
by Dharam CW2 | Mar 21, 2024 | Professional Development Webinars
Dive deep into the PMI’s latest enhancements to the Program Management Professional (PgMP)® credentials, tailored for senior project, program, and portfolio management professionals.
Registration Link: https://bit.ly/4c9un0j
Session Date : 26th March 2024
Session Time : 10:30 AM – 11:30 AM (PDT) / 11:30 AM – 12:30 PM (MDT) / 12:30 PM – 01:30 PM (CDT) / 01:30 PM – 02:30 PM (EDT) / 02:30 PM – 03:30 PM (BRT) / 05:30 PM – 06:30 PM (GMT) / 06:30 PM – 07:30 PM (CET) / 07:30 PM – 08:30 PM (SAST) / 08:30 PM – 09:30 PM (AST) / 09:30 PM – 10:30 PM (GST)
Webinar Agenda
– Simplified Application Insights: Grasp the updated application’s simplicity, from reduced experience summaries to a wider panel expediting reviews.
– Revised Standard for Program Management: Unpack the 5th Edition’s eight principles, spotlighting Stakeholders and Governance to elevate global program practices.
– Aligned Exam Content: Decode the subtle yet vital changes in the exam outline mirroring the new standard’s language.
– Exclusive PMI Membership Perks: Uncover the benefits, including complimentary access to crucial PMI standards, bolstering your certification pursuits.
– Industry Expertise & Dialogue: During our expert insights, benefit from the wisdom of a seasoned PgMP trainer. Clarify your doubts in our extensive Q&A segment.
– Preparation Roadmap: Walk away confidently with a strategic action plan, essential resources, and community backing to conquer the new PgMP exam.
🚀 Elevate Your Project Management Career:
– Book an obligation-free consultation session on Project management Career, training, and certifications: http://talktodharam.com
– Discover training offers and certification discounts: https://bit.ly/3jWVepD
– Stay updated with our Q&A series and certification success stories by subscribing to the vCare Project Management YouTube channel at https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
– Follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Feb 6, 2023 | General
The business world is unstable and ever-changing. Changes in competition and client preferences affect every organization. So, business leaders cannot rely only on competitive advantages to continue their businesses; thus, leaders must be aware of evolving business conditions.

Typical questions of employees and others in evolving business conditions
The following are typical questions that employees and others in similar situations may have:
- Was the company’s leadership aware of market developments?
- Was the leadership self-centred?
- As a market leader in the industry, did leadership think the company was not vulnerable?
Project/Program/Portfolio managers may help firm leadership by developing situational awareness and emotional intelligence to deliver essential leadership.
- The portfolio manager must understand the enterprise’s situational awareness.
- The program manager analyses the program for strategic goals and enterprise understanding and how the projects may be appropriately implemented as a program.
- The project manager must identify which strategic aim the project will assist in implementing or will accomplish.

In the dynamic environment managers want to know
Understanding the professional environment helps project leaders comprehend the politics of their projects. In today’s high-pressure, dynamic environment, managers want to know the following:
- What impacts the bottom line of the business?
- What are the profits?
- Can we fulfill our quarterly targets?
The project management professional must have the emotional intelligence to understand the company’s situation. Those unable to comprehend emotions, influence a project, program, or portfolio, and have a high emotional intelligence quotient are more likely to be attentive to how essential stakeholders perceive their competence.

Situational Awareness
Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is defined as “the perception of the elements in the environment in a volume of time and space, the comprehension of their meaning, and the projection of their status shortly.”
In many project management scenarios, situational awareness is essential for success. It is the capacity to observe what is happening around you and understand how it will affect your endeavor. Situational awareness is based on a simple observation. The tools, techniques, behaviors, and approaches that work well in one scenario may not work well in another. Simple best practices may sometimes be appropriate for the context and result in a positive conclusion; other times, they may result in disaster.
Emotional intelligence and situational awareness are skills that could be taught. However, situational awareness is a dynamic, ever-changing process, not a linear one. Depending on how the scenario progresses and one’s capacity to integrate existing information in the ongoing observation, interpretation, projection, and prediction process, one may have excellent situational awareness one moment and severely poor situational awareness the next. As a result, constant practice and training are required for portfolio, program, and project leadership skills in both emotional intelligence and situational awareness.
Situational Leadership
The Situational Leadership approach established by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard is a useful technique for project leaders to employ when choosing a leadership interaction style.
The core premise of situational leadership theory is that there is no single “best” leadership technique. Instead, effective leadership is task-relevant, and the most successful leaders adapt their leadership style to maturity (“the capacity to set high but attainable goals, willingness and ability to take responsibility for the task, and relevant education and experience of an individual or a group for the task”) of the individual or crowd they are trying to lead or influence. Effective leadership changes not just with the individual or group being influenced but also with the task, job, or function that needs to be completed.
The Situational Leadership approach can assist you in developing relationships with your team members since you will tailor your leadership style to their degree of development. Each team member necessitates a specific amount of hands-on, communication-based leadership. It is up to you to evaluate your team members’ skills, confidence, and motivation and to decide which leadership style to employ.
Every team member has different abilities, degrees of confidence, and motivation levels at work. Some team members may like your leadership, while others will feel underserved if you employ the same leadership approach for everyone. The Situational Leadership method is adaptable, allowing you to tailor your leadership style to match the demands of everyone.
The key to Situational Leadership is determining the followers’ readiness level. Readiness is classified into four categories based on the followers’ motivation and ability to complete the assigned project activity.

Categories of readiness level
Readiness 1: Low Motivation, Low Ability – This person is incompetent at the provided task and does not wish to complete the work or engage in the project.
Readiness 2: High Motivation, Low Ability – This person is eager to work on the project yet is incompetent at the tasks.
Readiness 3: Low Motivation, High Ability – This person is capable of performing project activities but does not choose to do so for personal or commercial reasons.
Readiness 4: High Motivation, High Ability – This person is capable and motivated.
Situational Theory of Leadership
Situational leadership theory assumes that the most successful leadership style varies depending on the context. Therefore, a leader must be able to change his style and approach to the evolving conditions to be most effective and successful.
Some employees, for example, perform better under a more dictatorial and directive CEO. Others will be more likely to succeed if the leader can step back and allow his team to make choices and carry out plans without his direct participation. Similarly, not all sectors and corporate contexts need the same abilities and leadership attributes.
Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
The term “situational leadership” is most generally associated with the Situational Leadership Theory developed by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard. This leadership strategy indicates that two main factors must be adequately matched: the leader’s leadership style and the followers’ maturity or preparation levels.

Four leadership styles
The theory recognizes four primary leadership styles:
- Telling (S1): Leaders must provide close supervision and precise directions to team members on what to do and how to accomplish it. When working with team members who are unwilling or unmotivated and need more knowledge and abilities, Style 1 is excellent.
- Selling (S2): The leader explains their decisions and allows team members to raise questions. Style 2 is best suited to followers who are driven to finish the work despite a lack of necessary information or skills.
- Participating (S3): Team members are encouraged to provide ideas and participate in decision-making. Style 3 suits followers with the necessary knowledge and skills to finish a task but who need more drive or motivation.
- Delegating (S4): The leader delegated greater responsibility to team members, allowing them to take ownership of the work. When dealing with high-commitment team members who are highly skilled and driven, Style 4 is acceptable since they have the knowledge, abilities, and desire to finish the assignment without much input from the leader.
While knowing the different situational leadership styles is important, their implementation may determine how effective a leader seems to their team. Examine its impact on team loyalty and the qualities of effective situational leaders.
The qualities of situational leaders

The qualities of situational leaders
- Flexibility: Situational leaders are adaptable enough to change their approach depending on the level of growth of each team member.
- Trustworthiness: Good situational leaders are capable of acquiring the trust of others.
- Ability to delegate:You must be able to delegate successfully to team members with high levels of competence and commitment to employ the situational leadership approach.
- Coaching skills: When working with team members who lack confidence or ability, one must deliver clear directions for task accomplishment.
- Courage: It takes courage to change your leadership style when everyone else is comfortable with the same stale approach.
Situational Leadership: Team Development
Situational leadership is a wonderful way of establishing your team. But first, figure out how you’ll address the learning needs of your project team members, who make up your core team.
Leadership team development provides your core project team with the abilities necessary to complete the duties assigned to them. As a situational leader, you can examine what is needed at any given time. One of the most critical areas to concentrate on is assisting the team in overcoming complacency.
Final Thoughts
Successfully using the situational leadership theory is an excellent method for becoming a competent leader. The idea divides leadership into several parts, explains each, and makes it simpler to increase one’s leadership skills successfully. It also demonstrates that leadership skills may be developed with appropriate training.
Situational leadership is a concept that may help any company, especially those that are already successful, enhance its performance and development. However, when done right, incorporating situational leadership into daily operations cannot affect a company. Instead, it can only help the company’s employees and, thus, its growth.
Finally, a leader must first come to know the employees to lead and inspire them successfully. Understanding leadership and motivation is the theoretical cornerstone of being a successful leader, but knowing one’s followers is equally important. To properly apply leadership and motivating concepts, leaders must understand their members’ personalities, cultural backgrounds, and developmental levels. Frequent personal interaction with their employees is the best way for a leader to get to know them, which is quickly done when the leader becomes a team member.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Apr 20, 2021 | General
According to the PMI (Project Management Institute), “Ethics is about making the best possible decisions concerning people, resources and the environment. Ethical choices diminish risk, advance positive results, increase trust, determine long term success, and build reputations. Leadership is dependent on ethical choices”. Ethics represent a crucial differentiator in a highly competitive market where reputation and values are highly appreciated among the Project Management Professionals.

The Time Is Always Right to Do What Is Right
Martin Luther King Jr. said, “The Time Is Always Right to Do What Is Right”. As project managers/program managers or portfolio managers, we must make critical decisions daily. Though in the evolving digital transformation world, many decisions might go unnoticed, few do get noticed, as critical ones. These decisions have a profound impact on people, resources, and the environment. Some decisions might have led to conflicts, dilemma, or the creation of new risks.
What is Ethics, and what is the Role of PMI?
Ethics is the branch of knowledge that deals with moral principles. It involves steps, including systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behaviours.
Regarding ethics at PMI, in the year 1981, the PMI team formed the PMI Board of Directors on Ethics, Standards, and Accreditation. The current PMI ethics document outlines the essentials of ethics based on Vision, Responsibility, Respect, Fairness, and Honesty. PMI expects its members to adhere to these codes of ethics to uphold its values.

Essentials of Ethics
When the whole world is fighting the COVID-19 situation, and demand for digital transformation projects is at an all-time high, PMI professionals need not ask for a better time to establish high ethical standards. Let’s understand the key challenges a PMI trained professional faces in the current digital transformation world.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is the process of using digital technologies to create new — or modify existing — business processes, culture, and customer experiences to meet changing business and market requirements.
There are four types of digital transformation: business process, business model, domain, and cultural/organizational. We often see corporations focused solely on the process or organizational transformation.
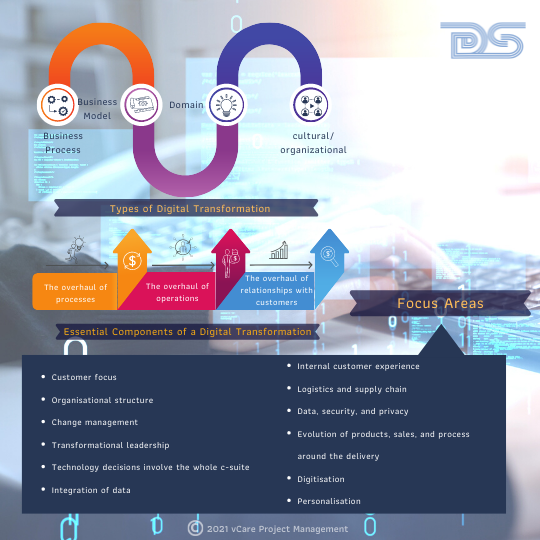
Digital Transformation
There are three essential components of a digital transformation:
- The overhaul of processes
- The overhaul of operations, and,
- The overhaul of relationships with customers.
The crucial elements that every digital transformation program needs to focus on are,
- Customer focus
- Organisational structure
- Change management
- Transformational leadership
- Technology decisions involve the whole c-suite
- Integration of data
- Internal customer experience
- Logistics and supply chain
- Data, security, and privacy
- Evolution of products, sales, and process around the delivery
- Digitisation
- Personalisation
The key aspects of the digital transformation world could have a major impact on Ethics.
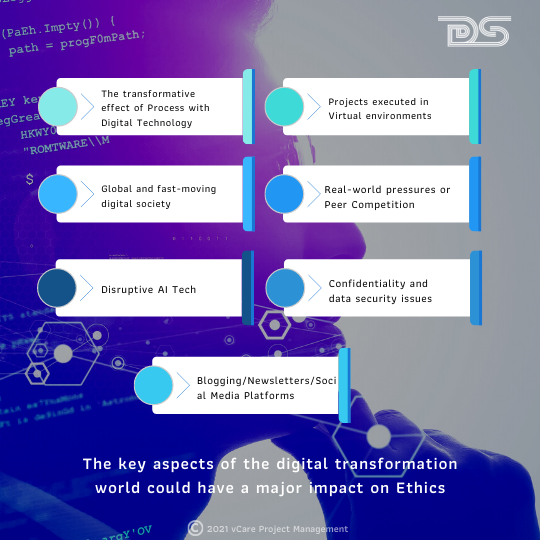
Major impact on Ethics
The transformative effect of Process with Digital Technology: Award-winning Author James Moor in 1985 mentions the transformative effect Digital Transformation could create. He cites the example transformation of manual votes to Electronic Voting Machines, which might benefit from speed and accuracy. On the contrary, it could impact security, vulnerability, transparency, and trustworthiness related issues.
Projects executed in Virtual environments: Today, the projects get implemented in remote places – Home/Office/Small Office combinations. People are working from remote, and it has become the new normal. People significantly use collaboration tools and in some occasions even communicate using social media, which could be manipulative.
Blogging/Newsletters/Social Media Platforms: Professionals tend to share the experience and insights reflecting upon the work ecosystem. Either sharing happens as an experience in a newsletter or a blog post, or it could be even a Twitter thread or a simple tweet reflecting a view. This act is typically done by those who tend to be expressive even within a professional organizational setup.
Global and fast-moving digital society: Communications spread very fast, and a diverse global culture leaves very little control. Digital technology, which is supposed to help leverage, could turn dangerous. The expectation for responsiveness sometimes leaves very little room for interpretation.
Real-world pressures or Peer Competition: Today’s real-world information sharing creates unwarranted peer pressure. This pressure might develop dilemmas and force individuals towards adverse decision-making. Sometimes, due to competitive peer pressures or financial pressures, even the employees’ health and safety concerns might get overseen.
Confidentiality and data security issues: Enhanced digital transformations across the globe have made data exchange easier. In the case of a data expose, it is vital to understand what is exchanged and what is the importance of the exchanged data. Lack of understanding of the data classification at appropriate levels could become risky when the proper accountability level could not be ascertained.
Disruptive AI Tech: Disruptive AI tech such as Chatbots, Speech Recognition Systems, etc., has made the way we think of data and decision making. Too much dependence or flawed inference might have an impact.
Ethics focus on PMIs Performance Domains & Digital Transformation
When a portfolio/program/project vision is established and defined, observable outcomes between the current state and future state as part of the digital transformation must be counted in. The key components that would impact the above said performance domains would be done with re-imagination, cultural change, and cross-functionality.
Digital transformation might have changed in a newer business model, new product focus, and a more contemporary way of working. Digital transformation is about getting the technology right and building necessary support and buy-in from the people managing resistance. Business processes need to be horizontally redesigned to enable collaboration across the teams.

PMI’s Program Management Standard
PMI’s Program Management Standard defines five performance domains that can be integrated with ethics, giving a significant shift in ethics adoption, and may help in improving overall digital transformation initiatives. They are:
- Benefits Management: Benefits profile, which would be based on outcomes and measurement, has to have the ingredients of the ethics as well.
- Strategy Alignment: Strategic alignment to focus on the changing business environment and strategic targets on digital transformation must be governed through ethics.
- Governance: Governance focus and establishes control related to programs. Governance would bring discipline and ethics into the broader organizational structure.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Stakeholders to be kept well informed on the ethical aspects of getting involved whenever any changes in stakeholders.
- Program Lifecycle: Given a structure and suggested flow for a program, the ethics principle has to be adopted to address dilemmas related to circumstances of a business and initiative.
5As Decision-Making framework
PMI has recommended the 5A’ss decision-making framework outlines with Assessment-Alternatives-Analysis-Application-Action. The 5A’s assessment helps to collate all the facts about the ethical dilemma. It considers all your choices. Subsequently, decision candidates are identified and tested for their validity. Apply these principles to the candidates and make the final decision.

5As Decision-Making framework
The decision-makers, when they adopt the 5A decision-making framework, the following checklist:
Assessment
- Does it adhere to the law?
- Does it comply with PMI code of ethics ?
- Does it comply with the organization code of ethics?
- Does it comply with the professional conduct ?
- Does it comply with the ethical values and culture of ecosystem?
Alternatives
- Whether alternatives are listed ?
- For the given choices do we have pros and cons ?
Analysis
- What kind of impact it would make ? (Positive/Negative)
- Does it count in cultural differences ?
- Is this decision taken considering long term impact ?
- Is this decision taken without any external influence ?
- Were you calm and unstressed during this decision ?
Application
- Will the decision be for larger good ?
- Has the decision is without any bias ?
- Is this fair for all concerned ?
Action
- Will you take responsibility ?
- Would you be ok to make your decision public ?
- Are you ready to act ?
Benefits:
When the portfolio managers and program managers adopt the above-said approach outlined in the PMI code of ethics, it provides the following benefits:
- Elevates the profession and raises future standards
- Increases the faith and trust among peers
- Imprints on individual moral mindsets and behaviors
- Improves business relationships across the board
- Promotes fair decision making
- Reduces project risks
- Reduces anxiety and stress and ultimately turnover in projects
Conclusion
Transparency and integrity must be the core values which has to be established by the professionals. The data must be used in responsible and ethical ways during the digital transformation initiative. Data collection has to be based on the ethics principle called “Informed Consent.” The actions cannot be intrusive, manipulative, or disrespectful to others.
Trust must be established among the individuals, groups, or organizations involved in the digital transformations. This trust can be created by establishing data provenance, traceability from the source to the user interface. Program managers or portfolio managers have to act without any bias and with a high level of integrity and impartiality. The same has to be established for the clients, suppliers, and subcontractors without any favoritism and giving them an unfair advantage.

by DharamCW | Mar 19, 2021 | How many PgMP | How many PfMP
Most project management professionals with a certain number of years of experience would like to move up their career ladder to senior positions that provide them with higher visibility, wider recognition, and a definite bump in their pay scale. They would aim to become a
- PMO Leader of their organization
- A Program Manager handling multiple connected projects
- A Portfolio Manager who drives the vision and mission of an organization through successful programs and projects
- An executive who is implementing a strategic initiative for the success of the organization
Some professionals might be looking to migrate from their current organization to a better/higher position in another organization and might be wondering what could be one of the keys that open that door to success.
Advanced Certifications might be the solution.

Move up the career ladder
Advanced Certifications
Advanced Certifications are for professionals,
- Who are established in their careers but want to climb up further
- Who want to increase their knowledge and improve professional ways of working
- Who are working in a role much more extensive than their current designation
- Who wants to prove a point to professionals in their space about their capabilities
- Who wants to prove a point to themselves for self-motivation and increase their self-worth
Advanced Certifications help you to,
- Change labels from being named an Experienced/Advanced professional to become an Expert/Master of the art.
- Change levels to elevate yourself to higher levels in the organizational hierarchy. Earn the birds-eye view.
- From “Doing the work right”, move to a phase where you start “Doing the right work” to ensure your organization’s mission and vision are accomplished through your actions. Go from Tactical to Strategic.
- It opens doors that were earlier closed in your career and creates new doors for you to venture. Gain global recognition. SKIP THE QUEUE IN PROFESSIONAL EVALUATIONS.
- Stand out from the crowd, Be that Differentiator.When all is Equal, the certified gets hired.
- Eliminate career shocks such as layoffs and retrenchments.

Advanced Certifications
Why PgMP® & PfMP®?
The PgMP® certification recognizes advanced experience, skill, and performance in overseeing multiple related projects and their resources aligned with an organizational objective. PgMP® certification holders oversee a program’s success — a way to group multiple related projects to achieve benefits that may not be realized if the projects were managed in a stand-alone fashion.
The PfMP® certification recognizes advanced experience, skill, and performance necessary to manage and align a portfolio of projects and programs to realize organizational strategy and objectives. PfMP® certification holders oversee one or more portfolios’ success, balance conflicting demands between programs and projects, and allocate resources based on corporate priorities and capacity. As portfolio management continues to grow and organizations adopt it to achieve strategic objectives, it becomes more critical to have individuals competent in this practice area. As employers demand portfolio managers who can support the organization’s strategic goals, PfMP® certification holders will gain a distinct advantage in employment and promotional opportunities over their peers.

Why PgMP® & PfMP®
Both PgMP® & PfMP® from PMI could help you achieve the possible elevation within your organization or get you the golden ticket to join your targeted organization. Compared with the PMP, which is more than a million globally, the numbers for PgMP® and PfMP® are still in the four digits, with PfMP® crossing the 4-digit mark just a few months ago.
The Numbers – What do they say?
Irrespective of the Pandemic concerns, professionals have been pursuing their PgMP® & PfMP® goals aided by the online/remote learning program options. PgMP® has crossed the 3500 number barrier, and as on 1st March 2021, it is now at 3543. PfMP® has crossed the 1000 number milestone, and as on 1st March 2021, it is now at 1035.
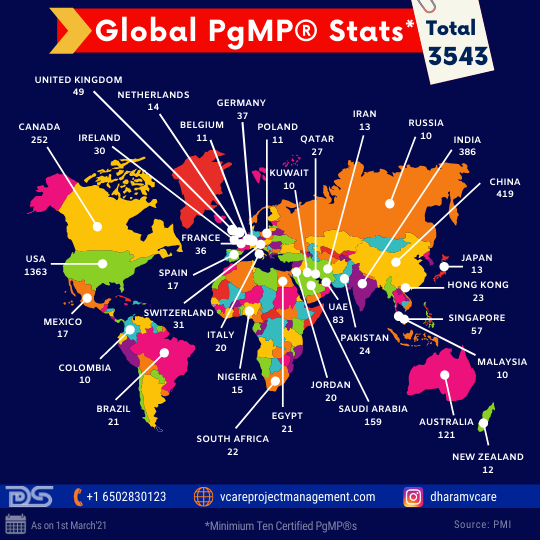
Global PgMP® Stats 2021
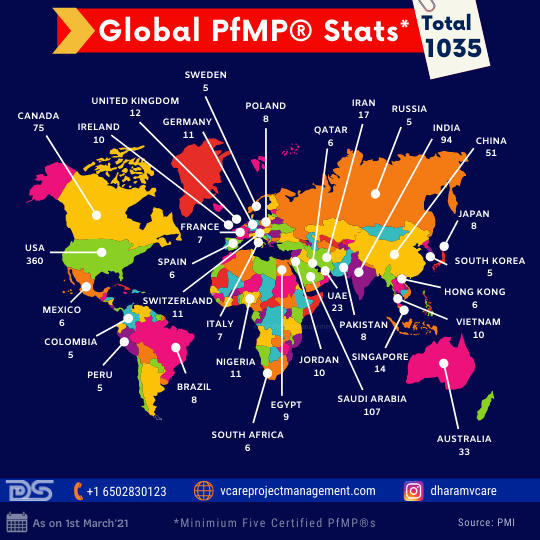
Global PfMP® Stats 2021
USA, China, India, Canada, and KSA contribute to the top 5 numbers in PgMP® and PfMP® numbers.
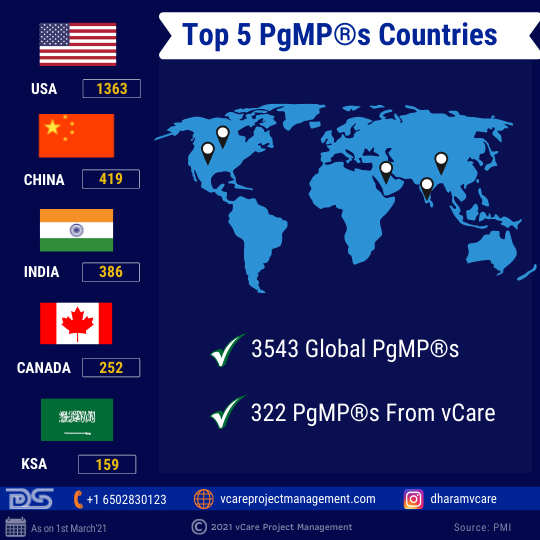
Top 5 PgMP® Countries
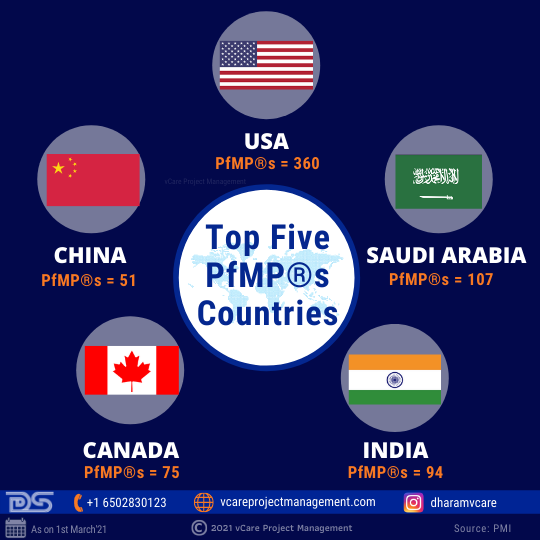
Top Five PfMP® Countries
A unique aspect in PfMP® numbers is the surge of certification holders from KSA, which has overtaken India to become the second country with the maximum number of PfMP® holders after the USA. With our training partnership with the PMI-KSA chapter, I wish the numbers of not only PfMP® but also that of PgMP® surge ahead. Students from KSA and the PMI-KSA chapter can reach out to me to avail offer associated with our partnership.
vCare Project Management is proud to have supported the following students in February 2021 in their successful pursuit of certification. This 2021, we have been producing excellent results with 10 PgMP®s and 6 PfMP®s achieving success in their certification goals aided by our training services thus far.

PfMP® & PgMP®s Success Stories | Feb’21
In the year 2020, we supported 48 PgMP®s and 16 PfMP®s in achieving success. As on 1st March 2021, we have thus far aided 322 PgMP®s of the 3543 PgMP® professionals and 58 PfMP®s of the 1035 PfMP® professionals. We have supported 322 students across 44 countries in their successful PgMP® journey.
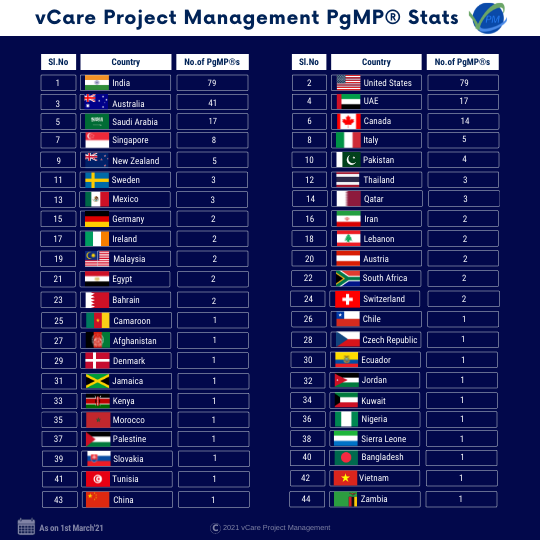
vCare Project Management PgMP® Stats
Because of the hardships that the companies and professionals are going through currently, I have decided to offer multiple discounts and flexible payment options to our upcoming mentoring and boot camp programs in 2021. These include,
- A 20% discount for Active Duty or Veteran professionals from Army, Marines, Navy, Air Force, Border, and Coast guards or any other valid military service branch
- A 20% discount for Women professionals
- A 20% discount for Differently abled professionals
- A 20% discount for professionals who are currently in dire financial constraints
Please email ([email protected]) or reach out to me on LinkedIn to avail of this discount post appropriate scrutiny.
Given below are the various online programs’ links. The online mentoring programs / virtual boot camps cover all time zones.
PgMP®: http://bit.ly/2oBKQXQ
PfMP®: http://bit.ly/39jOZSf
SAFe® / Disciplined Agile: http://bit.ly/3ogQY0N
PMP®: https://bit.ly/2BU0mFp
E-Learning: http://bit.ly/3b2HOid
Subscribe to vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to view our success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
We are planning to do more webinars in the coming weeks. Subscribe and follow my Podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd
Aspirants aiming to get the PgMP® / PfMP® / SAFe® / PMP® / Disciplined Agile Credentials in 2021 can book an obligation free session with me to find out how I can assist you in passing the exam in your very first attempt. For any questions related to Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
PgMP4U LinkedIn Group: http://bit.ly/2SBPwIp
PfMP4U LinkedIn Group: http://bit.ly/31P7GKR
Conclusion
Going by the numbers and the process involved in gaining the PgMP® / PfMP® certifications, it isn’t that easy for everyone to climb this mountain. These certifications are elusive by nature, and only with a determined focus, dedication, and brilliance coupled with hard work can one be able to achieve success.
I believe that this makes these certifications elite when compared with other senior project management certification offerings. This aspect alone could be the differentiator that highlights you from your peers in the project management community, helping you achieve your objectives.

by DharamCW | Aug 14, 2020 | General
Responsibility and Responsiveness have the same Latin root, Responsus. Responsible means being morally accountable for one’s actions. Responsive means reacting quickly with positive outcomes for all. In today’s digital world, your customers, irrespective of whether they are internal or external, are looking for faster response times, coupled with the appropriate action. Even some large organizations have been unable to compete with small players because of being non-responsive.
Today’s organizations and their projects need to be both responsive and responsible on a day-to-day basis. Especially when handling and delivering projects, a project manager, needs to be both responsible and responsive.
Defining Responsibilities
Right from the startup stage the project board or the corporate must define attributes such as tolerances, change authority, severity ratings, priority ratings, project initiation related documents etc., In fact, right from the business case validation stage, various responsibilities need to be assigned to stakeholders such as Corporate Management, Executive, Senior Users, Senior Suppliers and Project managers. Defining the responsibilities helps to bring upon the clarity on the job function they need to perform. It also helps in the alignment with business goals and brings about a common vision.

Responsibility
In the Project Management Office, different stakeholders have a different set of responsibilities for effectively meeting the project objectives in alignment with the program or portfolio objectives.
Examples of PMO Responsibilities would include:
- Aligning the project resources and their goals towards project work and organizational strategy
- Establishing governance structure and coordination of the same
- Performing portfolio management functions
- Ensure strategy alignment
- Tracking benefits realization
- Managing and Tracking data related to projects
- Administration to support project/project team.
- Managing communication to multiple stakeholders
- Defining roles and responsibilities

PMO Responsibilities
When the corporate management sets a mandate, they also set forth any standards to be fixed or followed. An outline of the expected benefits will be shared. Senior Users will outline the desired outcome, anticipated benefits, etc.,
Project Managers Responsibilities
Project Managers responsibilities cut across Planning, Organizing, Leading, Monitoring, Communicating and Managing the risks. Responsibilities need to be well defined and communicated effectively. It is always recommended to have well established and agreed, roles and responsibilities for all the people involved in the project as it will be a means for effective communication. This aspect will also apply to the other stakeholders in a project. A Project manager will be playing multiple roles and will have larger responsibilities in a project assigned to him/her including but not limited to Quality Control, Management Reporting, Risk Planning, etc

Project Manager | Roles and responsibilities
The Project manager must do justice to the roles and responsibilities he/she is assigned and needs to cultivate the necessary skills to do so. Skills such as communication, negotiation are some other essential skills to name a few. The project manager also assesses and reports on the project performance during the closure stage.
Establishing Responsibilities
Responsibilities come along with the role. One person might play a different role and might take up different responsibilities based on that. These responsibilities can be accomplished using various tools and nature of the business and operational aspects aligned with the goals. How can this be done?
- Audit what you have from an organizational standpoint, i.e. take inventory of Staff, Roles in the company.
- Identify business operations and enumerate the tasks being performed in it.
- Identify the gaps between project-program-portfolio
- Identify functions that are lacking and in what functional area.
- Identify required new positions, eliminate positions which are becoming irrelevant, and process which is no more required, etc.,
- Outline Job Role, Description, Task/Functions, Responsibilities, Skills required, Experience needed, Performance indicators, etc.,
- Prepare final organization chart for the project.
- Get to the Collaborate, Review and Approval process at the executive level.
- Establish RACI – Responsible, Accountable, Consulted and Informed
- Communicate the roles and responsibilities across the organization through RACI

Establishing responsibilities
Importance of RACI and how to get that done
When implementing the roles and responsibilities, it’s also easier to bring upon the necessary changes through RACI Rollout.
- Responsible – Doing the Task – The person/role which is going to act on the task
- Accountable – Owning the job – Responsible for the overall completion
- Consulting – Consulted/Assisted during the task analysis/planning/execution/completion – Mostly individual
- Informed – Keeping aware – Making cognizant of the task-related progress. Can also give feedback

Responsibility Assignment Matrix
RACI charts would be deployed across different phases of the project and various stakeholders’ groups with roles. When clarity and focus are established with the help of the RACI charts, it can bring upon good results as they remove ambiguities in communication.
Problems in owning responsibilities
Responsibilities are effective only when the person/role can do something about a problem and provide actionable oversight for the group or stakeholders where the problem occurs.
- What are the different existing issues concerning owning up of responsibilities?
- Why people are not owning up are having problems in taking responsibilities?
Problems in owning responsibilities
Some reasons could be:
- Fear of failure
- Lacking interest in the areas of responsibilities
- Missing deadlines
- Challenging tasks
- Inability to take risks
- Lack of trust with the team members and stakeholders
- Unfair treatment by team leaders and members
- Frequent excuses
Having these problems, how can we resolve them or how can we encourage ownership by responsibility?
Just replacing people would not solve the problem. Rather leaders need to back them and identify the different perspectives and indicators mentioned above in the context of the issues and help alleviate them. Take initiatives to help them by providing training, skill up-gradation courses, aided with additional resources and tools that could support decision making. Allowing them to make mistakes and backing them up could be a way forward. Having frequent interactions with the project managers would be very helpful to solve problems and providing constructive feedback on how it can be handled better would be of definite help. Reinforce or communicate the roles and responsibilities and their alignment with organizational goals. Highlight their roles importance and its impact on the organization. Motivate small deeds without micromanaging things.

Find the right people
Being Responsive
Nowadays, being responsive has been one of the key factors which are part of the CSAT (Customer Satisfaction) quarterly evaluations in large engagements. So, responsive is an essential ingredient required for any project engagement from a holistic perspective which needs to be reflected across the project team. Its core components are value and speed. It is contrary to being reactive, which is acting without any specific plan or giving due thoughts and given as an excuse for speed.
Being responsive will become a critical component when there are specific deadlines to be met. Examples of such projects would be GDPR compliance, HL7 migration, Compliance within a timeline, as any delays would attract huge penalties. In such cases, the project managers who need to act on matters of urgent/immediate basis, with risks also involved, need to think of long term and short-term goals to be accomplished without giving in to any knee jerk reactions.
Becoming more responsive will take time and would require bringing upon a daily incremental change at the behavioral level. This activity would naturally be inhibited both in Leadership and team level. However, we all know that procrastination is the biggest enemy for being responsive. Here are five ways in which you can improve your responsiveness in projects.
- Identify and note down the events where you became reactive in the past.
- Practice mindfulness and at the same time, be aware of a timeline to respond. Try the SOBER Method (Stop, Observe, Breathe, Expand, and Respond mindfully)
- Understand the culture shift in Agile methodology
- Identify and categorize the areas you can practice being responsive.
- Adopt tools such as Agility Evaluation Matrix, Todo List, Kanban Board, Alerting Tools etc.

Becoming more responsive
After the implementation of these tools and methods, how will one know and track whether improvements are happening? Evaluation can be carried out at different levels, and some examples are provided here. Questions which might lead an evaluation of responsiveness improvement could be,
- How much time does it take to respond to queries?
- How much time do we choose to respond to emails on project engagements?
- How much are we addressing/adhering to SLAs with our response for the first time?
- How many outcomes have been successful with this change in responsiveness strategy?
- How many times have we missed being responsive, and has it been escalated?
Handling problems of Poor Responsiveness
Project managers, most of the time, are responsive due to their experience and maturity. But in some cases, their responsiveness might be impacted due to dependencies. Though, it is always important to remember that expectation on the project team being responsive falls under their responsibility. What can be done in this case?

Being Responsive
Be responsive first. Walk the talk. Always our followers inspire from us. As a lead project manager, you must be responsive with respect to key communication made with the peers and followers. When he/she walks the talk about being responsive, they would be the one who acts first and be demonstrable on the expectations.
Make any expectations explicit and set up an SLA on when you expect a response on your communication. Be fair with them. Define timelines when you want them to respond – in hours, days, weeks. Also, ask about how quickly they want your responses to be. Make it a two-way road.
Be Proactive if the other person is not responding according to the timeline, and follow-up to remind them. Contact them for an acknowledgement. Ask again and follow up with them if they drop the ball. Ask them if they have any other dependencies which you can help to get resolved if its a top priority.
Being responsible and responsive are both important in the current business world. Communication holds the key to being both responsible and responsive. Being mindful of these can help one to be a successful project manager.
For any questions related to Project Management career, training and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
For the latest PgMP®/PfMP® stats visit https://bit.ly/38SSGiS
Subscribe to vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to view our PgMP® and PfMP® Success Stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
Subscribe and follow my Podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd






































Recent Comments