
by DharamCW | Sep 26, 2024 | Leadership in Project Management
Project management is becoming an essential component of modern business operations. Organizations increasingly use project management to monitor and assess projects and ensure they meet their objectives. Project management entails several complex processes, including project planning, organization, management, control, budgeting, monitoring, testing, and implementation.

Vance Packard Quote
Project leadership is the art and science of guiding a team to successful project completion. When project leadership brings people together to work toward a similar objective, the team can do more than they could individually.
Project Management Leadership
Leadership in project management is a necessary ability for completing the project. Like in other business areas, leadership necessitates demonstrating several talents and behaviors in a project context. Leadership is essential to ensure the success of the projects, from team leadership to project governance.
Leadership and project management are closely intertwined. Setting the vision and encouraging the team to work together to accomplish the project goal are vital components of leadership. In a project environment, this is particularly significant. Delivering any project requires a team effort. While some teams work without a clear leader, in business, it is customary for someone to be in the leadership role, guiding and directing the team toward their goals. On the other hand, project management systematically applies processes, methods, knowledge, skills, and experience to achieve the project objectives. Effective project management often requires strong leadership to guide the team through the project’s complexities and challenges.
5 Essential Project Leadership Skills
Project managers execute allocated project tasks through their project teams. They learn the technical, business, and leadership skills to manage their project teams effectively. In addition, they use strong leadership skills to motivate their teams to complete project deliverables and achieve project goals.
Project managers’ essential leadership skills begin with encouraging and inspiring their teams. However, the five critical project leadership skills are equally vital in enhancing team performance.

5 Essential Project Leadership Skills
- Communication
One of the most important project management skills is communication. Leaders must communicate effectively because a significant portion of their work includes collaboration. If you can communicate, you can collaborate properly.
Leaders can communicate ideas to people and groups in person, over the phone, or via web conferencing. They can also present their ideas to ensure the message is shared and understood. However, communication is more than just passing on messages and conversing with people. Communication is one of the most important characteristics of a project manager, especially in a leadership role.
- Team leadership
The leader establishes the vision and motivates others. Someone with outstanding project leadership skills fosters team agreement and togetherness while managing day-to-day operations.
Team leadership on projects entails establishing an environment in which everyone may thrive. People are lured to the project culture that surrounds them. Stakeholders want to be part of the project because they know you will complete the task while creating a pleasant working environment.
- Conflict resolution
Conflict is unavoidable when introducing or modifying something. However, effective leaders understand how to use conflict to their advantage since the finest solutions emerge when ideas are challenged.
Conflict may benefit teams by allowing all voices to be heard and opposing viewpoints to be expressed, frequently resulting in a better solution and more successful project outcomes. However, leaders must be equipped with conflict resolution skills to recognize and address conflict before it becomes a problem for the team. Therefore, another crucial core competency of project management is dealing with conflict in various ways.
- Motivation
Leaders motivate others to act even when they are not technically in charge. As a project manager, one determines what makes the other team members feel they’re giving their best. The project leader should do their best to deliver this. Everyone is driven differently, and motivation changes over time. Great leaders see these disparities and establish a great work environment to enable their workers to achieve their full potential.
- Crafting solutions
Empowering the team and the larger stakeholder community to participate in developing solutions is part of fostering a positive working culture. That entails removing roadblocks so that each team member may fulfill their work and contribute new ideas without concern about something getting in the way.
Empowering leaders also allows them to make decisions down the hierarchy to the lowest feasible level, allowing specialists to judge the solutions required to keep the project going. This empowerment fosters a positive working culture and inspires team members to take ownership of their work and contribute to the project’s success.
Leadership Styles and Theories
There is no single style to leadership, nor is there a particular type of person who makes a great leader. Instead, according to project leadership theory, a great leader is a mix of traits and the capacity to adapt to diverse conditions. This adaptability reassures individuals that leadership is not a fixed trait but a skill that can be developed and enhanced.
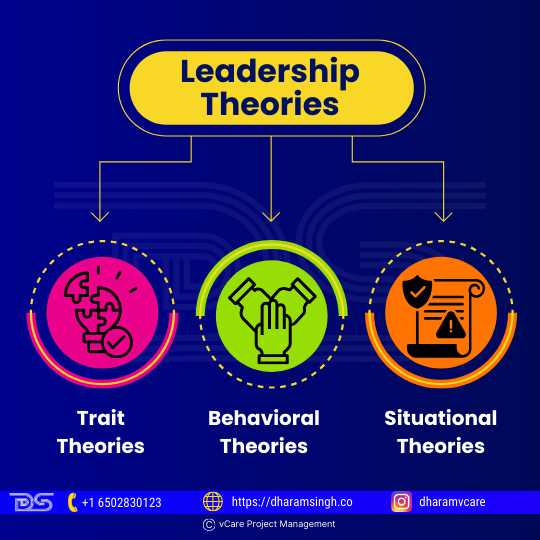
Leadership is something one can learn, and one can enhance one’s talents by understanding leadership theories in management. The three basic leadership theory categories that apply to project delivery are:
Leadership Theories
- Trait theories
Project manager strengths are related to trait theories. This perspective on leadership identifies the abilities and attributes that are beneficial while leading a team. Resilience, honesty, trustworthiness, aggressiveness, and so on are examples.
There was a system of thinking that stated certain characteristics were innate and that you were either born with them or not. Fortunately, this notion is no longer present in leadership concepts and theories. We know that an individual can act to become more aggressive and resilient or develop any other leadership trait.
- Behavioral theories
Behavioral leadership theories concern what a leader does. For example, some Corporate leaders are dictatorial and make decisions without consulting their employees. Others are more collaborative, inviting feedback and empowering their employees.
Both strategies are acceptable, and any combination of the two. However, there is a time and place for every style: you wouldn’t expect a combat leader to order a huddle so the team could discuss possibilities, would you? In that case, a choice must be taken immediately. Thus, a collaborative, listening leadership style would better engage the community.
- Situational theories
Situational leadership is deciding which leadership style to employ in any given scenario. These leadership theories are often known as contingency theories.
They analyze whether using a task-based or a people-based approach is more effective. They also take into account the individuals you lead. What type of encouragement and support do they require? A leader tailors their leadership style to the demands of the team, the business environment, and project circumstances. Someone who has never done specific work before will require more hands-on assistance from their team leader than someone confident in completing that activity.
Project Management Leadership Styles
Leadership in project management is essential for success. A project is a substantial and necessary endeavor in any business organization that requires full concentration and dedication from all participants. The success or failure of any business project can influence the company’s path. Project management is a critical role that may be entrusted to anybody, especially in today’s technology-driven business environment, where change is inescapable.
The ultimate success of every project is determined by project leaders, who have the authority to manage and oversee all project activities and make critical project choices. Similarly, failure to accomplish project objectives is the responsibility of the project’s leaders or management. Failure or inability to use the authority conferred upon them to ensure the project’s success is regarded as a point of accountability.
It is important to note that any project a firm does should strive to achieve certain goals that will enhance business operations and increase profitability, performance, output, and overall success in its objectives. As a result, project management is a critical function that leaders and anybody charged with project leadership must take seriously and utilize their effective leadership skills to ensure success.
Here are the six important project management leadership styles.

Project Management Leadership Styles
- Affiliative Leadership
This leadership style has a positive impact on a project team. This leader aims to create emotional bonds inside the organization to generate a sense of belonging and connection. When teammates require personal assistance or the team has to rebuild trust, the affiliative strategy is most successful. Because a single focus on praising and nurturing may result in poor performance and a lack of direction, this strategy should be used in various ways.
- Authoritative Leadership
Authoritarian leaders generate an entrepreneurial spirit and a strong devotion to the cause. Moreover, the traditional method works effectively when the team needs a new vision owing to changing circumstances or when clear guidance is unnecessary. Therefore, more utilization of this style would result in better project team outcomes without negative consequences, as this style has a generally positive effect throughout the organization.
- Coaching Leadership
This project management approach encourages team members to expand their capacity and capability as project contributors, which benefits the whole project team. This approach is the most effective coaching technique when a leader wants to assist colleagues in creating long-term personal characteristics that will help them succeed. However, it falls short when teammates are relentless about staying the same or learning or when the leader needs more aptitude.
- Coercive Leadership
Project managers rarely use this tactic, which would be more evident in times of crisis, such as when a project deadline was approaching and at risk of being missed.
- Democratic Leadership
This leader achieves successful compromises through teamwork. In a PMO, for example, each team member contributes to defining and measuring the PMO’s objectives. When the leader wants the team to buy into or own a decision, strategy, or goal, or when they are unsure and need new ideas from competent colleagues, the democratic method works well.
- Pacesetting Leadership
This leader anticipates self-management. The pacesetting approach works most effectively when the team is already motivated and talented and the leader demands quick results. This approach is popular, especially when a project nears major milestones. Although this method generally harms project teams, it can be beneficial in some situations.
Impact of Good Leadership on a Project
Many studies have highlighted leadership as one of the key reasons for project failure. On the other hand, projects with strong leadership and organizational support outperform those without.
Impact of Good Leaders on a Project
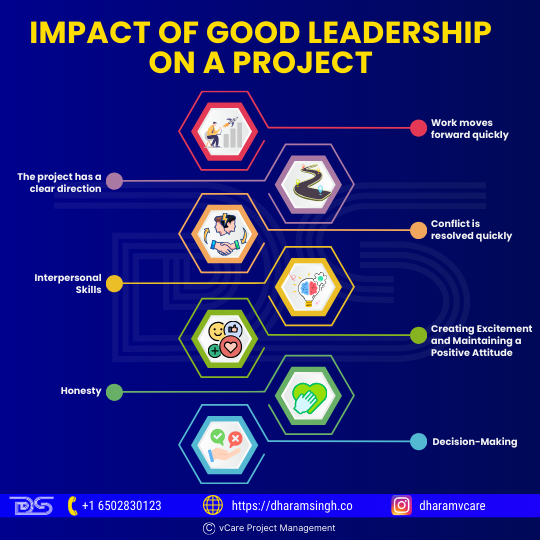
- Work moves forward quickly
When an individual actively leads, the work proceeds quickly as the choices are made on time. This move allows the project to be completed on schedule while delivering all planned project scope elements.
- The project has a clear direction
A leader ensures that the team knows and supports a common goal. A clear direction gives context for decision-making and ensures that everyone knows what the project will deliver.
- Conflict is resolved quickly
The project leader is constantly looking for conflict and can intervene to handle it before it escalates into a crisis.
- Interpersonal Skills
Project leaders must have interpersonal skills such as questioning, listening, and speaking to establish successful and compelling interactions with team members.
Experts in project management believe that projects are more likely to fail if project managers lack excellent interpersonal skills. Because much of a project manager’s duties involve communicating with stakeholders, one must have great interpersonal skills to lead from the front.
- Creating Excitement and Maintaining a Positive Attitude
The most crucial project manager leadership skills are boosting team members’ enthusiasm and displaying an optimistic attitude, especially in times of crisis. In addition, project management and leadership are about instilling trust in teams that there will always be a solution, no matter how serious a situation is.
- Honesty
When defining ethical guidelines and supporting transparency in communication, project manager leadership skills should embrace honesty.
Honesty and integrity are two fundamental traits of project management leadership that project managers should cultivate to increase trust among customers, members, management, and other stakeholders.
- Decision-Making
The project manager has the last say in simplifying processes and solving difficulties. As a result, the project manager’s capacity to make informed judgments is a critical function of leadership in project management.
Decision-making is an important project manager leadership skill that directly influences project outcomes. Therefore, to advance in their careers, all prospective project management professionals must master decision-making abilities.
Leadership mindsets are driving the new economy
Mindsets are mental maps that reflect and govern how individuals act in organizations. They convey how individuals work and what they stand for. So, what leadership characteristics do respondents and experts believe are necessary for success in the digital economy? World Economic Forum survey data states four leadership mindsets driving the new economy: producers, investors, connectors, and explorers.

Leadership Mindsets Driving the Digital Economy
- Producers
The producers’ mindset blends with creating consumer value, emphasizing analytics, digital savvy, execution, and outcomes. Producers use analytics to expedite innovation that addresses shifts in customer preferences and enhances customer and user experiences.
- Investors
Leaders with an investor mindset seek a purpose for their firm beyond improving shareholder returns. They are committed to growth but in a sustainable way. They are concerned about the areas in which they operate, their personnel’s welfare, and ongoing development. They focus on increasing the value of their clients rather than treating them as money sources.
- Connectors
Leaders with a connector’s mindset see that mastering connections and networks is the new currency driving corporate performance in the new economy. Connectors understand this fundamentally. It’s how they work. They constantly bring various stakeholders from within the organization and ecosystem partners together. Connectors recognize the importance of building a feeling of community and belonging, which is especially vital in today’s fast-paced, breakneck-speed world when losing contact with the human touch is too easy.
- Explorers
Leaders with an explorer’s mindset are curious and innovative and thrive on ambiguity. They constantly experiment and learn by listening to a wide range of voices. Establishing behavioral standards encouraging risk-taking and failure, reverse mentorship, and a deep curiosity about how new forces shape the competitive environment are strong indicators of an explorer’s attitude.
Final Thoughts
Project management is a demanding task requiring effective leadership styles and traits for the project’s overall success. Successful project leadership involves team building, adaptability, communication, and effective planning skills. As a result, leaders play a fundamental and crucial role in project management since their approach decides whether a project will succeed or fail.
Project management is different from leadership. Successful project managers may need to be more effective leaders. However, they can learn leadership qualities and become successful leaders. In today’s firms, competent project managers must also be strong leaders. Successful project managers may use their innovative and creative capabilities to assist them in acquiring leadership skills that will complement their project management abilities by recognizing the difference between project management and leadership and adopting the road to becoming influential leaders.
The common component of project management and leadership is the standard by which the project manager and leader’s performance is judged. A project manager’s success and a leader’s effectiveness are evaluated in terms of the performance of the followers—the team’s performance. As a result, improving project managers’ leadership skills with an emphasis on abilities to increase team performance should be a key factor.
Leadership is critical in project management and must be balanced. It impacts project success and the value offered to the organization. The good news is that the finest project management training incorporates leadership concepts, providing employees with a well-rounded understanding of what it takes to lead a project.
With advanced certifications like PMP®, Agile, PgMP®, and PfMP® certifications, one can develop project management skills, be a good problem solver, be a more competitive candidate for positions, and be a successful project leader. In today’s competitive business world, one must be skilled and experienced to succeed and grow their career.

by Dharam CW2 | May 19, 2023 | General
Emotional intelligence in the workplace is becoming increasingly important for leaders and project managers as remote work became more prevalent due to the pandemic. Success in project management and managing cross-functional remote teams is only possible with emotional intelligence.

Capterra Survey
According to a Capterra survey, emotionally intelligent project managers (PMs) are approximately 11% more successful at managing processes, engaging stakeholders, avoiding scope creep, and efficiently using resources than PMs who lack this skill.

Emotional Intelligence
What is Emotional Intelligence?
Emotional intelligence refers to our ability to recognize, control, and communicate emotions. People with high emotional intelligence understand how they feel, what their feelings imply, and how their feelings affect others. In interpersonal situations, it is also the ability to empathize with others. Emotional intelligence is about creating a positive work environment, which is critical to the success of any project.
As Per LiquidPlanner Study
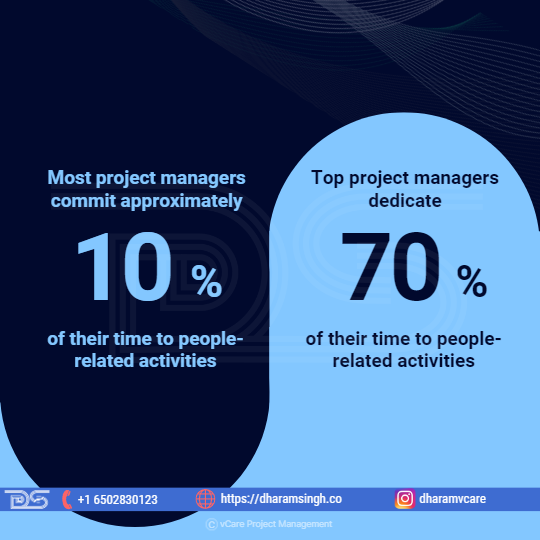
According to a LiquidPlanner study, most project managers commit approximately 10% of their time to people-related activities. Top project managers dedicate 70% of their time to these activities. As a result, we can conclude that emotional intelligence is crucial for project success.

Importance of Emotional Intelligence for Project Managers
Importance of Emotional Intelligence for Project Managers
- Emotional intelligence is essential for leading cohesive, high-performing teams.
- According to researchers and behavioral scientists, Emotional intelligence impacts how leaders communicate with their teams and how team members interact.
- Emotionally intelligent leaders and managers understand how to control their emotions and behavior at work, which includes providing safe environments for exchanging ideas and feedback, productive teamwork and performance, good morale, employee engagement, and job satisfaction. They manage workplace stress and conflict with care and educate their team members to do the same.
Characteristics of Emotional Intelligence
What can project managers do to help themselves develop and become more aware? First, let’s examine five abilities for raising emotional intelligence:
- Self-Awareness – The ability to sense, identify, and comprehend emotions is self-awareness. Unfortunately, many of us were taught to ignore our emotions in the past. However, it is critical to be aware of your feelings to make appropriate decisions and act accordingly. Those with high self-awareness are self-assured, authentic, open to feedback, and capable of maintaining perspective throughout all project phases.

Characteristics of Emotional Intelligence
- Self-Management – Self-management is the ability to reason well while understanding feelings. Many frequently react based on their frame of reference rather than selecting a response based on their current unique circumstances. Self-managers are deliberate in decision-making, taking the initiative, framing events appropriately, maintaining perspective, and responding quickly. They understand their feelings and why they have them and effectively manage their responses.
- Self-Motivation – Self-motivation is the ability to channel the power of your emotions toward a specific goal. When project teams have a purpose, these ‘P’s follow peace, passion, power, perspective, and potential leverage. Self-motivators who are influential are optimistic and have a positive attitude. They can delay gratification and assert themselves.
- Interpersonal Management – The capability to identify and respond properly to the emotions of others is referred to as interpersonal management. If you can connect with people and acknowledge their humanity, they will answer openly, leading to common trust.
- Leadership – An emotionally intelligent project manager inspires guides, challenges, and supports the team. Leadership is defined as the ability to create and communicate vision and passion for assisting individuals and organizations in reaching their full potential.
Tips for improving Emotional Intelligence
Tips for improving Emotional Intelligence
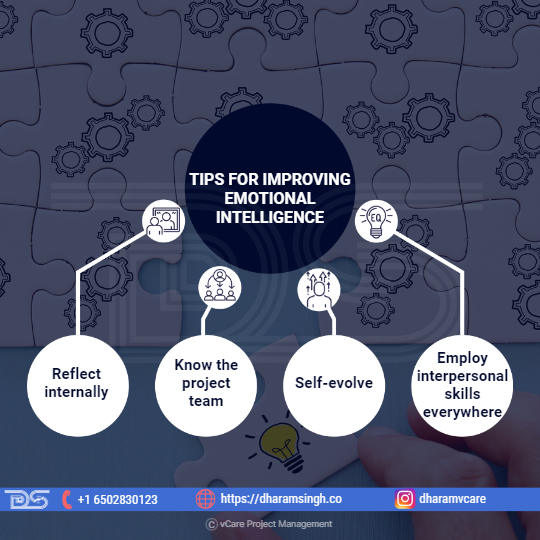
- Reflect internally – To become more emotionally aware, one must first understand their emotions and then regulate them in stressful situations. Next, they have to figure out what motivates them. Finally, authenticity is necessary to develop emotional intelligence by leading a successful project team and establishing meaningful relationships with stakeholders.
- Know the project team – Project managers are usually aware of the people they must contact when working on a project. However, understanding the project team, from team dynamics to personalities to dealing with conflict and stress, is just as important. To improve emotional intelligence, one must first get to know their team, communicate with them, and understand their emotions. It will also help the success of their project. This job becomes even more important for teams that operate in multiple locations and are diverse.
- Self-evolve – Along with other important leadership talents, project managers should work to improve their emotional intelligence regularly. Conditions surrounding a project frequently change; its scope may shift, the number of stakeholders may increase, and projects may eventually end.Every project is distinct, and no project manager can complete a project independently. Therefore, it is advantageous for project managers to consider what they learn during and after a project. For example, consider how a project team operated, what they witnessed during critical times with stakeholders, and their team’s performance.
- Employ interpersonal skills everywhere – Emotional intelligence can be helpful in almost any project management situation. For example, people may feel compelled to sign off on a strategy to minimize delays while managing scope changes or project risk. Following the resolution of such issues, an emotionally intelligent project manager would pursue people because they notice that this could lead to more severe problems in the future.
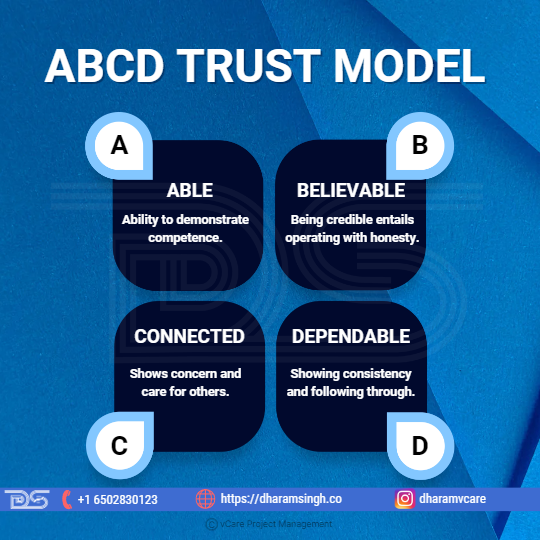
ABCD Trust model
ABCD Trust model
Better relationships will result in better outcomes. That is why developing trusted connections is critical to the success of your organization. When individuals trust one another, they may work efficiently together.
It is well known that low trust harms morale, productivity, and turnover. To prevent these traps, Ken Blanchard created the ABCD Trust Model to help executives understand the activities that affect creating trustworthy relationships.
Blanchard suggests four critical aspects for leaders to develop trust with people: Able, Believable, Connected, and Dependable.
- Able – The term able refers to the ability to demonstrate competence. Leaders demonstrate competence by possessing the necessary skills, education, credentials, and experience. They also exhibit their capacity to lead by accomplishing achievements. Able leaders can encourage people and collaborate with them to achieve goals.
- Believable – Being credible entails operating with honesty. Believable leaders adhere to a set of core beliefs. They know what they stand for and will not compromise their principles under pressure. Being credible also means maintaining promises and not lying or stretching the truth.
- Connected – Connected shows concern and care for others. This aspect fosters trust and contributes to a more engaged workplace atmosphere. Being linked entails attending to people’s needs and promoting their well-being. Leaders also build relationships by giving information not only about the organization but also about themselves. Employees are significantly more likely to provide their best effort when they feel linked to leaders.
- Dependable – Dependable means showing consistency and following through. It entails holding oneself and others accountable for commitments. A trustworthy leader will accept responsibility for their acts and help their followers face adversity.
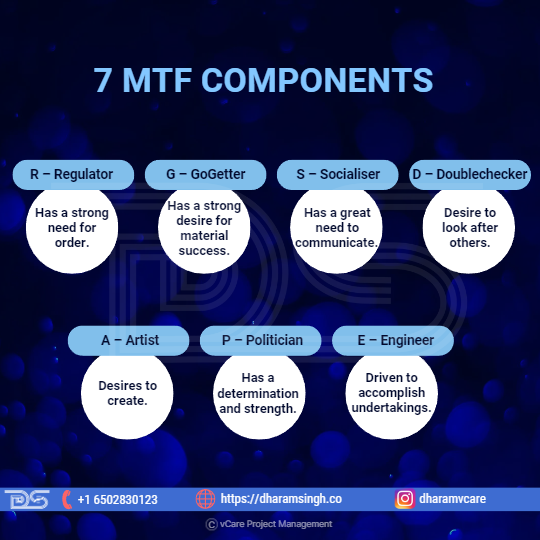
7MTF Components
7MTF Components
The 7MTF model is composed of seven components. We all have all 7 in our personalities; as adults, 2 to 4 will be strong, some will be weak, and others will be ordinary. This mix of elements is one of the most significant variables in deciding our temperament – our emotional predisposition.
- The R – Regulator (formerly known as the Normal) – A person with a ‘strong R’ has a strong need for Order. They will be mature, responsible, calm, and emotionless. You may hear the words ‘should,’ ‘ought,’ and ‘logical’ in their language. They have high expectations of themselves and others, including those with whom they live and work.
- The G – GoGetter (formerly known as the Hustler) – A person with a ‘strong G’ has a strong desire for material success. This individual entails enjoying money and the things it can purchase. The G is quick, opportunistic, intelligent, enterprising, and charming. They are short-term in nature, expecting results immediately or very soon. Promising a G a large monetary reward next year is unlikely to pique their attention.
- The S – Socialiser (formerly known as the Mover) – The ‘strong S’ personality has a great need to communicate. This aspect implies talking about people, fun, events, what you did over the weekend, or anything related to life. Hence, their straightforward, friendly, and frequent grin immediately.
- The D – Doublechecker – The ‘strong D’ is characterized by a desire to look after others and ensure everyone is safe. When you encounter a strong D, expect someone obedient, loyal, and concerned with doing the right thing. One of their greatest assets is their ability to anticipate difficulties and hazards.
- The A – Artist – A person with a ‘strong A’ desires to create. “I want to be different,” is what they would say. These hardworking individuals are conscientious and do not wish to offend anyone. Seek for anything unusual about their attire, such as innovative earrings, cufflinks, a six-button jacket, or an all-black ensemble!
- The P – Politician – A solid handshake and direct eye contact indicate that the ‘strong P’ is determined to win. This person has a determination and strength that others may find challenging. The spoken word is the strong P’s stock in trade – look for status markers like the huge Mercedes in metallic blue.
- The E – Engineer – A person with a ‘strong E’ personality is driven to accomplish undertakings. The strong E has traits such as process, detail, and procedure. This individual can form a strategy and make it happen as soon as they see anything. The E is concerned with completion. So, unless you can assist, you should avoid getting in the way!
Wisdom – strive for mental stability and individual resilience – 10 Competencies
Wikipedia defines wisdom as the “ability to contemplate and act using knowledge, experience, understanding, common sense, and insight.” Psychologists have created a list of ten competencies that are typical therapies in their field and are referred to as wisdom. Self-awareness, self-control, and empathy are the three components of emotional intelligence (EI). Although the fourth component of EI is not formally mentioned among the ten competencies, social influence or influencing others may be considered a result of being highly effective in the other areas.
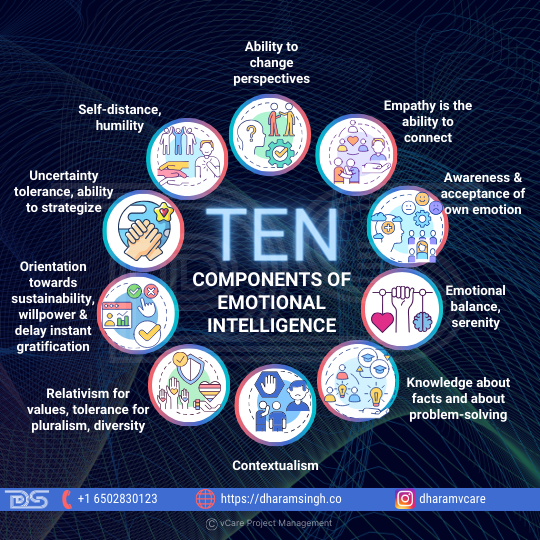
Ten Components of Emotional Intelligence
- Ability to change perspectives – In a bipolar environment, it is possible to remain trapped in one thought and dislike the other viewpoint with strong emotions, which may lead to violence. The ability to look for and identify more points of view implies a shift in viewpoint. Some of the therapies used to treat mental illnesses can help with this. Examples include role-playing, acting, visiting people in various countries, learning about diverse cultures, and brainstorming.
- Empathy is the ability to connect – Understanding people’s intentions, current state of mind, emotions, and mindsets is necessary for being heard, establishing trust, and influencing others. In addition, active listening techniques may help you focus outside yourself and view others as humans who vary from ourselves.
- Awareness & acceptance of own emotions (self-awareness) – Self-awareness leads to increased self-confidence and sincerity. It refers to mindfulness, or being aware of one’s feelings, and is required for self-control and emotional balance.
- Emotional balance, serenity (self-control) – Patience, serenity, and avoiding knee-jerk reactions make you more popular and respected and contribute to mental tranquility. Having a mentor can help you develop and fine-tune this skill.
- Knowledge about facts (know what, assimilation) and about problem-solving (know-how, accommodation) – Wisdom includes knowledge; therefore, it has two components.
- On the one hand, we have factual knowledge about a topic; on the other, we may be specialists in a (typically technical) area. This heuristic knowledge and assimilation are how we apply established systems to circumstances.
- On the other hand, when we encounter new situations or topics, we use accommodation to apply our problem-solving skills. We employ our epistemic intelligence and heuristics to do this.
- Contextualism (consider the situation, timeline, and social relevance) – Even though we have theories and may find similarities in new scenarios, each situation is unique and depends on the circumstances, the context in which the problem develops, and the societal importance. This capacity is achieved via awareness and avoiding picking a solution that works in another context without first examining the present dependencies of the situation.
- Relativism for values, tolerance for pluralism, diversity (which is hard if you are part of the same belief systems for most of your life, like nations and churches) – There are many truths (this is known as non-monism), and yours is only one of them. Others have the right to their realities, which are based on the cultures in which they live, their beliefs and experiences, and the facts to which they have access. Value relativism allows one to accept and appreciate the values of others.
- Orientation towards sustainability, willpower, and delay instant gratification (perspective of linear and circular time flow) – We can pursue long-term goals and make decisions with both short and long-term consequences in mind.
- Uncertainty tolerance, ability to strategize (imaging solutions for scenarios) – Accept that life is unpredictable and swim through it like a river, adapting to currents and waves as they come.
- Self-distance, humility – Do not believe you are the center of the universe, which will remain when you die. Avoid being a taker rather than a giver by avoiding jealousy, bragging, pride, and greed.
Final Thoughts
For today’s project managers, emotional intelligence is a critical concept. Many companies are looking for project managers with strong technical and soft skills. Emotional intelligence is crucial in project management because it enables project managers to improve communication and collaboration in the workplace. It is essential to mention that emotional intelligence can be imparted and nurtured. This aspect implies that as a project manager, one can better oneself by controlling feelings and emotions and developing positive behaviors to influence others at work. One will make better decisions about other people’s emotions, strengths, and weaknesses once they have recognized their thoughts.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Apr 21, 2023 | General
What makes a successful Project/Program/Portfolio Manager? Is it the number of years of experience? Technical know-how? Or the one who is good at managing people?
Creating objectives, critical path analysis, work breakdown structures, resource scheduling, and risk management are just a few of the technical areas of project management that project managers usually get training in. However, understanding pertinent people and management issues is important to a project’s success. In addition, a project manager must also continually deal with clients and other stakeholders. As a result, project managers’ people skills, also known as soft skills, are becoming increasingly important.

People Skills
People skills
People skills are linked with behavioral patterns or behavioral interactions that assist one in communicating effectively with people. Project leaders with strong people skills may favorably influence others, socialize effortlessly, and overcome public anxiety.

Project Leaders With Strong People Skills
They are transferrable social abilities that allow one to collaborate well with others. The three main types are personal, interaction, and interpersonal skills. These categories achieve the same overall objective: making the working connections with others mutually satisfying, pleasant, and productive.
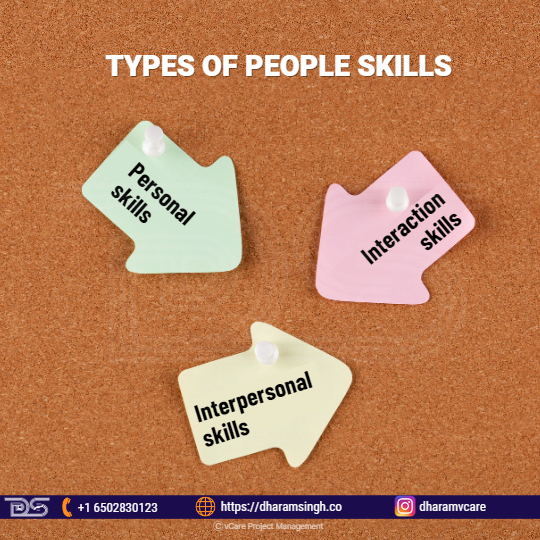
Types Of People Skills
Types of People Skills
- Personal skills: These include the capacity to communicate your skills and exhibit yourself to others successfully. It comprises characteristics such as self-assurance, honesty, and aggressiveness. Furthermore, one must be able to recognize their limitations and make sound judgments based on logic rather than emotion.

Personal Skills
- Interaction skills: It is essential for understanding the behavior and ideas of others while preserving limits and creating connections. A project manager, for example, should have social etiquettes that need empathy and listening skills to know that you have listened to them and given respect for their limits and requirements to connect with co-workers and clients productively.

Interaction Skills
- Interpersonal skills: These are related to intercession skills, but they apply mainly to situations in which the persons involved have opposing interests or viewpoints.
Contrary to popular belief, people skills are not subjective concepts. On the contrary, these skills are critical, particularly in the project management role, which is largely concerned with people.

Interpersonal Skills
Project management is more than just completing the project; it is also about how you lead and assist your team. Leading others and leading them through the whole project lifecycle entails a certain amount of responsibility and necessitates certain abilities.
Furthermore, as work evolves, businesses embrace a varied workforce. As a result, people skills are essential for embracing tolerance and diversity. In short, good project management is based on human communication and connection.
Essential People Skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers
A successful project professional must possess a wide range of skills. Those that come to mind first are the technical skills required to create a project plan, schedule, budget, and all relevant paperwork. One must also have the conceptual skills to “see” the project as it develops.
However, such talents will only assure project success if the project manager can supplement their technical skills with a wide range of interpersonal skills or people skills. Here are some of the essential people skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers:
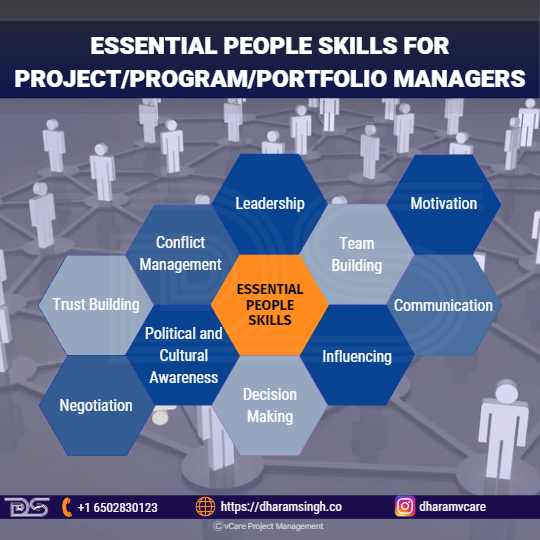
Essential People Skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers
- Leadership
One of the crucial skills a successful project manager has to have is leadership. This skill is essential because the project manager frequently has little control over the team members involved. This aspect calls for leadership on their part to handle the project. Although managing via leadership rather than authority might be more challenging, it is typically more effective since it is based on respect and trust.
At the start of a project, a leader must establish their vision and express it to the team. It makes supporting the project’s objectives easier for everyone on the team. Effective leadership will also keep the team members inspired and motivated to perform at their highest level.
- Team Building
Another vital skill for a competent project manager is team building. Because of the nature of projects, personnel from diverse departments are engaged. Most employees might have never worked together and may not even be familiar with one other’s departments. If the project manager can unite these individuals into a cohesive team with the same goal, the project may stay within its objectives.
Although some of the project’s individuals or sub-teams may execute their jobs individually, they must feel like they are part of the overall team. When choosing their part of the project, they must consider what is best for the project, not simply what is best for them and their departmental problem. A sense of belonging to a team that solves an issue for the entire company (rather than playing departmental favoritism) may go a long way.
Creating a team in which each member feels comfortable reaching out to the others will also guarantee that minor problems do not escalate into major concerns later in the project. It is consequently critical that project managers not only understand the duties and procedures involved in team building but also have the skill and finesse to apply them correctly.
- Motivation
If you want your project to succeed, you should concentrate on improving your motivating skills. Having these qualities will assist your project team members to stay interested in the project, strive for excellence, and work toward a common objective.
Good motivating skills will enable a project leader to create an environment where team members can fulfill project objectives while being satisfied with their work.
- Communication
Most professions require excellent communication skills. Some project managers believe the communication part of project management to be their primary job obligation.
Excellent communication skills are essential for building relationships among project team members, establishing trust, and keeping everyone motivated and on track.
A project involves several stakeholders informed of its status, timeframes, progress, risks, and concerns. A skilled project leader must convey all of these facts to project stakeholders on time and in the manner they anticipate. Project managers must also interact effectively with top management within their business.
Giving the interested stakeholders too much or not enough information might prevent the project from reaching its full potential.
- Influencing
It is critical to be able to influence people if you want to be a successful project manager. But what is important is understanding when and how to utilize such skills and avoid becoming a manipulator. There is a narrow path to follow.
A project manager’s responsibility is to bring employees from disparate departments together and get them to work together toward a similar objective. Sometimes, getting these diverse people to comprehend and agree on the specifics of achieving that goal might not be easy. A skilled project leader will utilize their skills to persuade others and assist them in reaching an agreement.
So, think about your relationship and influence over people not just for the time of the project but also for how things will proceed long after the project is complete. After the project, customers and end-users will utilize the goods, deliverables, and outcomes developed by the project. A powerful and positive effect creates a trusting atmosphere among all team members during and even after the project.
- Decision Making
A successful project manager must acquire various talents, one of which is decision-making skills. There are four primary decision-making styles: Directive, Analytical, Conceptual, and Behavioral. Project managers should be conversant with all four since either has to be leveraged at some time. In addition, consultation, consensus, command, and random styles are provided.
Having a decision-making model will facilitate this process. In addition, since so many people who may disagree with a decision are involved in the project, having a process to follow can be very helpful in gaining consensus with the group.
- Political and Cultural Awareness
In today’s world, project managers work in a more globalized context than in the past. As a result, cultural diversity is another critical component of effectively navigating the corporate world as a project leader. A successful project manager must be able to notice and comprehend cultural differences and incorporate them into the project plan.
Cultural differences can impact decision-making and the pace with which work is performed. It can also lead to members acting without sufficient forethought. Recognizing cultural differences can lead to conflict and stress within the project, further delaying it.
Furthermore, it is critical to understand the politics at work in the project environment. The use of political skills can greatly aid a project manager’s success. More significantly, failing to recognize the politics involved can lead to substantial challenges and impediments that can cause a project to be delayed or even destroyed.
- Negotiation
The nature of a project manager’s work necessitates being skilled negotiators. Typically, several stakeholders are involved in the project, and most projects include team members from many departments. This aspect frequently leads to a variety of points of view, which can make it challenging to keep the project on track and within the intended scope.
Negotiation skills can assist a project manager in obtaining an agreement or making a compromise on an issue that may be causing difficulty or delay.
There are several negotiation skills that the project leader should be able to employ. These include assessing each scenario, being an engaged listener, and communicating coherently throughout the dialogue. It can be important to distinguish between the wants and requirements of the people concerned. Another critical focus is recognizing the distinction between people’s perspectives and their interests and concerns directly relevant to the project.
- Trust Building
When collaborating on a project, trust is really valuable. A trusting environment promotes effective relationships and communication among team members and stakeholders. Therefore, a project leader wants to foster an atmosphere of mutual trust. This trust helps to maintain morale, keep conflict at a minimum, and keep everyone working effectively together.
If you were working on a project, you would want everyone participating and working hard to see it through to completion. When you work hard, you expect that others are also working hard to achieve the project objectives. The team leader wants to trust a team member who suggests they can execute a task properly and on time. If someone in the team wants assistance, they want a team that will support and collaborate to achieve the work. So don’t waste time second-guessing someone who isn’t telling the truth or has bad motives.
There are several approaches for a project manager to establish trust. First, a project leader must be a great and open communicator to reduce misunderstandings and build confidence among team members. Often, one may have to put their self-interests aside for the team’s sake and must model and display the behavior they demand from others.
- Conflict Management
On a project, conflict is almost unavoidable. Members of the project team and stakeholders may have differing perspectives, areas of expertise, interests, personalities, work styles, and so on. When one adds additional factors to the mix, such as tight deadlines, resource limits, and communication challenges, it’s easy to understand how conflict might arise.
Conflict often leads to a better solution to a problem. For example, if a team member would prefer to agree or accept the status quo, then risk causing conflict by pointing out a problem, asking a question, or suggesting an improvement. In that case, it is simpler to accept a suboptimal solution. However, disagreement frequently stops the team from working successfully together and diverts attention away from the duties at hand.
The goal is to prevent conflict or its escalation or to know how to regulate or lessen it when it arises if they cannot avoid it. For example, a project manager may use several tactics or methods when dealing with a dispute. They can be aggressive, accommodating, avoiding, or compromising. Some approaches work better in particular situations than others.
The project manager and team members involved in the conflict influence the team’s efficacy. A project manager can also utilize many approaches; if one fails, they may have to try another to see if it is more successful.
Why are people skills important?
People skills are crucial because it is much more difficult for people in an organization to work together to achieve common goals if they fail to express themselves or understand how their co-workers feel about a certain project, task, or difficulty.
As a result, the organization’s production and profitability suffer while creativity and innovation endure. People skills, in particular, may assist us in the following:

Why Are People Skills Important?
- Avoid misunderstandings: People are less likely to misinterpret what you’re saying if you communicate ideas and instructions.
- Win support: If you can communicate effectively and understand what your team wants to hear, it will be much simpler to persuade them and get them “on board.”
- Improve customer support: You’ll be better positioned to fix their difficulties if you can get inside their minds and comprehend their key problems.
- Solve conflicts: Conflict isn’t always unpleasant, but if it goes unresolved, it can harm morale and productivity. Strong people skills allow us to see things from a new perspective and identify similarities, which reduces the likelihood of significant conflicts.
How to develop people skills?
Even while people skills are critical, they are frequently undervalued by employers when it comes to job advancement. Internal training sessions are frequently centered on teaching hard skills, such as completing a given activity or utilizing a specific piece of software. These methods make it more difficult for professionals to build their interpersonal skills.
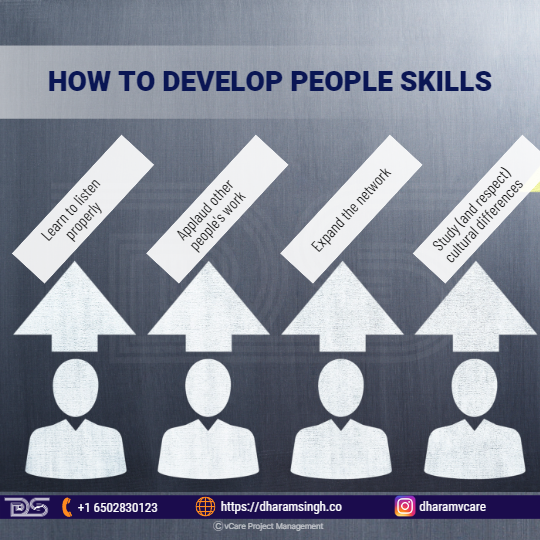
How To Develop People Skills?
But just because something is more difficult does not make it impossible. Here are four suggestions for improving people skills and becoming a more attractive prospect are:
- Learn to listen properly
- Applaud other people’s work
- Expand the network
- Study (and respect) cultural differences
Final Thoughts
Effective project management is challenging but having people skills may help project leaders run projects more efficiently and with less stress. Furthermore, it enables building a team that can handle the most challenging tasks and is more successful and resilient during difficult times.
People skills, on their own, will not keep a project team motivated and engaged. However, arming oneself with the necessary technical skills and intelligent tools may dramatically enhance the workflow and contribute to the project’s success.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd






























Recent Comments