
by admin | Dec 13, 2024 | Industry Trends and Insights
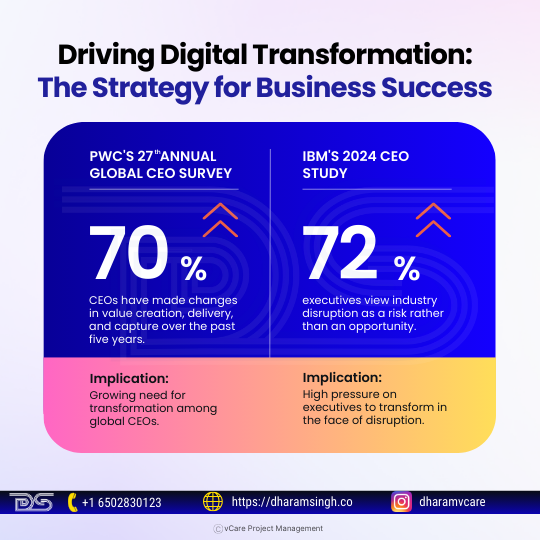
Digital transformation is a strategy that modernizes business processes and introduces new services to engage customers, support employees, improve operations, and drive business value. PwC’s 27th Annual Global CEO Survey shows a growing need for transformation, with 70% of CEOs making changes in value creation, delivery, and capture over the past five years. IBM’s 2024 CEO Study reveals high pressure on executives to transform, with 72% viewing industry disruption as a risk rather than an opportunity. A business-centric approach to modernizing organizations through digital technologies is crucial for long-term business survival. Organizations must reinvent their operations and business models in the modern era, integrating digital technologies into all aspects to improve products and services, streamline processes, and introduce new revenue streams.
The global market for digital transformation technology and services is expected to reach $3.9 trillion by 2027, despite 70% of projects failing to meet objectives. To avoid falling into the 70% failure rate, organizations must make the right investments and adopt reversed leadership to foster resilience.
Driving Digital transformation
Peter Drucker’s theory emphasizes inverted leadership in businesses to promote resilience. He argues that the biggest danger in instability is not the turbulence itself, but acting on outdated thinking. To address this, companies must reject outdated methods and create adaptive structures that welcome change.
In today’s competitive environment, the Transformation Management Office (TMO) is critical for driving progress, building a value proposition, and providing comprehensive transformation guidance.
What Sets TMOs Apart?
The Transformation Management Organization (TMO) is a vital structure that oversees the planning, management, and monitoring of transformation activities. It unites diverse teams, driving accountability and clear direction. It serves as the link between strategy and implementation, ensuring the successful execution of a transformation initiative. The TMO’s key functions support the organization’s transformation program, making it valuable for businesses.
TMO and PMO
A Project Management Office (PMO) supervises specific projects inside a business, but a Transformation Management Office (TMO) controls the overall transformation path, which includes various projects and initiatives. A PMO manages project-specific goals, schedules, and resources to ensure timely and cost-effective completion.

TMO and PMO
Key differences include:
- Scope: TMOs manage large-scale changes involving several interconnected projects, whereas PMOs focus on a group of individual projects.
- Duration: TMOs are transient entities that dissolve during transformation, but PMOs can become permanent fixtures within an organization.
Transformation Management Office Importance:
- Aligns the company’s transformation plan with business goals.
- Provides control and monitoring in decision-making and risk management.
- Effectively manages organizational change, involves stakeholders, and promotes new procedures.
- Monitors and measures transformation progress to ensure expected benefits and ROI.
- Acts as a focal point for organizing activities and ensuring coordination across departments.
Bridging the Gap Between Expectation and Reality
Digital transformation is a major strategic objective for organizations, necessitating a fundamental shift in operations, customer interaction, and value delivery. This shift affects all parts of a company, from business model to culture, and necessitates extensive change management. Navigating these obstacles is critical for firms to adapt and succeed in the digital era. Change management involves preparing individuals and teams to adapt, often facing resistance, misunderstanding, and fear in large, fast-paced digital transformations. Understanding potential challenges can help organizations navigate this complexity efficiently. Strategic planning, effective change management, and a strong understanding of these challenges can position businesses for long-term success in the digital era.
Digital Transformation Challenges to Overcome
Digital transformation offers innovative opportunities for organizations but also necessitates critical thinking and reimagining core business aspects. Regardless of industry, from manufacturing to pharma, a few key challenges to consider when implementing digital transformation projects in 2024 include:
- Absence of a change management plan
A well-structured change management strategy significantly boosts digital transformation success, involving identifying root causes and building relationships with stakeholders and employees, thereby reducing the likelihood of project failure.
- Complex software and technology
Organizations undergoing digital transformation face challenges in complex enterprise software, data integration, and end-user experience.
- Driving the uptake of new tools and procedures
Organizations must provide comprehensive on boarding training and continuous performance support for new software implementations to help employees become productive and proficient with the new processes, overcoming resistance from tenured employees.
- Lack of a digital transformation strategy
Before implementing a digital transformation process, it’s crucial to understand the reasons for replacing legacy systems, the organization’s plan for advanced systems, and the readiness to migrate existing systems. Choose from various models based on improvement areas and company needs.
- Lack of proper IT skills
A tech worker shortage is impeding firms’ digital transformation efforts, with 54% claiming a lack of technically qualified employees. Cybersecurity, application architecture, software integrations, data analytics, and migration are all challenges that must be addressed by either outsourced or in-house teams.
- Security concerns
Enterprise organizations in data-sensitive industries face privacy and cybersecurity concerns due to digital transformation, which involves integrating data into a centralized system. Cyberattacks can target system vulnerabilities and poor setups, necessitating proactive mitigation plans and cybersecurity training for employees.
- Budget constraints
Digital transformation is a costly investment, with scope creep, consultation work, customer changes, and IT errors increasing costs. To manage this, organizations should identify long-term goals and ROI, determining what spending is too much and budget room for budget increase.
- Poor organizational structure
Organizational isolation can hinder collaboration, communication, resource allocation, and innovation in digital transformation initiatives, affecting decision-making and the flow of ideas.
- Measuring ROI
Since the advantages of projects involving digital transformation cannot be immediately perceived or measurable, calculating return on investment (ROI) can be difficult. Progress may be impeded as a result of uncertainty and a failure to invest in future projects.
Tips to Overcome Digital Transformation Challenges

Tips to Overcome Digital Transformation Challenges
- Invest in a digital adoption platform
Investing in a digital adoption platform (DAP) is vital for successful digital transformation projects, as it provides adequate on boarding, training, and support for employees.
- Establish a change leadership team
Identify influential, innovative, and trustworthy employees in your workforce and form a cross-functional change leadership team to create a vision for digital transformation aligned with business goals, allowing organizations to take a proactive approach and accelerate change.
- Hire a digital transformation consultant
Digital transformation involves realigning core processes, tools, and experiences, often challenging organizations with a lack of internal change agents. Hiring a digital transformation consulting company offers a proven framework and success-based framework for successful change.
- Align business objectives with the digital transformation plan
An organization’s digital transformation should prioritize understanding customer needs, pain points, and friction areas in offerings, products, and services. Analyse current processes to identify outdated systems and align with core business goals, empowering employees, overcoming customer experience challenges, and driving revenue.
- Be agile
Digital transformation projects require organizational vulnerability, as leaders must adapt and innovate in a rapidly changing technology landscape. Being agile means pivoting and seizing opportunities, and embracing new processes, tools, and practices, even if they’re already underway.
- Encourage employee feedback
Employee involvement in digital transformation can help organizations overcome challenges by involving them in decision-making, identifying obstacles, and devising effective solutions, fostering a sense of ownership and accelerating the success of digital transformation initiatives.
- Continue to monitor and adapt
For real-time changes, alignment with corporate objectives, efficient resource allocation, and resolving possible problems before they become worse, it is essential to continuously monitor, measure, and evaluate digital transformation projects.
Leadership in Transformation: The CTO’s Role
According to the PwC CEO Survey, 22% of UK CEOs are predicting their current business model will not last for the next decade due to changing consumer and regulatory needs, talent shortages, climate, digitalization, economy, and geopolitics. This necessitates immediate changes in the supply chain, operational model, product portfolio, strategy, and culture.
The growth of strategic leadership skills among Chief Transformation Officers (CTOs)
Transformation is crucial for organizations, but there is no clear leader. Three approaches exist: top-down, devolved, and dedicated.
- Top-down involves the CEO leading, and delegating to C-Suite colleagues, while devolved involves other C-Suite members rotating.
- The devolved approach involves other C-Suite members, potentially on rotation.
- The third approach involves a dedicated individual focused on developing and delivering the transformation strategy.
The need for a dedicated transformation leader depends on the scale, complexity, and ambition of the strategy. As transformation becomes ‘business as usual’, organizations are increasingly creating board or C-suite roles like transformation director or Chief Transformation Officer.
The demand for a dedicated and elevated transformation leader
A transformation leader is responsible for driving an organization’s change ambitions, elevating them to the top, and ensuring transformation remains a key agenda item. They must set the tone, challenge current wisdom, and integrate functional and organizational priorities like sustainability, purpose, and digital transformation to create a viable future. The leader’s role involves gathering insights, identifying change impetus, devising a vision, and designing key steps.
Top leadership skills for a CTO Role

Top leadership skills for a CTO Role
- Strategic thinking
A CTO must be able to think strategically to foresee market trends, develop a strategy, communicate clearly, and compile a variety of perspectives. This skill aids with innovation, value creation, and competitiveness.
- Technical competence
A CTO must possess technical expertise, which calls for an extensive understanding of modern tools, technologies, and frameworks as well as the capacity to assess, choose, and put into practice scalable, secure, and dependable solutions.
- Team leadership
CTOs require strong team leadership skills to recruit, train, and motivate diverse teams, foster collaboration, and provide clear direction. This builds trust, engagement, and productivity, enhancing productivity.
- Business acumen
CTOs must possess business acumen in order to analyze effect, match technological solutions with business strategy, and comprehend the market, consumers, and competitors. Making informed, data-driven, and customer-focused decisions is facilitated by this ability.
- Communication skills
CTOs require strong communication skills to effectively communicate their vision, strategy, and objectives, establish rapport, credibility, and influence, and actively listen, inquire, and empathize with others.
- Learning agility
CTOs must learn agility, adapt to changing situations, learn from successes, embrace new challenges, foster a learning environment, seek knowledge, and seek feedback to grow, innovate, and improve.
How the CTO and TMO collaborate to advance organizational success?
The CTO and TMO work together to align technology strategies with enterprise-wide transformation goals, with a focus on innovation, scalable solutions, and leveraging new technologies for competitive advantage. Through advanced analytics and efficient project and change management, they maximize resources, create a balance between technical and operational requirements, and promote data-driven decision-making. Through this collaboration, technology is certain to play a significant part in transformation, fostering agility, operational effectiveness, and quantifiable results throughout the company.
Here’s how they work together in detail:
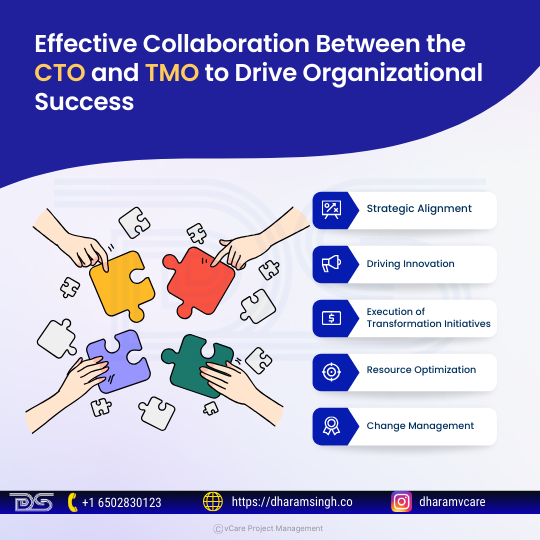
Effective collaboration between CTO and TMO
- Strategic Alignment
The CTO and TMO collaborate to develop a long-term technology roadmap, aligning IT and operational changes with the organization’s strategic vision and ensuring value.
- Driving Innovation
The CTO implements new technologies to enhance operational efficiency and customer experiences, while the TMO facilitates their integration within the organization, collaborating on technical expertise.
- Execution of Transformation Initiatives
The CTO provides tools for transformation projects, while the TMO manages them efficiently, ensuring milestones are met and the technical enablers are effectively utilized.
- Resource Optimization
In order to prevent redundancy and guarantee the economical deployment of technology and human capital, the CTO and TMO collaborate to optimize technical resources, assign resources for transformation initiatives, and work collectively.
- Change Management
The CTO manages technical challenges and resistance during technology implementation, while the TMO manages organizational resistance and ensures cultural buy-in for changes.
Building the Team Behind the Transformation
Effective digital transformation strategy requires assembling the right team, considering factors like experience, education, skillsets, influence, and teamwork abilities. Digital teams are led by C-level executives, who may hold titles like CIO, CTO, or COO, and have other responsibilities. The CEO appoints the leader for all digital transformation initiatives, based on their view of the process. Finding the right team members is a challenge in digital transformation projects.
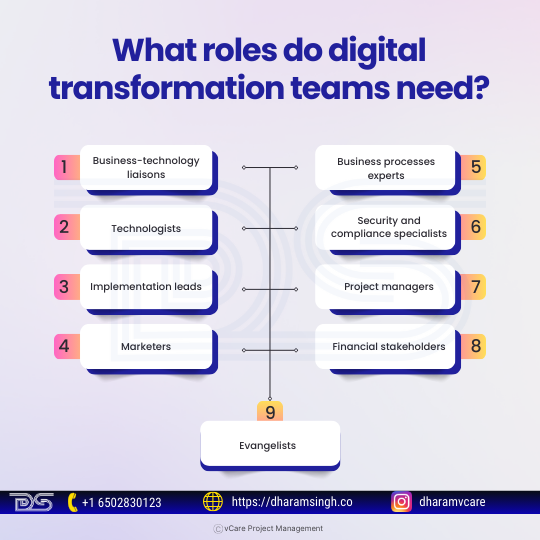
What roles do digital transformation teams need?
Digital transformation requires nine key positions, but on average, 12-20 people are on each team, with multiple people working within each role in most companies.
What roles do digital transformation teams need?
- Business-technology liaisons
Business technology liaisons work with business unit executives to identify opportunities and challenges by examining business models, customer experience, and technology strategy as part of initiatives to transform their businesses.
- Technologists
Technologists identify business issues for transformation, select appropriate technology and providers, and evaluate the technical success of digital transformation projects.
- Implementation leads
This role involves leading the digital transformation roadmap, focusing on technology and process change implementation, with additional daily implementations.
- Marketers
IT staff often implement new technology to enhance customer experiences, but employees often lack understanding. Marketers should understand the project’s goals, technology impact, and effective marketing strategies to engage employees, customers, and business partners, ensuring customer engagement.
- Business processes experts
Business process experts are essential for digital transformation, optimizing workflows, recommending AI, machine learning, and automation, and fostering new digital strategies for a digital-forward approach.
- Security and compliance specialists
Digital team leaders should involve security and compliance specialists from the start to avoid potential project halts due to potential security policy violations, ensuring a smoother and more secure project.
- Project managers
Project managers develop detailed plans, maintain staff, schedule, and budget, set meetings, and schedules, raise red flags, and reset expectations to ensure the project stays on track.
- Financial stakeholders
Digital transformation initiatives are financed by financial stakeholders, who also persuade other budget holders to obtain further financing. They demand weekly, monthly, or quarterly updates to monitor progress and ensure the budget is well spent. C-level executives often serve as ultimate financial stakeholders.
- Evangelists
Evangelists use their influence and communication skills to generate excitement and secure funding for projects, often through well-received internal blogs and videos, and provide honest evaluations to budget control authorities.
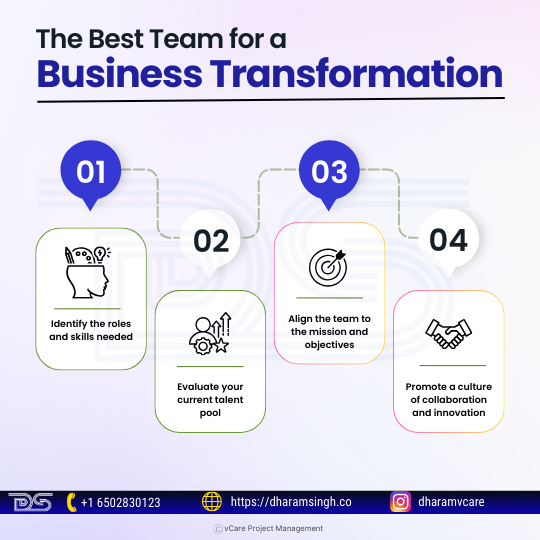
Ways to select the best team for a business transformation
Building a team for technology transformations requires effort, approval from supervisors, and discipline. Best practices include finding suitable individuals, ensuring discipline, and integrating them into daily tasks.
Ways to select the best team for a business transformation
- Identify the roles and skills needed
Define roles and skills for your business transformation team, including project management, change management, business analysis, technical skills, communication, and stakeholder engagement, considering their authority and responsibility, and their interaction with the organization.
- Evaluate your current talent pool
Utilize various assessment methods to evaluate your talent pool, focusing on adaptability and learning potential, and consider external recruitment for skill gaps or fresh perspectives.
- Align the team to the mission and objectives
Select team members and align them with business transformation goals. Communicate project purpose, scope, benefits, risks, organization strategy, values, expectations, accountability, measurement, reward, and resources. Provide support and training for effective performance.
- Promote a culture of collaboration and innovation
Foster a culture of collaboration and innovation within your business transformation team by encouraging open communication, experimentation, and improvement. Celebrate team achievements and milestones to select the best team for your transformation and increase the chances of achieving desired outcomes.
Speed vs. Sustainability: Achieving the Right Balance
Striking the correct balance between speed and sustainability is the primary barrier to implementing organizational change. On the one hand, it may be swiftly implemented, providing competitive advantages and results right away. On the other hand, long-term success and preventing exhaustion or inefficiency will depend on ensuring that improvements are sustainable. A transformation management office is essential in striking this delicate balance to ensure both immediate effect and long-term value.
Need for Speed in Transformation
In transformation projects, speed is typically the primary concern, particularly in settings where external pressures like market rivalry, technology disruption, or regulatory changes need quick reactions. Quick action might offer several advantages:
- First-Mover Advantage: Quick deployment can help a company surpass its rivals, increase market share, or reshape industry norms.
- Momentum and Engagement: Stakeholders are excited by quick wins, which generates momentum for more change.
- Crisis Management: Speed may be a useful reaction to stabilize operations and preserve company flow during crises like recessions or supply chain disruptions.
- Customer demands: In general, meeting evolving customer demands necessitates a quick adoption of new procedures or technology.
Yet, the need for speed comes with hazards, such as making rapid choices, failing to involve stakeholders, and putting in place short-term solutions that might not last.
The Case for Sustainability
The focus of transformation sustainability is on making adjustments to the systems, procedures, and organizational culture in a way that will yield long-term benefits. The following are some advantages of sustainable change:
- Cultural Incorporation: Because employees can adapt and adopt new behaviours, changes that take into consideration the company culture have a higher chance of success.
- Resilience: Systems and procedures that are able to adapt over time and withstand future disruptions are the result of sustainable adjustments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While such quick adjustments may lead to waste and rework, sustainable projects are made to be as efficient as possible while maximizing return on investment.
- Establishing Stakeholder Trust: Stakeholders will remain committed and helpful if a progressive approach is taken to gain their confidence.
This approach to sustainability has the drawback of lengthening timeframes, which gives competitors a chance to outstrip them or opportunities to fall away.
How the TMO Achieves the Balance
An effective TMO makes sure that sustainability and speed are beneficial not detrimental, components of a successful transition. A TMO accomplishes this balance in the following ways:
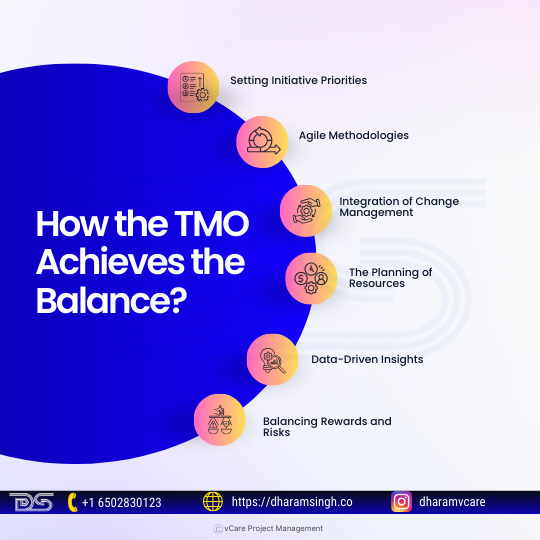
How the TMO Achieves the Balance
- Setting Initiative Priorities
Transformation initiatives undergo a thorough study by the TMO, which then classifies them based on their long-term worth and urgency. The TMO guarantees that important objectives are fulfilled without sacrificing the sustainability component by distinguishing between urgent and non-urgent initiatives that may be phased in.
- Agile Methodologies
Using agile frameworks, the TMO promotes iterative progress. In this manner, the company may provide immediate results while also gradually improving procedures in the direction of long-term goals.
- Integration of Change Management
Rapid adoption and deep integration into the organization’s culture are two goals of change management techniques implemented through the TMO. As an example:
- Short-term: Employees will be assisted in understanding the instantaneous advantages of changes through training and direct communication.
- Long-term: Constant interaction via feedback loops guarantees acceptance and embracing change.
- The Planning of Resources
Rapid projects usually demand significant resource expenditures, while sustainable projects call for the balanced use of the same. Resources are managed by TMO to prevent burnout, overstretching, or underinvestment in vital projects.
- Data-Driven Insights
A TMO may make quick course corrections without compromising long-term objectives like employee engagement or consumer satisfaction by using data to monitor transformation progress in real time.
- Balancing Rewards and Risks
The risks of moving too quickly or too slowly are examined by the TMO. Using risk assessments and backup plans that balance thoroughness and speed, ensures that the company moves at the proper pace.
Crucial Elements of Success
Here are some action-oriented tactics for striking a balance between flexibility and discipline:
- Set Clear Objectives: Specify both immediate and long-term objectives. To evaluate progress and effort alignment, use them as checkpoints.
- Build Leadership: Give leaders the power and resources they need to make choices that promote sustainability and speed.
- Foster an Experimentation Culture: Encourage small pilot studies and experiments that can yield rapid insights without running the risk of more significant failures.
- Transparency: Explain the rationale behind the schedules, resource distributions, and decision-making procedure to all parties involved.
It is the practice of balancing speed and sustainability via strategic oversight, meticulous preparation, and adaptation. A Transformation Management Office is ideally positioned to balance these goals, allowing firms to adapt to current difficulties while maintaining long-term stability. With the appropriate methodology, businesses may achieve transformative success that is both timely and sustainable.
The Future of TMOs in a Disruptive Landscape
Transformation Management Offices (TMOs) evolve with enterprises as they traverse a fast-changing world marked by technological developments, transformations in worker demographics, and global issues. Today, in this age of disruption, TMOs have evolved from typical project monitoring bodies to critical facilitators of innovation, flexibility, and long-term sustainability.
Emerging Innovations: The 15 tech trends
Organizations increasingly turn to data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) to assist them make business choices. When it involves incorporating artificial intelligence for resource efficiency, process automation, and predictive analytics, TMOs are essential. This integration can improve decision-making, and operational efficiency, and lead digital transformation initiatives. Hybrid workforces are also changing the way organizations work, necessitating inclusive and collaborative transformation. TMOs must embrace digital tools and communication platforms that enable virtual collaboration across global teams. This global collaboration helps businesses remain competitive and agile in the fast-paced market.
The McKinsey Technology Trends Outlook 2024 categorizes 15 trends into five groups: AI revolution, digital future, compute and connectivity, cutting-edge engineering, and a sustainable world, assessing their status through innovation, interest scores, and adoption levels.

Emerging Innovations: The 15 tech trends
- Generative AI
Unstructured data, such as natural language and pictures, are used by generative AI systems like ChatGPT to create new audio, code, images, text, simulations, and movies.
- Applied AI
AI technologies utilize machine learning models to solve classification, prediction, and control problems, automate activities, enhance capabilities, and improve decision-making.
- Industrializing machine learning
The industrializing machine learning trend entails a fast-growing ecosystem of software and hardware solutions that accelerates and lowers the development, implementation, and maintenance of machine learning systems.
- Next-generation software development
Next-generation software development utilizes advanced tools and technologies for efficient code deployment, automated code generation, testing, refactoring, and translation, thereby enhancing application quality and development processes.
- Digital trust and cybersecurity
Digital trust and cybersecurity include trust architectures, digital identity, cybersecurity, and Web3, which allow enterprises to develop, grow, and retain stakeholder trust.
- Advanced connectivity
Low-Earth-orbit satellites, 5G and 6G cellular, Wi-Fi 6 and 7, and wireless low-power networks are all examples of advanced connection.
- Immersive-reality technologies
Immersive-reality technologies enable real-time interactions in three-dimensional virtual worlds, ranging from fully computer-generated VR to mixed reality and AR. They use spatial computing to interpret physical space and simulate data, objects, and people addition.
- Cloud and edge computing
Cloud and edge computing involves distributing workloads across locations like hyperscale data centers, regional centers, and local nodes to optimize latency, data transfer costs, data sovereignty, and security.
- Quantum technologies
Quantum-based technologies utilize quantum mechanics’ unique properties to perform complex calculations faster, secure communication networks, and produce higher-sensitivity sensors than classical counterparts.
- Future of robotics
The future of robotics will see advancements in robots from fixed-purpose tasks to adapting to real-life inputs with increasing autonomy and dexterity.
- Future of mobility
The efficiency and sustainability of land and air transportation are intended to be improved by mobility technologies, such as electric and driverless cars, urban air mobility, and ACES technology.
- Future of bioengineering
Bioengineering is the application of engineering concepts to biology, using technology breakthroughs to enhance health and human performance, restructure food value chains, and develop innovative offers.
- Future of space technologies
Space technologies include satellites, launchers, and habitation systems that enable new space activities and services.
- Electrification and renewables
The electrification and renewables trend encompasses the entire energy production, storage, and distribution value chain, utilizing renewable sources like solar and wind power, clean energy sources, and energy storage solutions.
- Climate technologies beyond electrification and renewables
Climate technologies aim to reduce resource consumption by removing CO2 from the atmosphere or producing materials and inputs with lower carbon equivalents.
TMO as an Enabler of Innovation and Adaptation in a Constantly Changing Environment
TMOs are becoming key drivers of innovation in a world marked by constant disruption. They help projects remain responsive and adaptable, such as during the pandemic when they focused on remote work transitions and digital-first strategies. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and agile methodologies, TMOs enable organizations to innovate at scale, test new ideas, assess emerging technologies, and adapt to the business environment without losing sight of long-term objectives. In the future, TMOs will become centres for experimenting and scaling innovations.
The Changing Role of TMOs in a Post-Pandemic World
Organizations’ approaches to change have been permanently impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic A new function has been introduced to the TMO in the post-pandemic environment with reference to crisis management, recovery, and restructuring organizational structures. TMOs are increasingly in charge of managing hybrid work arrangements, supervising the change to more digital-first models, and negotiating emerging issues like cybersecurity, employee well-being, and changing consumer expectations.
Additionally, post-pandemic methods call for greater function and geographic cooperation, which makes a strong TMO even more essential. Leading resilience in an era of future disruption is now the office’s responsibility in order to keep the company flexible and responsive. As businesses consider their post-pandemic needs, TMOs must emphasize adaptability, foster innovation, and take on the role of sustainability champions.
Conclusion
Investing in the Future of Transformation Management Offices (TMOs)
Organizations that implement a Transformation Management Office (TMO) now will not only survive but thrive in future difficulties. Maintaining a competitive advantage requires employees who are committed to driving change and ensuring that transformation efforts are executed seamlessly. TMOs are critical in today’s fast-paced, digital-first business environment because they oversee and align transformation activities, balance rapid wins with long-term development, manage evolving technologies and promote continuous improvement. They facilitate innovation, help firms navigate digital transformation, maximize resources, and successfully manage change. TMOs can help firms be resilient and adaptable in the face of upheaval by catalysing adaptation and innovation.
Call to Action for Leaders
Leaders must invest in a Technology Management Organization (TMO) to navigate the complexity of the modern corporate world, which includes hybrid workforces, AI-driven decision-making, and a quickly changing competitive landscape. Proactively deploying TMOs can help firms navigate these changes, unleash new growth prospects, and assure long-term success.
TMOs will play a growing significance as firms adapt to a world that is changing all the time. In the years to come, TMOs will be the driving forces behind organizational change, from innovation and adaptation to AI-driven decision-making and hybrid workforce management. TMO will emerge as a strategic partner that helps companies not just survive but flourish in this disruptive environment as they confront an increasingly uncertain future.


















Recent Comments