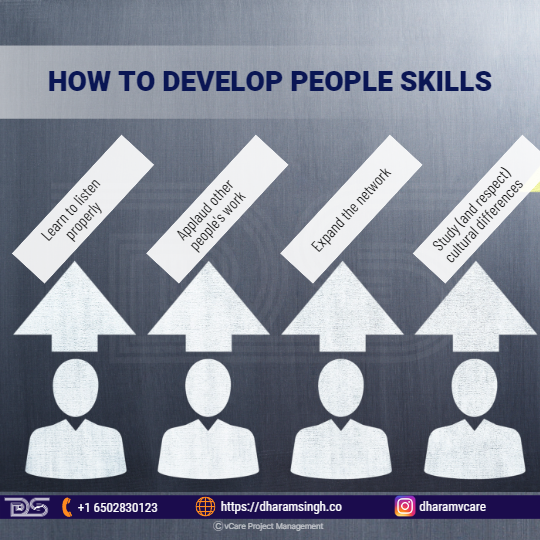
How To Develop People Skills?
But just because something is more difficult does not make it impossible. Here are four suggestions for improving people skills and becoming a more attractive prospect are:
- Learn to listen properly
- Applaud other people’s work
- Expand the network
- Study (and respect) cultural differences
Final Thoughts
Effective project management is challenging but having people skills may help project leaders run projects more efficiently and with less stress. Furthermore, it enables building a team that can handle the most challenging tasks and is more successful and resilient during difficult times.
People skills, on their own, will not keep a project team motivated and engaged. However, arming oneself with the necessary technical skills and intelligent tools may dramatically enhance the workflow and contribute to the project’s success.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd































Recent Comments