
by Dharam CW2 | Oct 13, 2023 | General
Organizations may stay profitable and competitive using project management practices that help identify process improvements or cost-cutting opportunities. Metrics may assist in discovering areas for improvement, data to focus on, and how to quantify the success and efficacy of a company’s efforts. Knowing more about project management metrics that can assess performance will help one acquire professional skills for any business and advance their career in project management.
Every organization needs to ask,
- “Are we getting the outcomes we want?”
- “Are we accomplishing our project objectives?”
- “Are we meeting the requirements for customer success?”
- “Are we getting the intended return on investment?”

Project Management Metrics May Assist
Success depends on the ability to forecast and meet product and service commitments. With projects becoming more common, it is critical to show additional value to the business using project management strategies, tools, and procedures. Therefore, a metrics program is required. Metrics may assist in identifying significant events and trends, distinguishing between challenges and opportunities, and guiding companies to make wise decisions.
How can we know whether the project management efforts make a difference and contribute to corporate success?
- It has long been known that suitable measuring methods are essential to basic management tasks, including project planning, monitoring, and control, and metrics are present at all stages of project management.
- As project management grows prominence and more firms embrace a project-based management approach, objective and performance-based management highly depend on measurement processes.
- To assist decision-making, project selection, portfolio management, and lead product and process improvement, metrics must be integrated into project life-cycle activities.
- In addition, metrics may be used to assess an organization’s project management maturity.
- Metrics aid in understanding capacities, allowing for developing strategies based on creating and delivering goods and services. They also enable people to recognize significant events and patterns and distinguish between challenges and opportunities.
- Metrics can assist in improved cost and schedule management, decrease risks, increase quality, and guarantee that objectives are met.
Measuring is an end goal in some businesses. Individuals in such businesses who have obtained project management certification and use specific project management tools and processes are the ones who often recognize the significance of project management. At the same time, individuals at the top may only accept this value partially. A metrics practice put in place is one of the best methods for successfully explaining the benefits of project management to top executives.
What are Project Management Metrics
What are Project Management Metrics?
Project management metrics are data sets, algorithms, and calculations that allow businesses to assess the performance of a project. They assist managers and organizations in reviewing how a project progresses, evaluating team productivity, project completion deadlines, and costs, and identifying, reducing, or eliminating risks. Project management metrics are numerical instruments that firms use to build successful strategies, carry out continuous improvement initiatives, and assess employee and customer sentiment.
Benefits of using metrics in project management
Project management metrics are an efficient approach to assessing a project’s progress. Measuring the project’s performance against key parameters helps to understand the management process. These indicators in project management also assist in steering project objectives, allowing teams to assess success and make improvements as needed.
Following and evaluating the right indications can provide the company with critical insights regarding the team’s performance – from both a high-level and individual standpoint. In addition, you’ll be able to identify process bottlenecks and other inefficiencies, which one can subsequently fix, adding to the project assumptions list and enhancing future project performance.
Furthermore, tracking and collecting this sort of data might be useful when the time comes for the project management performance review. Taking responsibility for the team’s work by analyzing project outcomes, identifying inefficiencies, and developing improvement plans sends a strong message to management. It displays that one can be a real leader committed to the business’s success.

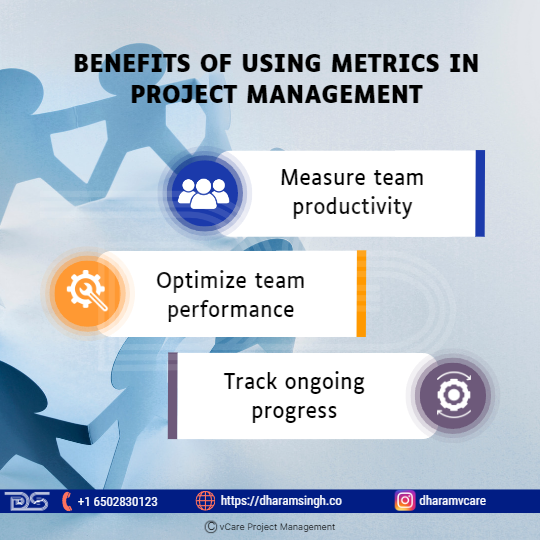
Benefits of Using Metrics in Project Management
- Measure team productivity
Relevant metrics in project management can reflect a team’s productivity. For example, the on-time delivery (OTD) rate or service level agreement (SLA) rate might be used to calculate the project’s ROI.
- Optimize team performance
While it is critical to maintain the team’s performance, forward-thinking management seeks development opportunities. Relevant project metrics enable one to broaden their understanding of project-related aspects. Project performance measurement reduces uncertainty and allows individuals to make better, more informed decisions.
- Track ongoing progress
Management performance metrics also track a project’s progress over time. These metrics are critical to discover obstacles early and help adjust the track as needed.
Project Management Metrics: How to Measure and Track Success
Relevant project management metrics will help enhance our understanding by eliminating uncertainty and making well-informed decisions.
Metrics prove value
Cost-related project management indicators may demonstrate the value of a team—for example, a rate of on-time delivery or a rate of satisfying SLA. Return on Investment (ROI) is a popular statistic for demonstrating this value. If a department fails to generate or contribute to a firm’s measurable objectives, a smart business would dissolve the department and redirect resources to another area that provides results.
How to choose the Metrics
Metrics improve performance
While demonstrating value is crucial, forward-thinking management prioritizes performance improvement. Relevant metrics help you have a better grasp of project management. This aspect reduces ambiguity, allowing all parties involved to make informed decisions. For example, assume that the given slack time is causing the completion of the following task to be delayed. You can adjust the slack time to keep the project deadline.
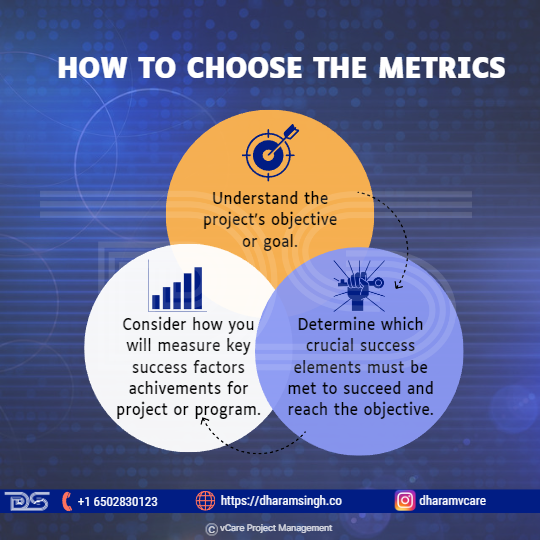
How to choose the metrics?
Each business or project requires metrics specific to its purpose or aim. Metrics are determined in three steps:
- Understand the project’s objective or goal.
- Determine which crucial success elements must be met to succeed and reach the objective.
- Consider how you will measure the achievement of each key success factor for the project or program.

What makes a successful project?
What makes a successful project?
Before starting any project, you and your team should know what constitutes a successful project. After all, you want to avoid being known for a famous failed project. So what makes a project successful? First, you should establish a set of success criteria for your project, including the following:
- Delivers on time: Completing a project on schedule and under budget is one measure of success, especially for external parties, such as clients.
- Stays within budget: A budget is in place for all initiatives. You will have succeeded if you can finish yours without incurring more fees and expenses.
- Achieves its objectives: If your project was completed and met its objectives — as stated at the outset — that’s a huge accomplishment.
- Gets positive feedback: Assessing a project’s internal and external success is simple. But how did it fare? If stakeholders and clients offer positive feedback, the project will be considered a success.
Key Project management metrics
Project management metrics may be established based on the purpose and complexity of the project. However, the ten key project metrics listed below often cover the most important measurements:

Key Project management metrics
- Productivity
This indicator examines a company’s total skills — how well it uses its resources. Productivity demonstrates the connection between inputs and outcomes. For example, how much do you get out of a project after your efforts? The optimal productivity outcome is to produce more with less.
Productivity = Units of Input/Units of Output
- Gross Profit Margin
Numbers are more powerful than words. Indicators directly related to the bottom line indicate success or failure faster than other metrics.
The larger the profit margin, the better the business. Any program or effort done should add to a company’s financial profit. The margin is the proportion of each dollar generated after expenses are deducted.
Gross Profit Margin = (Total Profit-Total Costs)/100
- Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on investment especially considers the dollar amount earned for the amount spent on a project. This metric is a financial calculation similar to gross margin. However, instead of focusing on a total profit, it considers the specific benefit of the project divided by the costs.
To use this metric, a dollar value must be assigned to each unit of data to calculate the net benefits, which may include:
- Contribution to profit
- Cost savings
- Increased output
Costs may include resources, labor, training, and overhead.
ROI = (Net Benefits/Costs) x 100
- Earned Value
Earned value provides strategic guidance by displaying how much you have derived from the money invested in a project to date. It compares the value of work performed by a given date to the project’s approved budget.
Earned value is often called the Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP). This statistic serves as a reality check during the project’s execution.
Earned Value (EV) = % of Completed Work / Budget at Completion (BAC)
- Customer Satisfaction
A customer satisfaction score is a quality indicator for your service or product—the findings of a customer survey influence this metric. In addition, the product or service should perform as intended and meet genuine client demands.
Each organization may create a unique score by weighing each component depending on its value. Customer survey results, money earned from clients, repeat or lost clients, and complaints are examples of variables.
The Customer Satisfaction Index (CSI) is the most extensively used metric for customer satisfaction. Another technique for measuring customer satisfaction is the Net Promoter Score (NPS). NPS measures customer loyalty by determining the chance of a consumer suggesting a product or service.
Customer Satisfaction Score = (Total Survey Point Score / Total Questions) x 100
- Employee Satisfaction Score
Survey data determines employee satisfaction in the same way that customer satisfaction is. So why should workers be included while evaluating project management? The answer is straightforward: employee morale is directly related to project performance.
In the end, a satisfied employee does better work and more efficiently. In addition, the high costs of employee turnover for a firm — which may range from 50% to 200% of an employee’s salary — should be motivation enough to focus on the people closest to the project.
The Gallup Q12 Employee Engagement Survey is a well-known data collection tool. An ESI procedure yields an index score.
Employee Satisfaction Score = (Total Survey Point Score / Total Questions) x 100
- Actual Cost
The Actual cost is a simple statistic that displays how much money is spent on a project rather than simply an estimate. This cost is calculated by adding all the expenses for a specific project across the timeline.
Actual Cost (AC) = Total Costs per Time Period x Time Period
- Cost Variance
Cost variance describes the difference between the intended budget and actual expenses during a given time period. Is the estimate higher or lower than the actual costs?
- A project is over budgetif the cost variance is negative.
- A project is under budgetif the cost variance is positive(a standard measure of success).
Cost Variance (CV) = Budgeted Cost of Work – Actual Cost of Work
- Schedule Variance
The schedule variance examines both budgeted and scheduled work. Is the project running ahead of or behind schedule?
The schedule variance is the difference between work scheduled and work accomplished, calculated as the budgeted cost of work executed minus the budgeted cost of work scheduled. A negative schedule variance indicates that the project is running late.
Schedule Variance (SV) = Budgeted Cost of Work Performed – Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled
- Cost Performance
Cost performance is a cost efficiency metric. Divide the value of the work performed (earned value) by the actual costs incurred to get the earned value. Forecasting cost performance provides for more precise budget estimates.
Cost Performance Index (CPI) = Earned Value / Actual Costs
Implementing Project Metrics
Once project metrics have been established to meet the company’s goals, it’s time to apply them. First, interact with users to help them understand the process, its value, and how analytics may enhance projects. Then, provide specific examples, such as “the dashboard will indicate where we need documentation, so we may prevent delays by gathering the necessary information.”
Create a project management metrics strategy with criteria everyone can understand to help you get support. Explain the significant indicators you’ll be measuring, how you’ll track them, and the goals you intend to achieve. The strategy should then be put into action. Understand that project metrics should lead to action; else, they are worthless. As you discover unusable metrics, revise the plan.
Final Thoughts
Project management metrics are critical to the success of any organization. They track the progress of initiatives, assist managers in defining success, and verify that the team is heading in the right direction.
It is complicated to analyze and evaluate a project’s development without appropriate metrics in project management. With precise, trackable KPIs, the company can assess project progress and identify when it’s time to change strategy or where the team is experiencing difficulty. If the company does not make the essential changes, it may face serious obstacles and lead to failure. As a result, measuring important project management metrics is vital to the company’s success.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
Register today for my FREE webinar series on PgMP® and PfMP® certifications! Don’t miss out on this opportunity to advance your project management career. Click the registration link to sign up: https://bit.ly/3Z7kzMl
Are you looking for project management training and certification discounts? Check out our various offers and discounts here: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
Have questions about your project management career, training, and certifications? Book an obligation-free 15-minute session with me and get the answers you need: http://bit.ly/2SbhTOK
Stay up to date on the latest in project management by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel. Catch our Q&A series and certification success stories here: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
Want to hear from project management experts? Subscribe and follow my podcasts and interviews on YouTube here: https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Jan 15, 2023 | General
A project can be a complex, nonroutine, one-time effort constrained by time, budget, schedule, satisfaction, quality, and scope to meet the customer’s needs. Today, many businesses prioritize project management because it focuses on meeting project objectives and achieving them successfully. Moreover, it got significant because it employs managerial processes and tools that give managers a good chance of achieving their project’s goal.
Project Management Today
Project management has become an essential part of various industrial segments because it crosses corporate and geographic boundaries, adapting to the unique characteristics of various businesses and teams. Here are some of the project trends on the project’s success/ failures.

Key Project Management Trends
The Most Important Project Management Trends for 2022
- The growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
- Hybrid project management approaches are getting increased.
- The significance of emotional intelligence (EQ)
- A greater emphasis on data analytics and numbers
- Tools and solutions for advanced project management
- Increased use of remote working
Key Project Management Statistics 2022 (Success and Failures)
Project Success Statistics
- Project management software is used by 77% of high-performing projects. (Hive, 2020)
- 35% of organizations are somewhat satisfied with their project management maturity level. (Wellingtone, 2020)
- 29% of projects are completed on time (Wellingtone, 2020).
- Surprisingly, 54% of organizations lack access to real-time KPIs (Wellingtone, 2020).
- Around 51% of organizations complete projects that meet the business objective or original goal. Meanwhile, 52% of organizations complete projects that meet the needs of stakeholders (KPMG, 2020).
Project Failure Statistics
- COVID-19 had a moderate or significant impact on 58% of organizations, causing project delays and cancellations (KPMG, 2020).
- Organizations with low-value delivery maturity have a project failure rate of 21%, which is significantly higher than the failure rate of organizations with high-value delivery maturity, which is 11% (PMI, 2020).
- 25% of organizations do not use technology suitable for team collaborations on informal projects, despite consuming 20% of their productive time at work (Wellingtone, 2020).
- The most challenging obstacles to implementing agile techniques in an organization are resistance to change (48%), a lack of leadership participation (46%), and inconsistent practices across teams (45%). (Digital.ai, 2020).
- 47% of agile projects are late, have budget overruns, or have dissatisfied customers (Scrum, 2021).
- Understanding these statistics allows project professionals to prepare better for what comes next and make more informed decisions.
Success and Failure of Projects
The business environment is constantly changing, and meeting the customer’s ever-changing needs has become challenging. In addition, customers’ expectations increase as competition in the global market increases. This is sometimes reflected in the pressure that Project Managers face when attempting to provide the best possible value to their customers.
While project management is constantly improving, there are some challenges for which solutions have yet to be found. Global projects are typically getting complex, and as a result, a similar project may be successful in one part of the world while failing in another. Let’s look at the factors for successes and failures on similar projects, as well as how leadership style can help to improve project performance as a contributing factor to the project’s outcome.
Causes of project failure
A project is considered a failure if it fails to deliver on time within the estimated budget. Most project managers have felt the agony of a failed project. In fact, according to a Pulse of the Profession® survey 2021, 12% of projects in an organization failed in the previous year.
When a project is considered a failure?
- First, the project did not meet the expectations.
- The client did not receive the desired deliverable.
- The work was not finished on time.

Reasons of Project Failure
So here’s to planning ahead of time and avoiding these common project pitfalls.
- Unclear Goals And Objectives
Businesses that fail to set clear employee goals and objectives waste significant time and effort. The following are the consequences of ambiguous project goals and objectives.
- Unclear objectives lead to ambiguous operational methods.
- Individually, the level of performance can be justified.
- It’s not always obvious when a project deviates from its original path.
- People involved in a project cannot work to their full potential.
- Lack Of Resource Planning
In project management, resources refer to people, money, and materials. Human resources are likely underutilized or overworked if you do not use a good task management tool.
Another critical aspect of project resource planning is financial planning. Projects with poor cost estimation and inconsistent tracking will almost certainly go over budget. In addition, project managers who do not understand how to track and manage finances are more likely to fail the project.
- Poor Communication
Poor communication in the workplace can have disastrous consequences for the project, including poor collaboration and decreased productivity, resulting in stressed employees, dissatisfied customers, and workplace mistrust.
Whether it’s delayed communication, a lack of communication, or no communication at all, the fact is that the project is likely to fall through the cracks if the project professionals don’t have an effective communication strategy in place.
- Stakeholder Management Is Inadequate
Stakeholders have an inherent interest in the project, for better or worse. Project managers are responsible for identifying and communicating with all stakeholders promptly and without delays. Unfortunately, there are numerous reasons for poor stakeholder management, some of which are listed below.
- Stakeholders are too narrowly defined.
- Failure to strike a balance between compliance and strategic opportunities
- Stakeholders are prematurely removing resources.
- Stakeholders’ disinterest
- Stakeholders are unaware of the project’s progress.
Engaged stakeholders provide support and insights to help a project succeed, whereas disengaged stakeholders can become barriers to success.
- Poorly Defined Project Scope
The project scope details everything you intend to do (and not going to do). In project management, scope creep refers to uncontrolled, continuous changes in the scope of a project. Conversely, a poorly defined project scope leads to scope creep, where the former is vaguely defined, documented, or controlled.
A project with an unclear project scope is more likely to fail and encounter a variety of issues, including:
- Failure to meet customer expectations
- Continual changes are being requested throughout the project’s life cycle.
- The budget exceeds the allocated budget.
- Failure to meet deadlines
- Inaccurate Cost And Time Estimates
Inaccurate cost and time estimate frequently result in team members making accurate predictions about the expected duration of tasks and the project’s cost based on an average duration of time and cost for previous projects.
Inaccurate estimates are frequently the result of two underlying causes:
- Upfront planning
- Poor estimation practices
- Inadequate Risk management
Risk management enables project managers to identify and analyze issues that may arise during the project and impede its progress. If risks are not effectively managed, they will likely emerge during the project’s later stages, causing significant scope creep. Conversely, poor risk management can lead to project delays, low user adoption, late assignments, overspent budgets, and project failure.
- Monitoring And Controlling
Monitoring and controlling the project is one of the lesser-known facts that project managers and their teams often overlook. However, a project manager needs to “track, review, and regulate the project’s progress; identify areas that require changes in the planning, and initiate the corresponding changes.”
Every effort should be made to keep the project on track, and if it falls behind budget or schedule, the plan should be adjusted to get the project back on track.
How to Recover a Failing Project?
Three key questions you can ask to quickly and clearly understand the project.
- Are the problems internal or external?
You can determine whether the source of the problem is internal (and thus correctable) or external (outside of your control).
Review project documents such as the charter, plan, and schedule for:
- Requirements from relevant stakeholders.
- A reasonable timetable with attainable goals.
- Allocation of resources
- A method of collecting and managing change requests.
- Unexpected expenses (internal and external).
- Success metrics.
- A procedure for upholding quality standards.
- Why are we behind schedule?
Next, determine why the project is running late.
- Were tasks properly prioritized?
- Were tasks clearly explained?
- Was the timetable overly ambitious?
- How frequently did the project manager provide status updates?
- Who made important project decisions?
- Is there a record of decisions and change requests?
- How were risks communicated and addressed?
- Was the initial budget adequate?
- Is the team working effectively?
Finally, consider how well the team worked together.
- Did the team understand the project’s goal and its roles and responsibilities?
- Was the team using the same procedures and tools?
- Did the team meet regularly to share updates and challenges?
- Was a clear communication strategy in place?
- Were the right people assigned to the project?
- Were there any issues with suppliers or vendors?

Techniques for Recovering Failing Projects
Techniques for recovering failing projects
While failures are unavoidable in project management, project professionals can always learn from the failures to succeed in the future. So, let’s look at how project managers can ensure that their next project runs smoothly and that any potential problems are identified and resolved before they become too large to cause project failure.
- Plan diligently and identify any gaps.
- Communicate effectively and frequently.
- Examine your Resources
- Set realistic goals for yourself.
- Use the Proper Methodology
- Monitor Project Development
Strategic alignment in project management
Strategic alignment in project management refers to aligning project goals with your organization’s long-term vision and mission.
Contrary to popular belief, strategic alignment in project management does not only refer to establishing and maintaining key financial metrics. Instead, it’s a broad concept that encompasses everything from key financial and quality indicators to customer satisfaction, brand recognition, and value proposition.
Every project has a goal. While some may seek to provide a service or product, others may seek intangible benefits such as positive customer relationships or company goodwill. These strategic goals guide a project professional’s day-to-day business operations and help them turn their ideas into desired results.
Importance of Strategic Alignment in Project Management
- Focus the energy in the right place
- Allow for productive team collaboration
- Describe the organization’s competitive advantages
- Manage priorities that conflict
- Avoid duplication.
- Accept market manoeuvrability
Leadership performance is significant to project success
Effective leadership in project management is the ability to persuade people of the need for change, stimulate new ways of thinking and problem solving, and encourage them to achieve project objectives. Leadership also guides team members to grow as professionals while completing their project responsibilities.
Today’s evidence-based theories of leadership can be characterized into six major classes, which include:
- Attributes
- Behavior
- Contingency
- Visionary
- Emotional intelligence
- Competency

PMI’s Talent Triangle
PMI’s Talent Triangle – How to Stand Out as a Successful Project Manager
Project managers must be more agile and resourceful than ever to keep up with and make an impact in a fast-changing world. PMI has always been dedicated to assisting project professionals in developing strong skills. Nonetheless, project managers now require a skill set that includes a variety of disciplines and practices, as well as other in-demand skills.
To assist project professionals in navigating this changing world of work and embracing smarter ways of working, project professionals need to focus on:
- Ways of Working: Formerly Technical Project Management
- Power Skills: Formerly Leadership
- Business Acumen: Formerly Strategic and Business Management
Factors of project success
Project success has been defined as a project that meets its objectives on time and within budget. A development project’s success extends beyond meeting schedule and budget objectives. It also includes meeting the expectations of beneficiaries, stakeholders, donors, and funding agencies. However, defining these dimensions of success is more complicated and can only be assessed years after the project is completed.
Measuring project success after the fact is important because it aids in determining future strategies when planning new projects. Continuous improvement based on data from past projects enables project managers to identify problems before they occur. Using past data allows new processes to be implemented with fewer errors and greater management success.

Factors of Project Success
Here are some of the factors for the project’s success:
- Goals and objectives
The project’s overall goal is specified and recognized by all stakeholders; it is not at odds with subsidiary objectives, and project leaders have a clear vision of the project’s outcomes.
- Capable sponsors
Sponsors play an active role in the project’s life cycle; they bear ultimate responsibility and accountability for the project’s outcomes.
- Secure funding
The project has a secure funding base; contingency funding is recognized from the start, and budgets are strictly regulated to ensure maximum value is realized.
- Project planning and review
Pre-project planning is thorough and considered; progress is monitored regularly and carefully; the project has realistic time schedules, active risk management, and a post-project review.
- End users and operators
End users or operators are involved in the project’s design; the project team works with users who can effectively and efficiently implement what the project has produced.
- Aligned supply chain
All direct and indirect suppliers know the project’s requirements, timelines, and quality standards. As a result, the supply chain’s higher and lower tiers are coordinated.
- Proven methods and tools
Good project management tools, methods, and techniques are used to maintain an effective balance of flexibility and robustness.
- Appropriate standards
Quality standards are actively used to drive output quality. In addition, other standards are regularly monitored to ensure delivery at the best practice levels.
Knowing what success factors are important at the end of a project is critical for assessing how that project went and making changes for the next one. It is critical to understand what distinguishes success from failure.
By investing time in learning about the future of project management, project professionals will be better prepared to capitalize on new opportunities and develop their skill set accordingly. So many opportunities for growth and success are on the horizon; use these trends and factors to propel your company, projects, and team to new heights!
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
















Recent Comments