
by DharamCW | Jun 12, 2022 | General
Two relevant quotes which quickly strike our minds when we think about the Entrepreneurial mindset are:
“Building a business is not rocket science; it’s about having a great idea and seeing it through with integrity.” Richard Branson
“At 211 degrees, water is hot. At 212 degrees, it boils. And with boiling water comes steam. And with steam, you can power a train.” S.L. Parker
Ideally, a project’s success is based on the critical success factors identified during the initial stages of the project, which would fall in various areas such as Process, Product, Project Management, Business, and Strategic. When the project can make a positive and long-standing impact on business value, a culture deeply imbibes into people’s minds. It creates an undeniable mark in the overall scheme of things.
Benefits and stakeholders’ satisfaction are the key factors that measure a project’s success. It’s also defined by the level of efficiency the project creates based on the set project objectives. Project success is based on the project success criteria and outcome. Typically, these criteria fall as Meeting the Scope identified, Deadlines and Milestones on time, Within the given budget, excellent satisfaction to the stakeholders, both internal and external, and with specified quality criteria.
Essentially, we all know that various tenets of project management contribute to success. Here, we will discuss how the entrepreneurial mindset would impact project success. Entrepreneurs have some unique characteristics such as being adaptive, decisive, risk-tolerant, persistent, able to handle failure, experimenting, building teams, etc.,
Mindset
One must believe that we can be malleable to unlock our growth as project managers or portfolio managers by transforming into an entrepreneurial mindset. We need to understand what mindset is, then understand the characteristics of an entrepreneurial mindset and how we can embark on that transformation journey from where we are to bring on project success in our project management career.
Mindset is an essential set of beliefs that provides a shape in terms of the view one has on the world and themselves. It influences how we think, act, feel and respond to a given situation. Typically, mindset falls into two categories as introduced by Carol S. Dweck, which we are all aware of: they are a) Fixed Mindset and b) Growth Mindset.
An entrepreneurial mindset is a growth mindset. Intelligence cannot be developed with a fixed mindset. A growth mindset is all about the belief that intelligence can be developed through personal effort, good learning strategies, and lots of mentoring and support from others. As introduced by Heider, the interpersonal process equation is a product of Ability, Motivation, and Environment.
An entrepreneurial mindset is a set of skills that allows people to recognize and capitalize on opportunities, overcome and learn from setbacks, and succeed amidst challenging backdrops. An entrepreneurial mentality is a method of thinking that helps achieve your business objectives. Entrepreneurs who learn from their mistakes and failures have a better chance of future success.
Entrepreneurs boost the economy by creating jobs and developing new products and services that benefit the entire world. A great entrepreneur must be able to think outside the box and come up with out-of-this-world ideas.
Entrepreneurial mindset and project management

7 Entrepreneurial Traits
Though there is a common belief that entrepreneurship cannot be taught, and they should be born, studies have proven that it’s a myth. Typically, entrepreneurs search, seize and exploit the opportunities while mitigating them through engagement, courage, and perseverance. The following are the entrepreneurial traits that are generally encompassed in an entrepreneur:
- Commitment and Determination
- Courage
- Obsession with opportunity
- Risk tolerance
- Creativity
- Motivation to excel
- Leadership
An entrepreneurial mindset fosters more value for projects. Your project teams are encouraged to solve business problems and develop creative and innovative ideas. When a leader allows the teams to be creative and innovative, they will be more productive and engaged in the project.
The journal “People’s confidence in innovation” indicates that confidence in innovation is a component of the entrepreneurial mindset. In several ways, confidence in innovation can be considered part of the entrepreneurial mindset.
- First, entrepreneurs have more confidence in innovation than non-entrepreneurs.
- Second, confidence in innovation is positively related to other aspects of the entrepreneurial mindset, most notably self-efficacy, opportunity alertness, risk propensity, and role-modelling.
- Third, according to (Nochian and Schtt’s 2012) study, entrepreneurs are not like other people. Instead, their network appears to be the source of their confidence. In the same way, highly networked owners or managers are highly confident in innovation.
- Fourth, their innovativeness appears to be a result of their confidence. The more confident entrepreneurs are, the more innovative they are.
Entrepreneurial mindset and Project success
Commitment & Determination
Commitment and Determination would encompass Decisiveness, Tenacity, Discipline, persistence in solving problems, willingness to sacrifice, and being completely immersed in the mission. In the context of project management, each of these characteristics would contribute to the project’s success. For example, it is being decisive in terms of critical path challenges and exhibiting tenacity for unblocking issues without giving excuses for the need of the project and solving problems. Being committed requires a lot of sacrifice and discipline to bring on consistency. When being disciplined, it would require more like a parenting skill which would always course correct in the larger interest of the project, though seen to be tough externally. Discipline is brought about by establishing an unalterable set of rules and regulations to follow for the project’s success.
Courage
The definition of courage is “mental or moral strength to venture, persevere, and withstand danger, fear, or difficulty” (Mish, 1994, 266). Courage could be implemented with excellent values through moral strength, fearless experimentation, unafraid of conflicts, no fear of failure, and intense curiosity amidst facing risk. A courageous project manager would tackle the controversies and conflicts in the project early. A fearless project manager could put his job on the line in the pursuit of doing The Right Thing for the project. Often, the project manager would not have the necessary support and face active resistance, which needs to be managed with resolve to move beyond personal discomfort through intense curiosity.
Obsession about opportunity
An entrepreneur constantly looks for opportunities for improvement. Similarly, project managers consistently look for opportunities for improvement daily by observing day-to-day activities seeking to do more, do better, and do differently. Obsession with opportunity would be recurring, which would preoccupy or intrude on the project manager’s mind. This obsession would naturally shape the opportunity and help focus on project needs. Obsession with opportunities drives business value through the project.
Risk Tolerance
Good project managers would tolerate risk while being calculated risk-taker and risk sharers, thereby minimizing the risks. He would exhibit the characteristic of an entrepreneur by showing the ability to manage stress/conflict and ambiguity. Especially when the project has larger integrations and frequent changes would increase the ambiguity and uncertainty proportionally. Generally, the unknowns which are in the project would cause ambiguity. The ability to understand those would help identify the risks involved. PMBOK defines these areas in terms of Risk tolerance, Risk appetite, and risk threshold. It guides the management of these effectively through appropriate processes involving planning, controlling, and appropriate level of communication.

Risk Tolerance
Project managers should learn how to maneuver ambiguity. As ambiguity would be sinusoidal over time, it would arise and settle. The project manager must manage risk/ambiguity and uncertainty by uncovering information, clarifying roles and responsibilities, establishing clear relationships, bringing clarity to the measurement of success, removing the vagueness, and understanding the cause and effect.
Creativity
So what is creativity? In “The Social Psychology of Creativity,” Amabile (1983) defines creativity as,
“A product or response will be judged as creative to the extent that (a) it is both a novel and appropriate, useful, correct or valuable response to the task at hand, and (b) the task is heuristic rather than algorithmic” (p. 33).
Creativity can be multiple things. It would always push your limits by being open-minded, lateral thinking, ability to conceptualize by going into details, and ability to adapt. Creativity can be unleashed in project setup during Brainstorming sessions, Root Cause Analysis, Force field analysis, Affinity Diagrams, SWOT Analysis, etc. Creativity can be fostered further by open communication and providing an environment for the resources involved. As a project manager, one needs to remove the mental blocks like “Always looking for the right answer,” “avoiding ambiguity,” “I’m not creative,” “Always looking for concrete answers,” and “That’s not my area,” etc., Encourage creative aspects through “Why not like that,” “Let’s explore more,” “what value it would bring in,” etc.,
Motivation to excel
There is a popular phrase. Projects don’t succeed; people do. Typically the project’s success is always attributed to the people. People tend to have a goal and result orientation and need a self-imposed drive to achieve the results. Typically entrepreneurs keep motivating themselves and others around them despite all odds. People involved in projects need interpersonal support, understanding of weaknesses, and guidance to overcome them. Essentially aspects like having a sense of humor and perspective on the value they are adding to the project would motivate them to do better. The project manager’s responsibility is to understand individuals and adopt appropriate motivations strategy based on their needs, desires, and goals. They reward the team and its members creatively by recognizing their strengths. Make the project goals and success factors visible to the entire team. They are clarifying how the performance will be validated as an exact measure.
Leadership
Leadership is one of the essential traits entrepreneurs have. They would be self-starters and have a strong internal locus of control. Locus of control is the degree to which people believe that they, as opposed to external forces (beyond their influence), have control over the outcome of events in their lives. The concept was developed by Julian B. Rotter in 1954 and has since become an aspect of personality psychology. Project managers with an Internal Locus of Control believe that every event in their life derives from factors under their control. These individuals tend to blame or praise themselves for whatever success or failure they experiment in life. They would have enormous patience, integrity, and reliability. They would build teams and more leaders. Key attributes of communicating with a project management mindset include empathy, clarity, authenticity, and flexibility.

Project leadership qualities and competencies
Successful projects come as an outcome of a well-coordinated team effort. Project managers as leaders know their team very well.
The entrepreneurial mindset’s key aspects of a project’s success
Being confident and open-minded is crucial for a project professional with an entrepreneurial mindset. It’s about being self-assured, optimistic, and never afraid to take risks. Every day, if you have an entrepreneurial mindset, you will be ready to take action to achieve your goals and acquire project success.
While some scholars have examined aspects of the entrepreneurial mindset and provided general insights into its attributes, qualities, and operations, the question remains how people tap into it.
- The cognitive aspect—how do entrepreneurs use mental models to think?
- The behavioral aspect—how do entrepreneurs engage or act for opportunities?
- The emotional aspects—what do entrepreneurs feel in entrepreneurship?
Project leadership qualities and competencies
When the project requires success, both project managers and project sponsors should take up the role of a project leader by demonstrating leadership talents, competencies, and entrepreneurial mindsets. The following are the most significant features of effective project management:
- Project management technical skills
- Product development and domain expertise
- Strategy and business acumen
- Leadership and change management skills
- Agility and adaptability
- Ethics and values
Conclusion
The entrepreneurial mindset is an important factor leading to project success. Many leading authors agree with this point of view and are researching to substantiate this grounded theory. This endeavor to bring out the factors associated with the project manager’s leadership style profoundly impacts project success.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
You can subscribe and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
You can subscribe to vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our certification Q&A series and student success stories using the link https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
For any questions related to Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com

by DharamCW | Apr 20, 2021 | General
According to the PMI (Project Management Institute), “Ethics is about making the best possible decisions concerning people, resources and the environment. Ethical choices diminish risk, advance positive results, increase trust, determine long term success, and build reputations. Leadership is dependent on ethical choices”. Ethics represent a crucial differentiator in a highly competitive market where reputation and values are highly appreciated among the Project Management Professionals.

The Time Is Always Right to Do What Is Right
Martin Luther King Jr. said, “The Time Is Always Right to Do What Is Right”. As project managers/program managers or portfolio managers, we must make critical decisions daily. Though in the evolving digital transformation world, many decisions might go unnoticed, few do get noticed, as critical ones. These decisions have a profound impact on people, resources, and the environment. Some decisions might have led to conflicts, dilemma, or the creation of new risks.
What is Ethics, and what is the Role of PMI?
Ethics is the branch of knowledge that deals with moral principles. It involves steps, including systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behaviours.
Regarding ethics at PMI, in the year 1981, the PMI team formed the PMI Board of Directors on Ethics, Standards, and Accreditation. The current PMI ethics document outlines the essentials of ethics based on Vision, Responsibility, Respect, Fairness, and Honesty. PMI expects its members to adhere to these codes of ethics to uphold its values.

Essentials of Ethics
When the whole world is fighting the COVID-19 situation, and demand for digital transformation projects is at an all-time high, PMI professionals need not ask for a better time to establish high ethical standards. Let’s understand the key challenges a PMI trained professional faces in the current digital transformation world.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is the process of using digital technologies to create new — or modify existing — business processes, culture, and customer experiences to meet changing business and market requirements.
There are four types of digital transformation: business process, business model, domain, and cultural/organizational. We often see corporations focused solely on the process or organizational transformation.
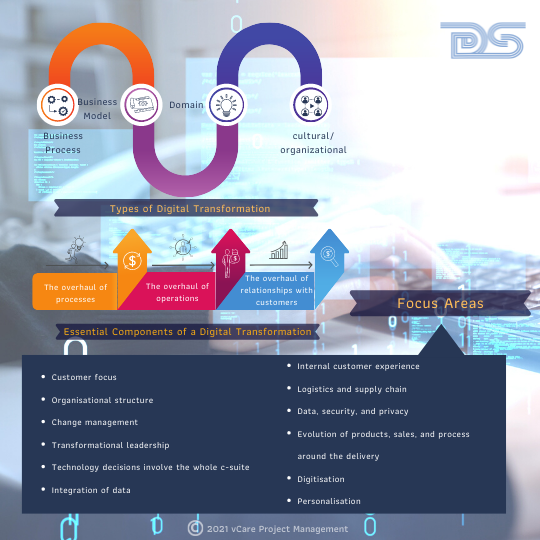
Digital Transformation
There are three essential components of a digital transformation:
- The overhaul of processes
- The overhaul of operations, and,
- The overhaul of relationships with customers.
The crucial elements that every digital transformation program needs to focus on are,
- Customer focus
- Organisational structure
- Change management
- Transformational leadership
- Technology decisions involve the whole c-suite
- Integration of data
- Internal customer experience
- Logistics and supply chain
- Data, security, and privacy
- Evolution of products, sales, and process around the delivery
- Digitisation
- Personalisation
The key aspects of the digital transformation world could have a major impact on Ethics.
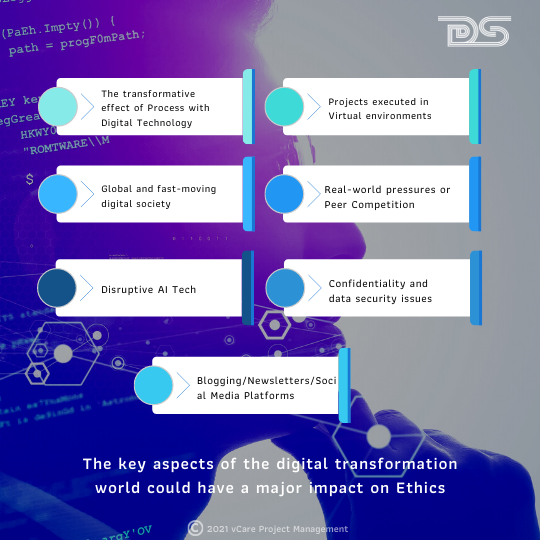
Major impact on Ethics
The transformative effect of Process with Digital Technology: Award-winning Author James Moor in 1985 mentions the transformative effect Digital Transformation could create. He cites the example transformation of manual votes to Electronic Voting Machines, which might benefit from speed and accuracy. On the contrary, it could impact security, vulnerability, transparency, and trustworthiness related issues.
Projects executed in Virtual environments: Today, the projects get implemented in remote places – Home/Office/Small Office combinations. People are working from remote, and it has become the new normal. People significantly use collaboration tools and in some occasions even communicate using social media, which could be manipulative.
Blogging/Newsletters/Social Media Platforms: Professionals tend to share the experience and insights reflecting upon the work ecosystem. Either sharing happens as an experience in a newsletter or a blog post, or it could be even a Twitter thread or a simple tweet reflecting a view. This act is typically done by those who tend to be expressive even within a professional organizational setup.
Global and fast-moving digital society: Communications spread very fast, and a diverse global culture leaves very little control. Digital technology, which is supposed to help leverage, could turn dangerous. The expectation for responsiveness sometimes leaves very little room for interpretation.
Real-world pressures or Peer Competition: Today’s real-world information sharing creates unwarranted peer pressure. This pressure might develop dilemmas and force individuals towards adverse decision-making. Sometimes, due to competitive peer pressures or financial pressures, even the employees’ health and safety concerns might get overseen.
Confidentiality and data security issues: Enhanced digital transformations across the globe have made data exchange easier. In the case of a data expose, it is vital to understand what is exchanged and what is the importance of the exchanged data. Lack of understanding of the data classification at appropriate levels could become risky when the proper accountability level could not be ascertained.
Disruptive AI Tech: Disruptive AI tech such as Chatbots, Speech Recognition Systems, etc., has made the way we think of data and decision making. Too much dependence or flawed inference might have an impact.
Ethics focus on PMIs Performance Domains & Digital Transformation
When a portfolio/program/project vision is established and defined, observable outcomes between the current state and future state as part of the digital transformation must be counted in. The key components that would impact the above said performance domains would be done with re-imagination, cultural change, and cross-functionality.
Digital transformation might have changed in a newer business model, new product focus, and a more contemporary way of working. Digital transformation is about getting the technology right and building necessary support and buy-in from the people managing resistance. Business processes need to be horizontally redesigned to enable collaboration across the teams.

PMI’s Program Management Standard
PMI’s Program Management Standard defines five performance domains that can be integrated with ethics, giving a significant shift in ethics adoption, and may help in improving overall digital transformation initiatives. They are:
- Benefits Management: Benefits profile, which would be based on outcomes and measurement, has to have the ingredients of the ethics as well.
- Strategy Alignment: Strategic alignment to focus on the changing business environment and strategic targets on digital transformation must be governed through ethics.
- Governance: Governance focus and establishes control related to programs. Governance would bring discipline and ethics into the broader organizational structure.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Stakeholders to be kept well informed on the ethical aspects of getting involved whenever any changes in stakeholders.
- Program Lifecycle: Given a structure and suggested flow for a program, the ethics principle has to be adopted to address dilemmas related to circumstances of a business and initiative.
5As Decision-Making framework
PMI has recommended the 5A’ss decision-making framework outlines with Assessment-Alternatives-Analysis-Application-Action. The 5A’s assessment helps to collate all the facts about the ethical dilemma. It considers all your choices. Subsequently, decision candidates are identified and tested for their validity. Apply these principles to the candidates and make the final decision.

5As Decision-Making framework
The decision-makers, when they adopt the 5A decision-making framework, the following checklist:
Assessment
- Does it adhere to the law?
- Does it comply with PMI code of ethics ?
- Does it comply with the organization code of ethics?
- Does it comply with the professional conduct ?
- Does it comply with the ethical values and culture of ecosystem?
Alternatives
- Whether alternatives are listed ?
- For the given choices do we have pros and cons ?
Analysis
- What kind of impact it would make ? (Positive/Negative)
- Does it count in cultural differences ?
- Is this decision taken considering long term impact ?
- Is this decision taken without any external influence ?
- Were you calm and unstressed during this decision ?
Application
- Will the decision be for larger good ?
- Has the decision is without any bias ?
- Is this fair for all concerned ?
Action
- Will you take responsibility ?
- Would you be ok to make your decision public ?
- Are you ready to act ?
Benefits:
When the portfolio managers and program managers adopt the above-said approach outlined in the PMI code of ethics, it provides the following benefits:
- Elevates the profession and raises future standards
- Increases the faith and trust among peers
- Imprints on individual moral mindsets and behaviors
- Improves business relationships across the board
- Promotes fair decision making
- Reduces project risks
- Reduces anxiety and stress and ultimately turnover in projects
Conclusion
Transparency and integrity must be the core values which has to be established by the professionals. The data must be used in responsible and ethical ways during the digital transformation initiative. Data collection has to be based on the ethics principle called “Informed Consent.” The actions cannot be intrusive, manipulative, or disrespectful to others.
Trust must be established among the individuals, groups, or organizations involved in the digital transformations. This trust can be created by establishing data provenance, traceability from the source to the user interface. Program managers or portfolio managers have to act without any bias and with a high level of integrity and impartiality. The same has to be established for the clients, suppliers, and subcontractors without any favoritism and giving them an unfair advantage.















Recent Comments