
by DharamCW | May 7, 2023 | General
The project management office (PMO) is increasingly evolving from an administrative role to one that is strategic and more closely connected with business drivers. As a result, the PMO plays an important role in generating corporate value as the pace of business rises along with the expectation of faster returns on investment.
Traditional administrative PMOs fall short of meeting this need. Therefore, a mindset change and a reinvented project delivery capability that is both commercially astute and agile are required. Furthermore, such a PMO must comprehend and implement the plan.
In this article, we’ll look at the factors driving the shift to strategic project management offices (SPMO), also known as Enterprise PMO or EPMO, the essential features of a value-adding PMO, and game changer ideas to help you alter your PMO and improve its profile in your business.

What is Strategic PMO (SPMO)?
Strategic PMO (SPMO)
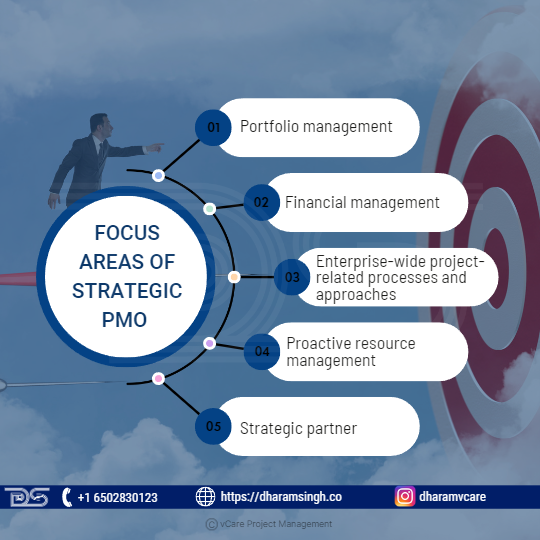
A Strategic PMO is a project-centric business department that should be structured and managed like other business departments – with enterprise leadership setting goals and objectives that assist the organization in thriving. The demands of individual organizations will lead to variations in what it means in specific terms. Still, we can expect a focus on the following areas:
- Portfolio management – Generation of ideas, selection, execution, and realization of benefits. Portfolio Management is a huge area, and organizations will adapt to it as it becomes increasingly crucial.
- Financial management – The PMO, closely linked to portfolio management, must be accountable for ensuring that project investments are acceptable and fit with business goals. The PMO must also guarantee competent budget management during project execution. Furthermore, the PMO should be held accountable for monitoring and tracking the benefit realization tasks of the business units.
- Enterprise-wide project-related processes and approaches Strategic risk management (i.e., managing the portfolio’s organizational risk exposure, proactive risk selection to match organizational tolerance, and so on), integration of finance and benefits, consistent quality standards, and so on.
Focus areas of Strategic PMO
- Proactive resource management – Capacity and capability planning, skills inventory management, and so on – ensuring that the project execution functions have the appropriate people with the right skills at the right time.
- Strategic partner – This borders on cultural change, creating the PMO as an independent and impartial consultant to the organization on project execution. PMOs, like IT, must demonstrate that they are business leaders supporting the organization’s work rather than a tactical execution-only function.
Different levels of PMO strategic alignment
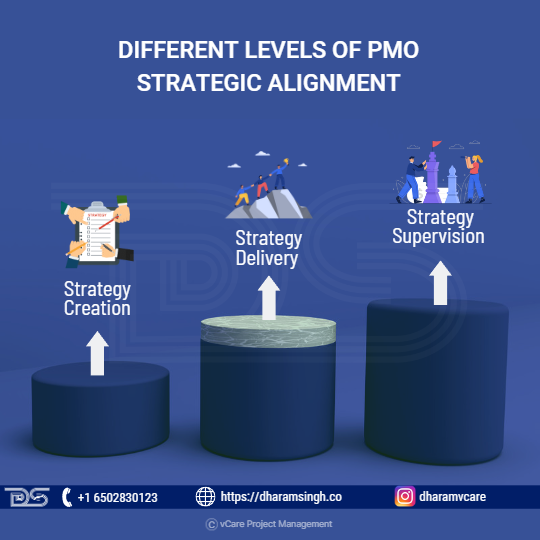
Within an organization, a PMO can function at three stages of ‘Strategic’ maturity:
Different levels of PMO strategic alignment
- Strategy Creation – Strategy Creation entails assisting organizations in determining which strategic options to pursue (and then translating them into projects – Strategy Delivery – and managing their success – Strategy Management). It is unusual for a PMO to achieve this level of trust and influence inside an organization. Still, it is the (possible) future for the enterprise PMO that is effectively embedded within an organization and fortunate with the right sponsorship.
- Strategy Delivery – Strategy Delivery is the process through which the PMO turns important strategy objectives into new projects to be added to the portfolio (and perhaps to remove some from the portfolio if such objectives have changed). The ‘Strategy Supervision’ capability backs up this ‘Strategy Delivery’ capability. The PMO may also take direct responsibility for the execution of large and complex programs (or projects) that are specifically critical to a key strategic effort, such as relocation activities.
- Strategy Supervision – Strategy Supervision of strategic intents through project ownership, each of which should directly or indirectly link to a strategic intention of the overall organization. ‘Strategy Supervision’ is where the PMO acts as the Executive’s governing and advisory body by:
- Validating that all projects undertaken correspond to one or more strategic initiatives.
- Monitoring the current and right alignment of projects and strategy.
- Making stall-and-kill recommendations for initiatives no longer correspond with current corporate strategic thinking.
Five Steps to Creating the Strategic Enterprise Project Management Office (SPMO)
Today’s organizations recognize that fewer and fewer initiatives are self-contained inside individual departments and increasingly straddle multiple business functions. Project management offices (PMOs) have traditionally been connected with IT, partly due to technology’s role in all projects. However, with technology increasingly transitioning to contribute to those business transformation initiatives, keeping the PMO as an IT role is ineffective.
The appropriate response to this trend is a single, enterprise-wide EPMO. Many firms using EPMOs, however, fail to perceive an increase in project execution speed. In addition, here are the five key steps to achieving long-term EPMO success:

Five Steps to Creating SPMO
- Define the company’s goal.
- Create appropriate leadership and accountability structures.
- Communicate the purpose, responsibilities, and alignment.
- Respond to measurements and outcomes.
- Create a road map for actual evolution into a business function.
The Rise of the Strategic PMO
The strategic PMO may play a crucial role as a custodian and evangelist for business benefits realization, giving important information to the Executive on which projects deliver value across the organization. In addition, the insights provided by the SPMO may help with crucial decisions like which initiatives to fund, which projects to kill, or re-prioritizing or re-balancing work portfolios to reflect changing business or market conditions.
Not all PMOs must be strategic in character. For example, a PMO embedded within a project or program might focus on the project’s day-to-day resource management and administrative needs. However, the decision to start the project should have been taken at a strategic level. From the start, the project-level PMO should have been aligned with the Strategic PMO’s reporting and governance structure. The SPMO should be able to make micro and macro business choices based on accurate and timely project data flow up into the program and, eventually, portfolio level.
The Strategic PMO plays a key role in championing and driving business value for the organization and being an effective change enabler. Here are the five major game changers that will propel the PMO and project organization to the next level.

5 Major game changers that will propel the PMO and project organization to the next level
- Demonstrating Project Leadership and Vision
- The Importance of Realistic Planning
- A Culture of Disciplined Execution
- Effective Stakeholder and Change Management
- Creating a “Value Lens” for Managing Enterprise Investment
The strategic project management office is critical to increasing project maturity and optimizing the organization’s business return on project investment. People, processes, data, and technologies must all be prioritized to achieve this objective. Project management is a multifaceted endeavor that is both an art and a science.
Leveraging the future of PMO to drive new strategic opportunities
In recent years, businesses have been subjected to a slew of external forces, the most significant of which has been Covid-19. These disruptors have caused firms to adapt, whether to work around obstacles, shift to new working methods, or adapt to Industry 4.0. All of these variables influence organizational complexity, both strategically and operationally. Businesses must not only respond proactively to all of this complexity; they must also prosper while operating in a resource-constrained environment. As a result, today, more than ever, the PMO’s ability to efficiently deliver projects and transform organizations of all kinds and across many locations is critical to achieving their goals.
Projects must be completed at scale to create transformation for a company effectively. A McKinsey & Company study of over 5000 large-scale projects discovered that 56% generated less value than planned, 45% went over budget, and 17% were so disastrous that the organization’s survival was threatened. This study highlights the need to make adequate efforts to select PMOs who can adapt to the future of work.
Historically, PMOs have been viewed as lacking a clear identity or purpose within an organization; however, the future-state PMO is an enabler of business value creation, collaborating with business leaders to provide a clear and achievable roadmap while making the best use of the organization’s limited resources.

3 Aspects that PMOs must embrace
PMOs must also adjust to the new normal and growing business demands. The three areas described below represent the fundamental features that PMOs of the present and future must embrace to manage change effectively.
- Technology & Automation
Because Covid-19 has accelerated the way we utilize technology in our daily work, technology is expected to be front and center, enabling PMOs to deliver more successfully. To effectively adapt to new methods of working and build a “single source of truth,” advanced technologies and cloud-based solutions will be required. This technology jump is critical for borderless operations in which progress and transparent communication must be readily available and updated in real-time to allow for swift decision-making.
In the future world, both artificial intelligence and machine learning will be important facilitators of automating PMO procedures, delivering superior insights, and allowing teams to spend less time on manual transactional processing and more time generating value for projects. For example, project planning is often based on data collection, industry benchmarking, and using the experience of project managers. However, according to PMI – AI Innovators, there is still a significant inefficiency in project management, with around 1/3 of traditional project management activities requiring one or more days of manually collating reports. Using IoT and big data to automate various tedious processes allows the PMO to create more realistic and effective timetables and spot potential disruptors.
However, it is unlikely that technology will completely replace project managers, with the PMI forecasting that businesses will require over 88 million project managers by 2027. As a result, PMs will be expected to improve their competencies and fully utilize the available technologies.
PMOs will be required to lead by example in their automation projects, advocating new methods of working with their collaborative organization in the future. As a result, the paradigm of efficiently providing workstreams may evolve, driving firms to become more digital.
- Agility
With an increased level of complexity for transformation and multiple stakeholders to handle, projects may need to adapt and pivot in other ways than originally planned. Changes in priorities (39%) and objectives (37%) and the inability to adapt are the two leading reasons for project failure, according to PMI.
As a result, PMOs that can be responsive to change needs continually are critical to fulfilling project milestones, which might mean the difference between being an industry leader or a laggard. An agile PMO’s guiding principles are as follows:
- Decentralization of planning and decision-making
- Agile resource allocation and reallocation
- Workflows that are effective for continuous project advancement
An agile PMO may demonstrate agility by altering priorities and reallocating resources to achieve new objectives while transitioning seamlessly from reorganization to continuous delivery. Furthermore, decisions are decentralized, allowing faster response rates for recognizing and reducing hazards. Finally, communication is critical, with fewer layers of approval, and output is assessed by how much work can be done in a particular sprint.
However, merely establishing an agile PMO will only solve some difficulties; 47% of agile projects are late, have budget overruns, or result in dissatisfied consumers. A cultural revolution is required to fully realize agile’s potential, beginning with the leadership team and spreading across the firm.
As a result, the PMO cannot only act as an intermediary but also as a business partner, working alongside the leadership team and the rest of the organization. Team members must be self-sufficient, accountable, and have complete insight into project progress and data.
- Strategy
The PMO’s role must evolve from a team offering mere assurance to becoming a strategic partner with a vested interest in aligning with the organization’s ability to carry out its plan. As a result, the team is expected to have stronger strategic oversight of all work streams to deliver value throughout the project.
PMOs will be required to go beyond task completion and monitoring to include:
- Portfolio planning entails generating ideas for the activities required to capitalize on the opportunity.
- Project prioritizing entails determining the most effective timeframe and budgeting by the company’s demands.
- Capacity planning entails assigning the appropriate skills and resources to each work team.
- Resilience planning entails anticipating future obstacles and reducing interruptions.
- The strategic partnership is a cultural transformation in management and the PMO. The PMO is viewed as a business leader and adviser with a stake in the organization’s goals.
The key to success is consistent stakeholder engagement, with the PMO and business leaders holding frequent strategic discussions to monitor and coordinate company strategy and broad strategic objectives. This consistency will build a collaborative strategic management process and a fluid communication channel to adjust quickly and efficiently.
The future PMO will be more strategic and intricate in character than conventional models, emphasizing driving decision-making, execution, and outcomes while becoming more decentralized to interact with each workstream to achieve one common goal efficiently. Finally, PMOs will be more crucial than ever in addressing the complexities that organizations are now confronting. An effective transformation will need PMOs to serve as the organization’s voice and face.

Strategic project management office’s role in strategy execution
Strategic project management office’s role in strategy execution
Identifying, implementing, and managing strategic initiatives is critical to strategy execution. The strategies are implemented by creating strategic initiatives to support strategic objectives and fill gaps in strategic measures, and the value gap is bridged. Only projects that are connected with the strategic goal should be accepted.
When defining strategic initiatives/projects, the sequence of initiative execution is crucial since all related strategic initiatives must finish and provide value. The strategic initiatives cover almost all departments and corporate shared services. As governance becomes more important in project management, portfolios and programs are defined.
- Strategic initiatives are linked to similar programs and project execution.
- The projects will be managed by program managers, project managers, and another project team.
- Connecting programs and projects creates portfolios for portfolio managers and other project governance teams.
- Project, program, and portfolio definition is an iterative process reviewed multiple times to ensure interconnectivity and value generation.
Portfolio, program, and project management are critical components of strategy execution. Hence, everything is referred to as a Strategic Project Management Office (SPMO) or Enterprise Project Management Office (EPMO).
Final Thoughts
Organizations can only thrive in a highly competitive world if they innovate. Such innovation must occur at all levels of the organization, including goods, services, business processes, and business models.
The PMO has the authority to execute the innovation at all levels. Good project management regulates and fosters innovation through projects—customer satisfaction and profit growth when consistent outcomes are predictable. Project and program management practices establish the foundation for dependable plan execution. The efficacy of the organization’s initiatives and programs will influence corporate success when such practices are implemented throughout the organization.
The project management office (PMO) is a key change management component, working with other organizational structures, such as functional units, to improve project management competencies. However, in today’s competitive environment, businesses must rely on more than just solid strategies to secure success.
To succeed, managers must build organizations capable of attaining their strategic objectives faster than their competitors. This initiative involves the creation of organizations capable of performing today’s tasks more effectively while anticipating future disruptions. Successful execution of creative and strategic concepts leads to innovation. Competitive advantage is as much about execution as it is about strategy.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Apr 21, 2023 | General
What makes a successful Project/Program/Portfolio Manager? Is it the number of years of experience? Technical know-how? Or the one who is good at managing people?
Creating objectives, critical path analysis, work breakdown structures, resource scheduling, and risk management are just a few of the technical areas of project management that project managers usually get training in. However, understanding pertinent people and management issues is important to a project’s success. In addition, a project manager must also continually deal with clients and other stakeholders. As a result, project managers’ people skills, also known as soft skills, are becoming increasingly important.

People Skills
People skills
People skills are linked with behavioral patterns or behavioral interactions that assist one in communicating effectively with people. Project leaders with strong people skills may favorably influence others, socialize effortlessly, and overcome public anxiety.

Project Leaders With Strong People Skills
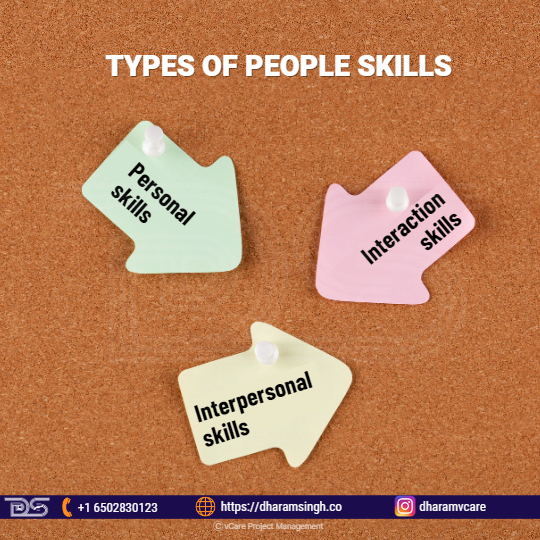
They are transferrable social abilities that allow one to collaborate well with others. The three main types are personal, interaction, and interpersonal skills. These categories achieve the same overall objective: making the working connections with others mutually satisfying, pleasant, and productive.
Types Of People Skills
Types of People Skills
- Personal skills: These include the capacity to communicate your skills and exhibit yourself to others successfully. It comprises characteristics such as self-assurance, honesty, and aggressiveness. Furthermore, one must be able to recognize their limitations and make sound judgments based on logic rather than emotion.

Personal Skills
- Interaction skills: It is essential for understanding the behavior and ideas of others while preserving limits and creating connections. A project manager, for example, should have social etiquettes that need empathy and listening skills to know that you have listened to them and given respect for their limits and requirements to connect with co-workers and clients productively.

Interaction Skills
- Interpersonal skills: These are related to intercession skills, but they apply mainly to situations in which the persons involved have opposing interests or viewpoints.
Contrary to popular belief, people skills are not subjective concepts. On the contrary, these skills are critical, particularly in the project management role, which is largely concerned with people.

Interpersonal Skills
Project management is more than just completing the project; it is also about how you lead and assist your team. Leading others and leading them through the whole project lifecycle entails a certain amount of responsibility and necessitates certain abilities.
Furthermore, as work evolves, businesses embrace a varied workforce. As a result, people skills are essential for embracing tolerance and diversity. In short, good project management is based on human communication and connection.
Essential People Skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers
A successful project professional must possess a wide range of skills. Those that come to mind first are the technical skills required to create a project plan, schedule, budget, and all relevant paperwork. One must also have the conceptual skills to “see” the project as it develops.
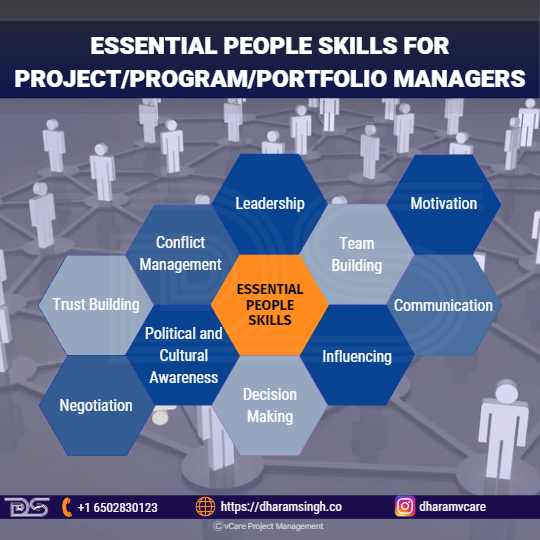
However, such talents will only assure project success if the project manager can supplement their technical skills with a wide range of interpersonal skills or people skills. Here are some of the essential people skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers:
Essential People Skills for Project/Program/Portfolio Managers
- Leadership
One of the crucial skills a successful project manager has to have is leadership. This skill is essential because the project manager frequently has little control over the team members involved. This aspect calls for leadership on their part to handle the project. Although managing via leadership rather than authority might be more challenging, it is typically more effective since it is based on respect and trust.
At the start of a project, a leader must establish their vision and express it to the team. It makes supporting the project’s objectives easier for everyone on the team. Effective leadership will also keep the team members inspired and motivated to perform at their highest level.
- Team Building
Another vital skill for a competent project manager is team building. Because of the nature of projects, personnel from diverse departments are engaged. Most employees might have never worked together and may not even be familiar with one other’s departments. If the project manager can unite these individuals into a cohesive team with the same goal, the project may stay within its objectives.
Although some of the project’s individuals or sub-teams may execute their jobs individually, they must feel like they are part of the overall team. When choosing their part of the project, they must consider what is best for the project, not simply what is best for them and their departmental problem. A sense of belonging to a team that solves an issue for the entire company (rather than playing departmental favoritism) may go a long way.
Creating a team in which each member feels comfortable reaching out to the others will also guarantee that minor problems do not escalate into major concerns later in the project. It is consequently critical that project managers not only understand the duties and procedures involved in team building but also have the skill and finesse to apply them correctly.
- Motivation
If you want your project to succeed, you should concentrate on improving your motivating skills. Having these qualities will assist your project team members to stay interested in the project, strive for excellence, and work toward a common objective.
Good motivating skills will enable a project leader to create an environment where team members can fulfill project objectives while being satisfied with their work.
- Communication
Most professions require excellent communication skills. Some project managers believe the communication part of project management to be their primary job obligation.
Excellent communication skills are essential for building relationships among project team members, establishing trust, and keeping everyone motivated and on track.
A project involves several stakeholders informed of its status, timeframes, progress, risks, and concerns. A skilled project leader must convey all of these facts to project stakeholders on time and in the manner they anticipate. Project managers must also interact effectively with top management within their business.
Giving the interested stakeholders too much or not enough information might prevent the project from reaching its full potential.
- Influencing
It is critical to be able to influence people if you want to be a successful project manager. But what is important is understanding when and how to utilize such skills and avoid becoming a manipulator. There is a narrow path to follow.
A project manager’s responsibility is to bring employees from disparate departments together and get them to work together toward a similar objective. Sometimes, getting these diverse people to comprehend and agree on the specifics of achieving that goal might not be easy. A skilled project leader will utilize their skills to persuade others and assist them in reaching an agreement.
So, think about your relationship and influence over people not just for the time of the project but also for how things will proceed long after the project is complete. After the project, customers and end-users will utilize the goods, deliverables, and outcomes developed by the project. A powerful and positive effect creates a trusting atmosphere among all team members during and even after the project.
- Decision Making
A successful project manager must acquire various talents, one of which is decision-making skills. There are four primary decision-making styles: Directive, Analytical, Conceptual, and Behavioral. Project managers should be conversant with all four since either has to be leveraged at some time. In addition, consultation, consensus, command, and random styles are provided.
Having a decision-making model will facilitate this process. In addition, since so many people who may disagree with a decision are involved in the project, having a process to follow can be very helpful in gaining consensus with the group.
- Political and Cultural Awareness
In today’s world, project managers work in a more globalized context than in the past. As a result, cultural diversity is another critical component of effectively navigating the corporate world as a project leader. A successful project manager must be able to notice and comprehend cultural differences and incorporate them into the project plan.
Cultural differences can impact decision-making and the pace with which work is performed. It can also lead to members acting without sufficient forethought. Recognizing cultural differences can lead to conflict and stress within the project, further delaying it.
Furthermore, it is critical to understand the politics at work in the project environment. The use of political skills can greatly aid a project manager’s success. More significantly, failing to recognize the politics involved can lead to substantial challenges and impediments that can cause a project to be delayed or even destroyed.
- Negotiation
The nature of a project manager’s work necessitates being skilled negotiators. Typically, several stakeholders are involved in the project, and most projects include team members from many departments. This aspect frequently leads to a variety of points of view, which can make it challenging to keep the project on track and within the intended scope.
Negotiation skills can assist a project manager in obtaining an agreement or making a compromise on an issue that may be causing difficulty or delay.
There are several negotiation skills that the project leader should be able to employ. These include assessing each scenario, being an engaged listener, and communicating coherently throughout the dialogue. It can be important to distinguish between the wants and requirements of the people concerned. Another critical focus is recognizing the distinction between people’s perspectives and their interests and concerns directly relevant to the project.
- Trust Building
When collaborating on a project, trust is really valuable. A trusting environment promotes effective relationships and communication among team members and stakeholders. Therefore, a project leader wants to foster an atmosphere of mutual trust. This trust helps to maintain morale, keep conflict at a minimum, and keep everyone working effectively together.
If you were working on a project, you would want everyone participating and working hard to see it through to completion. When you work hard, you expect that others are also working hard to achieve the project objectives. The team leader wants to trust a team member who suggests they can execute a task properly and on time. If someone in the team wants assistance, they want a team that will support and collaborate to achieve the work. So don’t waste time second-guessing someone who isn’t telling the truth or has bad motives.
There are several approaches for a project manager to establish trust. First, a project leader must be a great and open communicator to reduce misunderstandings and build confidence among team members. Often, one may have to put their self-interests aside for the team’s sake and must model and display the behavior they demand from others.
- Conflict Management
On a project, conflict is almost unavoidable. Members of the project team and stakeholders may have differing perspectives, areas of expertise, interests, personalities, work styles, and so on. When one adds additional factors to the mix, such as tight deadlines, resource limits, and communication challenges, it’s easy to understand how conflict might arise.
Conflict often leads to a better solution to a problem. For example, if a team member would prefer to agree or accept the status quo, then risk causing conflict by pointing out a problem, asking a question, or suggesting an improvement. In that case, it is simpler to accept a suboptimal solution. However, disagreement frequently stops the team from working successfully together and diverts attention away from the duties at hand.
The goal is to prevent conflict or its escalation or to know how to regulate or lessen it when it arises if they cannot avoid it. For example, a project manager may use several tactics or methods when dealing with a dispute. They can be aggressive, accommodating, avoiding, or compromising. Some approaches work better in particular situations than others.
The project manager and team members involved in the conflict influence the team’s efficacy. A project manager can also utilize many approaches; if one fails, they may have to try another to see if it is more successful.
Why are people skills important?
People skills are crucial because it is much more difficult for people in an organization to work together to achieve common goals if they fail to express themselves or understand how their co-workers feel about a certain project, task, or difficulty.
As a result, the organization’s production and profitability suffer while creativity and innovation endure. People skills, in particular, may assist us in the following:

Why Are People Skills Important?
- Avoid misunderstandings: People are less likely to misinterpret what you’re saying if you communicate ideas and instructions.
- Win support: If you can communicate effectively and understand what your team wants to hear, it will be much simpler to persuade them and get them “on board.”
- Improve customer support: You’ll be better positioned to fix their difficulties if you can get inside their minds and comprehend their key problems.
- Solve conflicts: Conflict isn’t always unpleasant, but if it goes unresolved, it can harm morale and productivity. Strong people skills allow us to see things from a new perspective and identify similarities, which reduces the likelihood of significant conflicts.
How to develop people skills?
Even while people skills are critical, they are frequently undervalued by employers when it comes to job advancement. Internal training sessions are frequently centered on teaching hard skills, such as completing a given activity or utilizing a specific piece of software. These methods make it more difficult for professionals to build their interpersonal skills.
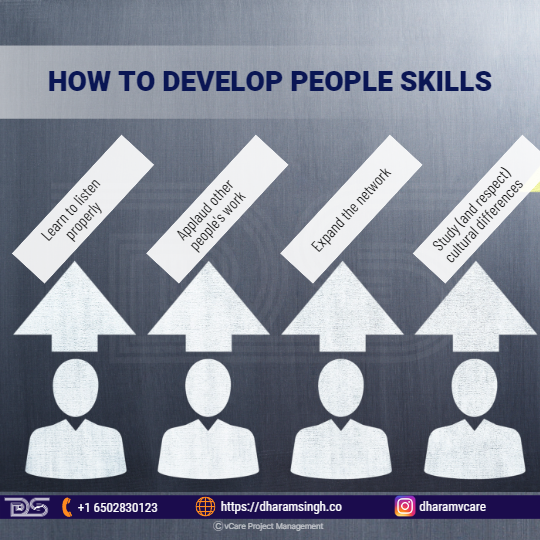
How To Develop People Skills?
But just because something is more difficult does not make it impossible. Here are four suggestions for improving people skills and becoming a more attractive prospect are:
- Learn to listen properly
- Applaud other people’s work
- Expand the network
- Study (and respect) cultural differences
Final Thoughts
Effective project management is challenging but having people skills may help project leaders run projects more efficiently and with less stress. Furthermore, it enables building a team that can handle the most challenging tasks and is more successful and resilient during difficult times.
People skills, on their own, will not keep a project team motivated and engaged. However, arming oneself with the necessary technical skills and intelligent tools may dramatically enhance the workflow and contribute to the project’s success.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Mar 10, 2023 | General
A project is deemed successful when it meets or exceeds the expectations of its stakeholders. Every project has a unique set of stakeholders—sometimes far too many. Trying to meet all of their requirements is more often an impossible task. Nonetheless, the project manager must deal with all stakeholder situations smoothly because the stakeholders and the people they represent often evaluate the project’s success.

Project Stakeholders
But who are the stakeholders? According to PMI, “Project stakeholders are individuals and organizations who are actively involved in the project, or whose interests may be positively or negatively affected as a result of project execution or successful project completion.”
Stakeholders can be internal or external to the organization that is carrying out the project.
“Project Sponsor” is also a stakeholder, typically an organization executive with authority to assign resources and enforce project decisions. Project sponsors are called internal stakeholders in the project. Stakeholders include the project manager, project team members, and managers from other departments within the organization. Identifying all project stakeholders as early as possible in a project is critical. Leaving out key stakeholders or the department’s function and not discovering the fault until the project is well underway could be disastrous.

Types of Stakeholders
Types of Stakeholders
There are two types of project stakeholders:
- Internal Stakeholders
- External Stakeholders
Internal stakeholders are individuals or businesses whose relationship with a company is determined by their position within its structure. As the name implies, these individuals are involved in a project from the inside. They are as follows:
- A project sponsor
- An internal customer or client
- A project team
- A program or portfolio manager
- Management
- Another team’s manager of the company
External stakeholders are those interested in a company’s operations. Still, they do not necessarily have a role in the decisions of the business. However, they can influence success or failure based on their vested interests. They can be just as powerful as internal stakeholders. These stakeholders are not directly involved in the project but are affected by its outcome.
- An external customer or client
- An end-user
- Subcontractors
- A supplier
- The government
- Local communities
- Media
Characteristics of Stakeholders in a Project
- When contributing to a project, stakeholders have varying levels of responsibility and authority. This level may change as the project progresses. It can range from one-time contributions to complete project sponsorship.
- Some stakeholders may also actively or passively undermine the project’s success. These stakeholders require the project manager’s attention throughout the project’s life cycle.
- Stakeholder identification is a continuous process throughout the project’s life cycle. Identifying them, understanding their level of impact on a project, and meeting their demands, needs, and expectations are critical to the project’s success.
- Just as they can positively or negatively impact a project’s objectives, stakeholders can perceive a project to have positive or negative outcomes.
- A project manager’s most important role is managing stakeholder expectations, which can be challenging because stakeholders often have different or conflicting goals.
Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management is the process of organizing, monitoring, and improving relationships with stakeholders. It entails systematically identifying stakeholders, analyzing their needs and expectations, and planning and carrying out various tasks to engage them. In addition, a good stakeholder management process will allow them to coordinate their interactions and evaluate the status and quality of their relationships with various stakeholders.
A critical component of running a successful project is developing and maintaining positive relationships with the affected communities and other stakeholders.
Investing time in identifying and prioritizing stakeholders, as well as assessing their interests, provides a solid foundation on which to build the stakeholder engagement strategy. In addition, good stakeholder management includes ‘business intelligence.

Benefits of Stakeholder Management
Benefits of Stakeholder Management
- Build Reputation
- Competitive advantage
- Corporate governance
- Risk management
- Social license to operate

7 Principles of Stakeholder Management
7 Principles of Stakeholder Management
Clarkson Centre created the seven principles of Stakeholder Management for Business Ethics under the leadership of Max Clarkson. The Clarkson Principles are, in many ways, “meta-principles” that encourage management to embrace specific stakeholder principles and implement them according to the norms.
- Managers must acknowledge and actively monitor all legitimate stakeholders’ concerns and consider their interests in decision-making and operations.
- Managers must listen to and communicate openly with stakeholders about their respective concerns and contributions and the risks they face from their involvement with the corporation.
- Managers must implement processes and behaviors sensitive to each stakeholder constituency’s concerns and capabilities.
- Managers should be aware of the interdependence of stakeholder efforts and rewards and make an effort to fairly distribute the costs and benefits of corporate activity among them while taking into account their risks and vulnerabilities.
- Managers should work with other public and private entities to ensure that risks and harms resulting from corporate activities are minimized and compensated appropriately where they cannot be avoided.
- Managers should avoid activities that could jeopardize inalienable human rights or create risks that, if clearly understood, would be patently unacceptable to relevant stakeholders.
- Managers should be aware of potential conflicts between their role as corporate stakeholders and their legal and moral obligations to all stakeholders and address such conflicts through open communication, appropriate reporting and incentive systems, and, if necessary, third-party review.
Understanding the Stakeholders
A good understanding of the stakeholders is the key to successful stakeholder engagement. In addition, understanding stakeholder concerns and interests can lead to product or service ideas that address stakeholder needs while allowing the company to cut costs and maximize value.
1. What else can you learn about stakeholders to better understand their needs, priorities, preferences, and concerns? Consider:
- Demographic data- Ensure to engage with a diverse community and stakeholder groups.
- Social networks- Focus on the important, often undocumented, social connections between stakeholders.
2. Stakeholder Mapping – Stakeholder mapping is the visual process of depicting all stakeholders of a product, project, or idea on a single map. The main advantage of a stakeholder map is that it provides a visual representation of all the people who can have an impact on your project and how they are connected.
3. Salience model – investigate the power, urgency (need for immediate action), and legitimacy (appropriate stakeholders), as well as the interaction or groups of stakeholders that result.
4. Determine stakeholder expectations and compare them to the scope and expectations of the project or organization for which the engagement program is being run. Is there a mismatch in expectations, and how will this be addressed? Consider the following:
- What information do they need from you, how often, and in what format/channel do they want it?
- What is their financial/social/emotional stake in the outcome of the work? Is it favorable or unfavorable?
- What primary motivations will shape their perceptions of your project or organization and their interactions with you?
- What are their current feelings about the organization and project? Is it founded on reliable data?
- Who influences their thoughts, and who are they influenced by?
Ways to deal with common stakeholder problems and challenges
- Stakeholder conflict occurs when different stakeholders have incompatible goals. It causes a “problem” for the company because it can impact its performance and success.
- Conflict necessitates that businesses effectively manage stakeholder interests. Not all stakeholders are strategically important to the company. As a result, businesses must determine which ones should be prioritized.
- Potential problems can be avoided by conducting an upfront analysis of who the stakeholders are and how and when to involve them in the project.

Analysis of common stakeholder issues
Analysis of common stakeholder issues
As no two stakeholders are the same, the issues they may introduce into a project will be vastly different. This factor means there could be many reasons why a project encounters stakeholder resistance or the project team struggles to gain traction. Identifying stakeholder issues during the project can help with planning ahead of time and preparing an appropriate response.
- Trying to align different stakeholders.
It is generally a good thing to have a variety of interests in the project and its outcome, but having a lot of different stakeholders can also pull the project team in too many different directions. In addition, it can be challenging for project managers to coordinate too many different stakeholders, which could add new difficulties to the project.
- Competing priorities between stakeholders
Stakeholders bring their objectives and expectations to the project. However, at least a few of these priorities frequently conflict with or compete with one another. In addition, priorities may vary depending on the department, the role, or the professional backgrounds of the individuals.
- Resource constraints
It’s possible that the team lacks some of the resources they require or that the project is utilizing resources that other stakeholders consider crucial to their projects. Resource competition is common in organizations and can lead to conflict.
- Breakdowns in communication
Effective communication between stakeholders and the project team is crucial for everyone to achieve their objectives and for the project to be successful. When there are communication breakdowns, the project may be delayed, or the team may not receive the necessary information. Without deliberate communication, stakeholders might unintentionally hinder the project’s success.
- Stakeholders are resistant to sharing information.
At times, important project sponsors are more focused on their success and fail to promptly or completely provide the stakeholders with the required information. As a result, stakeholders may attempt to disrupt a project unintentionally or on purpose.
- Potential implications of conflict with a sponsor
Conflict with project sponsors may have many consequences on the project management, such as these typical ones:
- The project’s progress is being slowed
- Reducing the effectiveness and timeliness of decision-making
- Putting team cohesion in jeopardy
- Undermining a project manager’s authority
- Fostering hostility and encouraging uncooperative behavior
- Creating a fearful environment for other stakeholders
- Obscuring the project’s vision

Methods for dealing with common stakeholder conflicts
Methods for dealing with common stakeholder conflicts
- Stakeholder analysis
Stakeholder analysis can offer insightful information and guidance, just as project managers must carefully examine resources and specifics. It can be helpful to respond appropriately by taking the time to consider how stakeholders affect the project’s progress.
By conducting a stakeholder analysis, one can learn how to control expectations, channel stakeholder influence toward project objectives, and deliver the information and updates that stakeholders expect from their team.
- Identify stakeholders
One must first identify the stakeholders to analyze them effectively. List every stakeholder that comes to mind, then include more individuals and organizations as necessary. As stakeholders, all parties involved in the project, those with authority over it or an interest in its success, should be listed.
- Prioritize stakeholders
The list of stakeholders can then be ranked according to impact, interest, and power. For instance:
- Key stakeholders: This first group heavily influences and controls the project. This group is frequently accurate for executive leadership at the company.
- Primary stakeholders: The project immediately affects the key stakeholders. This pack may include team members, departments, and internal or external clients who stand to gain from the project’s outcomes.
- Secondary stakeholders: The secondary stakeholders are those who play a supporting role, are indirectly impacted or have a less significant stake in the project.
Understand the key stakeholders
A few stakeholders are usually critical to the project. Key stakeholders invoke more power and may have a more significant stake in the project’s success than primary or secondary stakeholders. For example, key stakeholders could include their boss, company executives, or team leaders.
Finding the key stakeholders and understanding what they need can help keep the project on track because they may control important resources, have a significant impact on the project, or grant the necessary approval.
Create a communication plan
With a communication plan, project leaders will be better prepared to manage their stakeholders on the fly and keep the project moving forward.
- Create your communication strategy based on what the project leader knows about their stakeholders.
- Keeping track of what the stakeholders require from themselves allows project leaders to stay organized and focused on managing the project.
- Gaining the stakeholders’ trust is essential once the developed strategy has been implemented. Rather than dictating the project to them, make each stakeholder a priority – as appropriate – and give them space to contribute.
Final Thoughts
Different stakeholders in the project have different expectations. Project managers should look for potentially hazardous situations when those expectations might clash. Then, they must address and resolve the conflict or risk endangering the project and themselves.
Resolving stakeholder expectations conflicts is always linked to project success. Furthermore, using various forms of communication among the project team, such as senior management and stakeholders, increases the likelihood of mutual understanding. These techniques help project managers align stakeholder expectations and reduce the possibility of project distress.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Feb 24, 2023 | General
To be successful in project management, professionals must adhere to specific values like honesty, responsibility, respect, and fairness, which are central to the project management profession and are encompassed by ethics in project management. Therefore, understanding these values and how to apply them is essential for working in project management.
Ethics is important in day-to-day interactions and behaviors in the project management world. “Ethics is about making the best possible decisions concerning people, resources, and the environment,” according to the PMI (Project Management Institute). Ethical decisions can reduce risk, advance positive outcomes, build trust, determine long-term success, and build reputations.

Ethical Decisions
Corporate leaders are responsible for ensuring that their employees practice ethics in the workplace. Failing to follow ethics might result in numerous scandals. The project manager must ensure that all projects are managed and executed efficiently and ethically. If a project manager is ethical, they can influence the project team to work ethically and ensure that all project work is done ethically.
PMI has identified four values for ethical behavior in the project management profession, which can be applied amongst project team members to maintain project loyalty and ethics.
Honesty: Be genuine in your communication and behavior
Responsibility: Take responsibility for your decisions and actions and the consequences that result from them.
Respect: Admire yourself, others, and the resources entrusted to you, such as people, money, and reputation.
Fairness: Decisions and actions should be unbiased, and behavior should be free of favoritism, self-interest, and prejudice.
Therefore, project management professionals must follow the Project Management Institute’s (PMI) Code of Ethics to ensure that all decisions taken are in the best interests of stakeholders and the project team.

Project Management Institute’s (PMI) Code of Ethics
Transparency & Integrity in Project Management
Project management transparency characterizes a team’s open communication and visibility culture. Information in project management is on a need-to-know basis and is not readily available to everyone. A lack of transparency can lead to resentment or even distrust within the team. Transparency can advance a manager’s career, but it can harm the project manager’s reputation and career if carried out improperly. Therefore, there are many facts to believe that project managers should place a high value on openness and honesty.
The project manager’s transparency can lead to:
- Better performance and accountability
- Eliminates project derailment
- Enhancing teamwork
- Make sure people understand their tasks.
- Communicate openly and explain changes
- Provide and encourage feedback
- Promote knowledge-sharing
- Increase visibility with the right tools
- Focus on project budget
Project Integrity
As a project manager, acting with integrity with other project team members entails being open and honest about their expectations, intentions, and thoughts on their work. In addition, one must have the integrity to make the project team complete the project on time, within budget, and within the project’s scope.
Here are suggestions for acting with integrity with team members:
Be Impartial:
- Be objective and fair.
- Listen to both sides of the tale and different points of view without becoming attached to one in particular due to prejudice or favoritism.
- Rather than patching problems, objective decision-making fleshes them out and allows teams to get to the bottom of them.
Be Thorough:
Complete tasks entirely and thoroughly and validate the steps against a project management methodology of choice. This action ensures that a much more comprehensive project management plan and supporting documentation are created.
Be Focused on the End Business Result:
Regardless of when team members are introduced into the team, they should confirm initial business requirements and the work requested within the scope of their project role. This process enables them to provide their input based on their subject matter expertise, increasing the likelihood of project success.
Influence is a key component of leadership
To influence means to impact other people’s behavior, opinion, and choice. Influence is not the same as power or control. Instead, it is about recognizing what motivates employee commitment and applying that knowledge to boost performance and positive outcomes. The ability to influence others is a necessary leadership trait.
A leader’s ability to influence others is founded on trust; the project manager’s influence grows directly to the level of trust in a relationship. An effective leader motivates team members to act not through coercion but by eliciting their desire and conviction in the leader’s vision and goals. A leader who positively influences others through focused and deliberate effort will gain trust and become a driving force toward excellence.
Let’s look at how leaders can effectively build trust and influence with others.
- Establish credibility
- Engage with team members and build a connection
- Clarify expectations and practice accountability
- Share process knowledge
- Be open to influence
Relationship between stakeholders and project manager to maintain trustworthiness
Communication accounts for up to 90% of a project manager’s job. Conflicts can arise, and projects can fail if there is ineffective communication within the project team. Transparency in the project requires open, two-way communication with stakeholders about the status of a campaign. It keeps clients and stakeholders informed of campaign developments and other project activities.
Why is transparency important for stakeholders?
Transparency is essential in a client-facing project for one simple reason: it fosters trust. When project leader gains the trust of their stakeholders, they are more likely to gain their cooperation and guidance. Maintaining positive stakeholder relationships requires trust, and project stakeholders’ importance cannot be overstated. The support of the stakeholders is critical for project success.

Six Tips To Increase Project Transparency With Stakeholders
Six tips to increase project transparency with stakeholders
- Create a stakeholder register to track stakeholders
- Communicate the level of transparency upfront
- Inform the stakeholders of the expectations.
- Involve them in key decisions and milestones
- Be proactive about difficult stakeholders
- Communicate consistently
Digital Transformation’s Impact on Project Management
Project managers have continued to manage project planning, acquisition, and execution, but their work is evolving with digital transformation.
Most project managers have already incorporated workflow and process automation technology in a few specific areas, like reporting and scheduling. And the majority of them are using digital platforms for project management which can help them stand separate.
How does a project manager acquire the knowledge and experience necessary to lead a digital transformation? What qualities are essential for this type of leader?
PMI’s 2018 Pulse in-depth report ‘Digital PM Skills’ survey conducted by Forrester Consulting for PMI among HR professionals and project managers and identified the top 6 digital-age skills required to get adapted in the digital transformation, like:
- Data science skills
- Innovative mindset
- Security and privacy knowledge
- Legal and regulatory compliance knowledge
- Ability to make data-driven decisions
- Collaborative leadership skills
Cybersecurity’s impact on projects
Project management and the need to establish objectives that protect information security are necessary for today’s project management world. Organizational fragility and vulnerability have increased due to digital transformation, and the proliferation of data and information has become abundant, so it is necessary to safeguard the data from getting misused. Therefore, many businesses are incorporating new elements into their projects to protect their information’s vulnerability, like:
- Security Plan: For the project’s security, a project leader must be aware of the risks to be addressed to develop a security plan. Taking them into account will help them chart the course of the plan and focus on the project’s objectives.
- Business requirements: The project manager must understand the project’s security requirements and business objectives to ensure its completion and success.
- Responsibilities: Each team member should be clear about their responsibilities in terms of security. The well-known RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) responsibility assignment matrix is used by many project managers, which aids in ensuring that project objectives are met.
- Security by design: Information security must be considered from the start of a project and throughout the process. Automating processes will improve project success and builds project security.
Pointers to incorporate cybersecurity in project management:
- Determine the project’s sensitive information.
- Evaluate the members’ responsibilities.
- Implement a level of information sensitivity.
- Understand security standards and regulations.
- Include security goals in the project’s objectives.
- Determine the company’s legal responsibilities to the information.
Technology vs. Ethics
Every facet of an organization disrupted by technology shows a possibility of gaining or losing stakeholders’ confidence and commitment. Technology advances can easily outrun the ethical standards that govern their application. Technology’s impact on project ethics is progressing similarly, with employers establishing ethical boundaries that violate employee privacy rights and limit communication abilities.
Some of the technology’s impact on project ethics
- Monitoring Team’s Communications
Project team leaders have monitored employees’ communications during working hours to keep employees focused on work tasks. In addition, because of digital technology and Internet access, there are more chances that project team members can get diverted and utilize the facilities in their personal activities.
The changing definition of the workplace impacts the ethics that underpin the traditional eight-hour work time. It is not ethical simply because technology allows project leader to access their employees and request work at any time. Increasing the working hours to nearly more than their actual hours also blurs the ethical lines in employee compensation.
Employees with restricted access to company property, such as a cell phone or personal computer, may treat it as personal property. An ethical issue may arise when an employee uses office property for non-work-related activities, such as looking for a new job or making personal calls. An employer must establish a clear policy regarding using company property loaned to an employee for business purposes only. This policy enables an employer to develop an ethical standard for using technology.
Ethical Decision Making in Project Management
Decision-making in project management is essentially a great reminder to project success. A truly accomplished project leader inspires, motivates, and builds a strong group that aids their team objectives. The concept of ethical decision-making has also been a focal point in improving project decision-making.
The ethical decision-making process and its roadmap
Every day, a project manager might make thousands of decisions and can come up with the best solution within nanoseconds of hearing about a problem. However, managers must regularly make major decisions incorporating more diligence, forethought, and collaboration with their colleagues. The failure in decision-making can create severe implications and chaos. Thus, organizational performance depends on good decision-making.
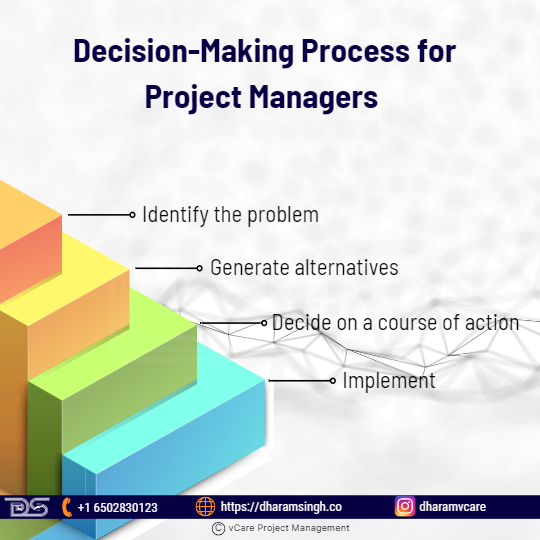
Decision-Making Process for Project Managers
Four steps that can comprise a basic framework for project managers’ decision-making process are:
1) Identify the problem
2) Generate alternatives
3) Decide on a course of action
4) Implement
Ethical Dilemmas in Project Management
The bigger the project, the greater the potential for people or businesses to compromise their moral standards to finish the project on schedule and within budget. The outcomes of project managers and other stakeholders ignoring debatable activity are disastrous, like blown budgets, legal concerns, and even criminal charges, which are too frequent in today’s project environment. Moreover, many businesses are aiming for 100% automation and implementation in the project management process. The project managers need to take charge of these initiatives, which might result in ethical dilemmas involving stakeholders, technology, or communities.
Ethical dilemmas arise when circumstances contradict the project manager’s professional standards or moral values. The project managers must ensure that a project fulfills its social responsibility and well-being commitments by keeping its long-term goals in mind.

Ethical Dilemmas in Projects
Some Ethical dilemmas in projects include
- Conflicts of interest
For project managers, conflict of interest is a major ethical concern. A conflict of interest occurs only when an individual or group has multiple interests in a project, which may hinder the integrity of the process.
- Accepting responsibility
When a project goes wrong, managers may be tempted to blame workers, supervisors, or vendors for protecting their position. The manager may also consider concealing any evidence that could implicate them in the project’s failure. However, when a project does not go as planned, project managers have an ethical responsibility to accept their failures and start focusing on finding solutions to problems and getting the project back on track.
- Maintain safety standards
Project managers who limit safety standards to save money eventually discover the high costs of not enforcing safety standards with their team. Conversely, a project manager who follows proper safety standards can save a project from incurring costs ranging from minor errors to severe injury or death.
- Favoritism and prejudice
A project leader must not “pick winners” or show bias toward team members. Project managers should choose the participants based on their abilities, not personal preferences. A project manager who shows prejudice toward workers based on race, ethnicity, religion, gender, or other criteria compromises the project’s integrity and exposes the company to a discrimination lawsuit.
- Health and Safety Concerns
Large enterprise projects have high risks and intense deadline pressure. This pressure, unfortunately, can occasionally cause stakeholders to overlook or even hide problems that could endanger the health and safety of project associates or the general public. Although these problems are more likely to occur in the manufacturing, healthcare, or construction sectors, project managers in all sectors should be ready to notify authorities whenever they spot a potentially dangerous situation.
Does project loyalty depend on the individual?
Ethical behavior is essential in all aspects of life, personal and professional. Being an ethical professional benefits everyone, both individually and on a societal and organizational level. Organizations that practice ethics can make their employees optimistic, boost their confidence, and increase their dedication. They can easily draw new clients and consumers due to their honest and ethical behavior, which can significantly improve the project’s sales and profits.
The project manager’s responsibility in Project Management is to manage projects effectively and ethically, as projects are the primary means by which organizations achieve their goals and objectives and develop new services and products. Suppose a new product development project is managed and executed with unethical decisions and actions. In that case, the product will fail to impress and attract customers, resulting in a huge failure and a significant loss in terms of time, project budget, and resources. Customers, clients, and employees value honest and ethical behavior. Thus, a project manager can ideally follow the PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct, which states that they must be honest, respectful, fair, and responsible.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Thomas Walenta in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting http://talktodharam.com/
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

by DharamCW | Feb 6, 2023 | General
The business world is unstable and ever-changing. Changes in competition and client preferences affect every organization. So, business leaders cannot rely only on competitive advantages to continue their businesses; thus, leaders must be aware of evolving business conditions.

Typical questions of employees and others in evolving business conditions
The following are typical questions that employees and others in similar situations may have:
- Was the company’s leadership aware of market developments?
- Was the leadership self-centred?
- As a market leader in the industry, did leadership think the company was not vulnerable?
Project/Program/Portfolio managers may help firm leadership by developing situational awareness and emotional intelligence to deliver essential leadership.
- The portfolio manager must understand the enterprise’s situational awareness.
- The program manager analyses the program for strategic goals and enterprise understanding and how the projects may be appropriately implemented as a program.
- The project manager must identify which strategic aim the project will assist in implementing or will accomplish.

In the dynamic environment managers want to know
Understanding the professional environment helps project leaders comprehend the politics of their projects. In today’s high-pressure, dynamic environment, managers want to know the following:
- What impacts the bottom line of the business?
- What are the profits?
- Can we fulfill our quarterly targets?
The project management professional must have the emotional intelligence to understand the company’s situation. Those unable to comprehend emotions, influence a project, program, or portfolio, and have a high emotional intelligence quotient are more likely to be attentive to how essential stakeholders perceive their competence.

Situational Awareness
Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is defined as “the perception of the elements in the environment in a volume of time and space, the comprehension of their meaning, and the projection of their status shortly.”
In many project management scenarios, situational awareness is essential for success. It is the capacity to observe what is happening around you and understand how it will affect your endeavor. Situational awareness is based on a simple observation. The tools, techniques, behaviors, and approaches that work well in one scenario may not work well in another. Simple best practices may sometimes be appropriate for the context and result in a positive conclusion; other times, they may result in disaster.
Emotional intelligence and situational awareness are skills that could be taught. However, situational awareness is a dynamic, ever-changing process, not a linear one. Depending on how the scenario progresses and one’s capacity to integrate existing information in the ongoing observation, interpretation, projection, and prediction process, one may have excellent situational awareness one moment and severely poor situational awareness the next. As a result, constant practice and training are required for portfolio, program, and project leadership skills in both emotional intelligence and situational awareness.
Situational Leadership
The Situational Leadership approach established by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard is a useful technique for project leaders to employ when choosing a leadership interaction style.
The core premise of situational leadership theory is that there is no single “best” leadership technique. Instead, effective leadership is task-relevant, and the most successful leaders adapt their leadership style to maturity (“the capacity to set high but attainable goals, willingness and ability to take responsibility for the task, and relevant education and experience of an individual or a group for the task”) of the individual or crowd they are trying to lead or influence. Effective leadership changes not just with the individual or group being influenced but also with the task, job, or function that needs to be completed.
The Situational Leadership approach can assist you in developing relationships with your team members since you will tailor your leadership style to their degree of development. Each team member necessitates a specific amount of hands-on, communication-based leadership. It is up to you to evaluate your team members’ skills, confidence, and motivation and to decide which leadership style to employ.
Every team member has different abilities, degrees of confidence, and motivation levels at work. Some team members may like your leadership, while others will feel underserved if you employ the same leadership approach for everyone. The Situational Leadership method is adaptable, allowing you to tailor your leadership style to match the demands of everyone.
The key to Situational Leadership is determining the followers’ readiness level. Readiness is classified into four categories based on the followers’ motivation and ability to complete the assigned project activity.

Categories of readiness level
Readiness 1: Low Motivation, Low Ability – This person is incompetent at the provided task and does not wish to complete the work or engage in the project.
Readiness 2: High Motivation, Low Ability – This person is eager to work on the project yet is incompetent at the tasks.
Readiness 3: Low Motivation, High Ability – This person is capable of performing project activities but does not choose to do so for personal or commercial reasons.
Readiness 4: High Motivation, High Ability – This person is capable and motivated.
Situational Theory of Leadership
Situational leadership theory assumes that the most successful leadership style varies depending on the context. Therefore, a leader must be able to change his style and approach to the evolving conditions to be most effective and successful.
Some employees, for example, perform better under a more dictatorial and directive CEO. Others will be more likely to succeed if the leader can step back and allow his team to make choices and carry out plans without his direct participation. Similarly, not all sectors and corporate contexts need the same abilities and leadership attributes.
Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
The term “situational leadership” is most generally associated with the Situational Leadership Theory developed by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard. This leadership strategy indicates that two main factors must be adequately matched: the leader’s leadership style and the followers’ maturity or preparation levels.

Four leadership styles
The theory recognizes four primary leadership styles:
- Telling (S1): Leaders must provide close supervision and precise directions to team members on what to do and how to accomplish it. When working with team members who are unwilling or unmotivated and need more knowledge and abilities, Style 1 is excellent.
- Selling (S2): The leader explains their decisions and allows team members to raise questions. Style 2 is best suited to followers who are driven to finish the work despite a lack of necessary information or skills.
- Participating (S3): Team members are encouraged to provide ideas and participate in decision-making. Style 3 suits followers with the necessary knowledge and skills to finish a task but who need more drive or motivation.
- Delegating (S4): The leader delegated greater responsibility to team members, allowing them to take ownership of the work. When dealing with high-commitment team members who are highly skilled and driven, Style 4 is acceptable since they have the knowledge, abilities, and desire to finish the assignment without much input from the leader.
While knowing the different situational leadership styles is important, their implementation may determine how effective a leader seems to their team. Examine its impact on team loyalty and the qualities of effective situational leaders.
The qualities of situational leaders

The qualities of situational leaders
- Flexibility: Situational leaders are adaptable enough to change their approach depending on the level of growth of each team member.
- Trustworthiness: Good situational leaders are capable of acquiring the trust of others.
- Ability to delegate:You must be able to delegate successfully to team members with high levels of competence and commitment to employ the situational leadership approach.
- Coaching skills: When working with team members who lack confidence or ability, one must deliver clear directions for task accomplishment.
- Courage: It takes courage to change your leadership style when everyone else is comfortable with the same stale approach.
Situational Leadership: Team Development
Situational leadership is a wonderful way of establishing your team. But first, figure out how you’ll address the learning needs of your project team members, who make up your core team.
Leadership team development provides your core project team with the abilities necessary to complete the duties assigned to them. As a situational leader, you can examine what is needed at any given time. One of the most critical areas to concentrate on is assisting the team in overcoming complacency.
Final Thoughts
Successfully using the situational leadership theory is an excellent method for becoming a competent leader. The idea divides leadership into several parts, explains each, and makes it simpler to increase one’s leadership skills successfully. It also demonstrates that leadership skills may be developed with appropriate training.
Situational leadership is a concept that may help any company, especially those that are already successful, enhance its performance and development. However, when done right, incorporating situational leadership into daily operations cannot affect a company. Instead, it can only help the company’s employees and, thus, its growth.
Finally, a leader must first come to know the employees to lead and inspire them successfully. Understanding leadership and motivation is the theoretical cornerstone of being a successful leader, but knowing one’s followers is equally important. To properly apply leadership and motivating concepts, leaders must understand their members’ personalities, cultural backgrounds, and developmental levels. Frequent personal interaction with their employees is the best way for a leader to get to know them, which is quickly done when the leader becomes a team member.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd












































Recent Comments