
by DharamCW | Sep 26, 2024 | Leadership in Project Management
Project management is becoming an essential component of modern business operations. Organizations increasingly use project management to monitor and assess projects and ensure they meet their objectives. Project management entails several complex processes, including project planning, organization, management, control, budgeting, monitoring, testing, and implementation.

Vance Packard Quote
Project leadership is the art and science of guiding a team to successful project completion. When project leadership brings people together to work toward a similar objective, the team can do more than they could individually.
Project Management Leadership
Leadership in project management is a necessary ability for completing the project. Like in other business areas, leadership necessitates demonstrating several talents and behaviors in a project context. Leadership is essential to ensure the success of the projects, from team leadership to project governance.
Leadership and project management are closely intertwined. Setting the vision and encouraging the team to work together to accomplish the project goal are vital components of leadership. In a project environment, this is particularly significant. Delivering any project requires a team effort. While some teams work without a clear leader, in business, it is customary for someone to be in the leadership role, guiding and directing the team toward their goals. On the other hand, project management systematically applies processes, methods, knowledge, skills, and experience to achieve the project objectives. Effective project management often requires strong leadership to guide the team through the project’s complexities and challenges.
5 Essential Project Leadership Skills
Project managers execute allocated project tasks through their project teams. They learn the technical, business, and leadership skills to manage their project teams effectively. In addition, they use strong leadership skills to motivate their teams to complete project deliverables and achieve project goals.
Project managers’ essential leadership skills begin with encouraging and inspiring their teams. However, the five critical project leadership skills are equally vital in enhancing team performance.

5 Essential Project Leadership Skills
- Communication
One of the most important project management skills is communication. Leaders must communicate effectively because a significant portion of their work includes collaboration. If you can communicate, you can collaborate properly.
Leaders can communicate ideas to people and groups in person, over the phone, or via web conferencing. They can also present their ideas to ensure the message is shared and understood. However, communication is more than just passing on messages and conversing with people. Communication is one of the most important characteristics of a project manager, especially in a leadership role.
- Team leadership
The leader establishes the vision and motivates others. Someone with outstanding project leadership skills fosters team agreement and togetherness while managing day-to-day operations.
Team leadership on projects entails establishing an environment in which everyone may thrive. People are lured to the project culture that surrounds them. Stakeholders want to be part of the project because they know you will complete the task while creating a pleasant working environment.
- Conflict resolution
Conflict is unavoidable when introducing or modifying something. However, effective leaders understand how to use conflict to their advantage since the finest solutions emerge when ideas are challenged.
Conflict may benefit teams by allowing all voices to be heard and opposing viewpoints to be expressed, frequently resulting in a better solution and more successful project outcomes. However, leaders must be equipped with conflict resolution skills to recognize and address conflict before it becomes a problem for the team. Therefore, another crucial core competency of project management is dealing with conflict in various ways.
- Motivation
Leaders motivate others to act even when they are not technically in charge. As a project manager, one determines what makes the other team members feel they’re giving their best. The project leader should do their best to deliver this. Everyone is driven differently, and motivation changes over time. Great leaders see these disparities and establish a great work environment to enable their workers to achieve their full potential.
- Crafting solutions
Empowering the team and the larger stakeholder community to participate in developing solutions is part of fostering a positive working culture. That entails removing roadblocks so that each team member may fulfill their work and contribute new ideas without concern about something getting in the way.
Empowering leaders also allows them to make decisions down the hierarchy to the lowest feasible level, allowing specialists to judge the solutions required to keep the project going. This empowerment fosters a positive working culture and inspires team members to take ownership of their work and contribute to the project’s success.
Leadership Styles and Theories
There is no single style to leadership, nor is there a particular type of person who makes a great leader. Instead, according to project leadership theory, a great leader is a mix of traits and the capacity to adapt to diverse conditions. This adaptability reassures individuals that leadership is not a fixed trait but a skill that can be developed and enhanced.
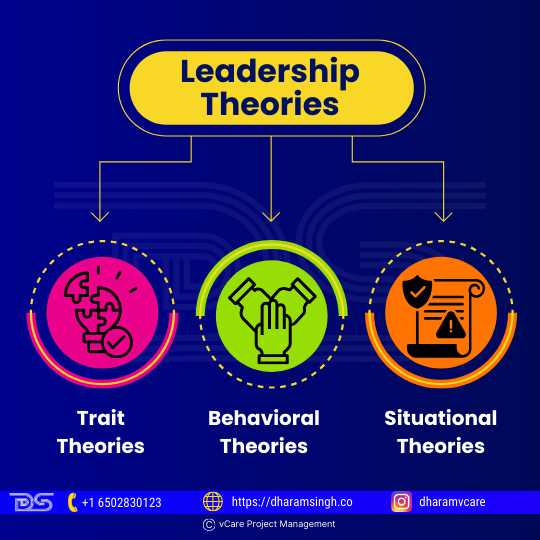
Leadership is something one can learn, and one can enhance one’s talents by understanding leadership theories in management. The three basic leadership theory categories that apply to project delivery are:
Leadership Theories
- Trait theories
Project manager strengths are related to trait theories. This perspective on leadership identifies the abilities and attributes that are beneficial while leading a team. Resilience, honesty, trustworthiness, aggressiveness, and so on are examples.
There was a system of thinking that stated certain characteristics were innate and that you were either born with them or not. Fortunately, this notion is no longer present in leadership concepts and theories. We know that an individual can act to become more aggressive and resilient or develop any other leadership trait.
- Behavioral theories
Behavioral leadership theories concern what a leader does. For example, some Corporate leaders are dictatorial and make decisions without consulting their employees. Others are more collaborative, inviting feedback and empowering their employees.
Both strategies are acceptable, and any combination of the two. However, there is a time and place for every style: you wouldn’t expect a combat leader to order a huddle so the team could discuss possibilities, would you? In that case, a choice must be taken immediately. Thus, a collaborative, listening leadership style would better engage the community.
- Situational theories
Situational leadership is deciding which leadership style to employ in any given scenario. These leadership theories are often known as contingency theories.
They analyze whether using a task-based or a people-based approach is more effective. They also take into account the individuals you lead. What type of encouragement and support do they require? A leader tailors their leadership style to the demands of the team, the business environment, and project circumstances. Someone who has never done specific work before will require more hands-on assistance from their team leader than someone confident in completing that activity.
Project Management Leadership Styles
Leadership in project management is essential for success. A project is a substantial and necessary endeavor in any business organization that requires full concentration and dedication from all participants. The success or failure of any business project can influence the company’s path. Project management is a critical role that may be entrusted to anybody, especially in today’s technology-driven business environment, where change is inescapable.
The ultimate success of every project is determined by project leaders, who have the authority to manage and oversee all project activities and make critical project choices. Similarly, failure to accomplish project objectives is the responsibility of the project’s leaders or management. Failure or inability to use the authority conferred upon them to ensure the project’s success is regarded as a point of accountability.
It is important to note that any project a firm does should strive to achieve certain goals that will enhance business operations and increase profitability, performance, output, and overall success in its objectives. As a result, project management is a critical function that leaders and anybody charged with project leadership must take seriously and utilize their effective leadership skills to ensure success.
Here are the six important project management leadership styles.

Project Management Leadership Styles
- Affiliative Leadership
This leadership style has a positive impact on a project team. This leader aims to create emotional bonds inside the organization to generate a sense of belonging and connection. When teammates require personal assistance or the team has to rebuild trust, the affiliative strategy is most successful. Because a single focus on praising and nurturing may result in poor performance and a lack of direction, this strategy should be used in various ways.
- Authoritative Leadership
Authoritarian leaders generate an entrepreneurial spirit and a strong devotion to the cause. Moreover, the traditional method works effectively when the team needs a new vision owing to changing circumstances or when clear guidance is unnecessary. Therefore, more utilization of this style would result in better project team outcomes without negative consequences, as this style has a generally positive effect throughout the organization.
- Coaching Leadership
This project management approach encourages team members to expand their capacity and capability as project contributors, which benefits the whole project team. This approach is the most effective coaching technique when a leader wants to assist colleagues in creating long-term personal characteristics that will help them succeed. However, it falls short when teammates are relentless about staying the same or learning or when the leader needs more aptitude.
- Coercive Leadership
Project managers rarely use this tactic, which would be more evident in times of crisis, such as when a project deadline was approaching and at risk of being missed.
- Democratic Leadership
This leader achieves successful compromises through teamwork. In a PMO, for example, each team member contributes to defining and measuring the PMO’s objectives. When the leader wants the team to buy into or own a decision, strategy, or goal, or when they are unsure and need new ideas from competent colleagues, the democratic method works well.
- Pacesetting Leadership
This leader anticipates self-management. The pacesetting approach works most effectively when the team is already motivated and talented and the leader demands quick results. This approach is popular, especially when a project nears major milestones. Although this method generally harms project teams, it can be beneficial in some situations.
Impact of Good Leadership on a Project
Many studies have highlighted leadership as one of the key reasons for project failure. On the other hand, projects with strong leadership and organizational support outperform those without.
Impact of Good Leaders on a Project
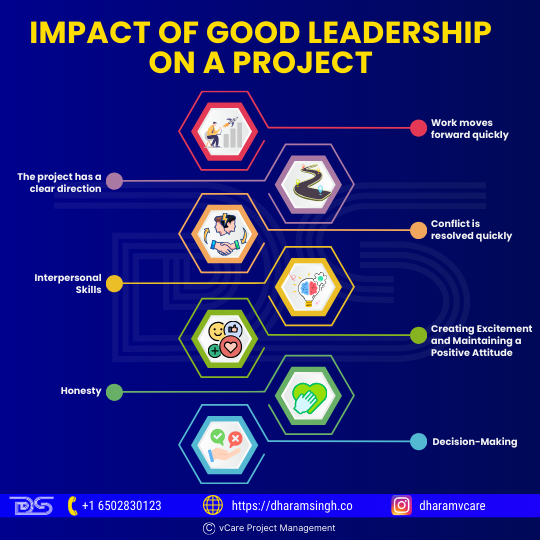
- Work moves forward quickly
When an individual actively leads, the work proceeds quickly as the choices are made on time. This move allows the project to be completed on schedule while delivering all planned project scope elements.
- The project has a clear direction
A leader ensures that the team knows and supports a common goal. A clear direction gives context for decision-making and ensures that everyone knows what the project will deliver.
- Conflict is resolved quickly
The project leader is constantly looking for conflict and can intervene to handle it before it escalates into a crisis.
- Interpersonal Skills
Project leaders must have interpersonal skills such as questioning, listening, and speaking to establish successful and compelling interactions with team members.
Experts in project management believe that projects are more likely to fail if project managers lack excellent interpersonal skills. Because much of a project manager’s duties involve communicating with stakeholders, one must have great interpersonal skills to lead from the front.
- Creating Excitement and Maintaining a Positive Attitude
The most crucial project manager leadership skills are boosting team members’ enthusiasm and displaying an optimistic attitude, especially in times of crisis. In addition, project management and leadership are about instilling trust in teams that there will always be a solution, no matter how serious a situation is.
- Honesty
When defining ethical guidelines and supporting transparency in communication, project manager leadership skills should embrace honesty.
Honesty and integrity are two fundamental traits of project management leadership that project managers should cultivate to increase trust among customers, members, management, and other stakeholders.
- Decision-Making
The project manager has the last say in simplifying processes and solving difficulties. As a result, the project manager’s capacity to make informed judgments is a critical function of leadership in project management.
Decision-making is an important project manager leadership skill that directly influences project outcomes. Therefore, to advance in their careers, all prospective project management professionals must master decision-making abilities.
Leadership mindsets are driving the new economy
Mindsets are mental maps that reflect and govern how individuals act in organizations. They convey how individuals work and what they stand for. So, what leadership characteristics do respondents and experts believe are necessary for success in the digital economy? World Economic Forum survey data states four leadership mindsets driving the new economy: producers, investors, connectors, and explorers.

Leadership Mindsets Driving the Digital Economy
- Producers
The producers’ mindset blends with creating consumer value, emphasizing analytics, digital savvy, execution, and outcomes. Producers use analytics to expedite innovation that addresses shifts in customer preferences and enhances customer and user experiences.
- Investors
Leaders with an investor mindset seek a purpose for their firm beyond improving shareholder returns. They are committed to growth but in a sustainable way. They are concerned about the areas in which they operate, their personnel’s welfare, and ongoing development. They focus on increasing the value of their clients rather than treating them as money sources.
- Connectors
Leaders with a connector’s mindset see that mastering connections and networks is the new currency driving corporate performance in the new economy. Connectors understand this fundamentally. It’s how they work. They constantly bring various stakeholders from within the organization and ecosystem partners together. Connectors recognize the importance of building a feeling of community and belonging, which is especially vital in today’s fast-paced, breakneck-speed world when losing contact with the human touch is too easy.
- Explorers
Leaders with an explorer’s mindset are curious and innovative and thrive on ambiguity. They constantly experiment and learn by listening to a wide range of voices. Establishing behavioral standards encouraging risk-taking and failure, reverse mentorship, and a deep curiosity about how new forces shape the competitive environment are strong indicators of an explorer’s attitude.
Final Thoughts
Project management is a demanding task requiring effective leadership styles and traits for the project’s overall success. Successful project leadership involves team building, adaptability, communication, and effective planning skills. As a result, leaders play a fundamental and crucial role in project management since their approach decides whether a project will succeed or fail.
Project management is different from leadership. Successful project managers may need to be more effective leaders. However, they can learn leadership qualities and become successful leaders. In today’s firms, competent project managers must also be strong leaders. Successful project managers may use their innovative and creative capabilities to assist them in acquiring leadership skills that will complement their project management abilities by recognizing the difference between project management and leadership and adopting the road to becoming influential leaders.
The common component of project management and leadership is the standard by which the project manager and leader’s performance is judged. A project manager’s success and a leader’s effectiveness are evaluated in terms of the performance of the followers—the team’s performance. As a result, improving project managers’ leadership skills with an emphasis on abilities to increase team performance should be a key factor.
Leadership is critical in project management and must be balanced. It impacts project success and the value offered to the organization. The good news is that the finest project management training incorporates leadership concepts, providing employees with a well-rounded understanding of what it takes to lead a project.
With advanced certifications like PMP®, Agile, PgMP®, and PfMP® certifications, one can develop project management skills, be a good problem solver, be a more competitive candidate for positions, and be a successful project leader. In today’s competitive business world, one must be skilled and experienced to succeed and grow their career.

by DharamCW | Feb 6, 2023 | General
The business world is unstable and ever-changing. Changes in competition and client preferences affect every organization. So, business leaders cannot rely only on competitive advantages to continue their businesses; thus, leaders must be aware of evolving business conditions.

Typical questions of employees and others in evolving business conditions
The following are typical questions that employees and others in similar situations may have:
- Was the company’s leadership aware of market developments?
- Was the leadership self-centred?
- As a market leader in the industry, did leadership think the company was not vulnerable?
Project/Program/Portfolio managers may help firm leadership by developing situational awareness and emotional intelligence to deliver essential leadership.
- The portfolio manager must understand the enterprise’s situational awareness.
- The program manager analyses the program for strategic goals and enterprise understanding and how the projects may be appropriately implemented as a program.
- The project manager must identify which strategic aim the project will assist in implementing or will accomplish.

In the dynamic environment managers want to know
Understanding the professional environment helps project leaders comprehend the politics of their projects. In today’s high-pressure, dynamic environment, managers want to know the following:
- What impacts the bottom line of the business?
- What are the profits?
- Can we fulfill our quarterly targets?
The project management professional must have the emotional intelligence to understand the company’s situation. Those unable to comprehend emotions, influence a project, program, or portfolio, and have a high emotional intelligence quotient are more likely to be attentive to how essential stakeholders perceive their competence.

Situational Awareness
Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is defined as “the perception of the elements in the environment in a volume of time and space, the comprehension of their meaning, and the projection of their status shortly.”
In many project management scenarios, situational awareness is essential for success. It is the capacity to observe what is happening around you and understand how it will affect your endeavor. Situational awareness is based on a simple observation. The tools, techniques, behaviors, and approaches that work well in one scenario may not work well in another. Simple best practices may sometimes be appropriate for the context and result in a positive conclusion; other times, they may result in disaster.
Emotional intelligence and situational awareness are skills that could be taught. However, situational awareness is a dynamic, ever-changing process, not a linear one. Depending on how the scenario progresses and one’s capacity to integrate existing information in the ongoing observation, interpretation, projection, and prediction process, one may have excellent situational awareness one moment and severely poor situational awareness the next. As a result, constant practice and training are required for portfolio, program, and project leadership skills in both emotional intelligence and situational awareness.
Situational Leadership
The Situational Leadership approach established by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard is a useful technique for project leaders to employ when choosing a leadership interaction style.
The core premise of situational leadership theory is that there is no single “best” leadership technique. Instead, effective leadership is task-relevant, and the most successful leaders adapt their leadership style to maturity (“the capacity to set high but attainable goals, willingness and ability to take responsibility for the task, and relevant education and experience of an individual or a group for the task”) of the individual or crowd they are trying to lead or influence. Effective leadership changes not just with the individual or group being influenced but also with the task, job, or function that needs to be completed.
The Situational Leadership approach can assist you in developing relationships with your team members since you will tailor your leadership style to their degree of development. Each team member necessitates a specific amount of hands-on, communication-based leadership. It is up to you to evaluate your team members’ skills, confidence, and motivation and to decide which leadership style to employ.
Every team member has different abilities, degrees of confidence, and motivation levels at work. Some team members may like your leadership, while others will feel underserved if you employ the same leadership approach for everyone. The Situational Leadership method is adaptable, allowing you to tailor your leadership style to match the demands of everyone.
The key to Situational Leadership is determining the followers’ readiness level. Readiness is classified into four categories based on the followers’ motivation and ability to complete the assigned project activity.

Categories of readiness level
Readiness 1: Low Motivation, Low Ability – This person is incompetent at the provided task and does not wish to complete the work or engage in the project.
Readiness 2: High Motivation, Low Ability – This person is eager to work on the project yet is incompetent at the tasks.
Readiness 3: Low Motivation, High Ability – This person is capable of performing project activities but does not choose to do so for personal or commercial reasons.
Readiness 4: High Motivation, High Ability – This person is capable and motivated.
Situational Theory of Leadership
Situational leadership theory assumes that the most successful leadership style varies depending on the context. Therefore, a leader must be able to change his style and approach to the evolving conditions to be most effective and successful.
Some employees, for example, perform better under a more dictatorial and directive CEO. Others will be more likely to succeed if the leader can step back and allow his team to make choices and carry out plans without his direct participation. Similarly, not all sectors and corporate contexts need the same abilities and leadership attributes.
Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory
The term “situational leadership” is most generally associated with the Situational Leadership Theory developed by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard. This leadership strategy indicates that two main factors must be adequately matched: the leader’s leadership style and the followers’ maturity or preparation levels.

Four leadership styles
The theory recognizes four primary leadership styles:
- Telling (S1): Leaders must provide close supervision and precise directions to team members on what to do and how to accomplish it. When working with team members who are unwilling or unmotivated and need more knowledge and abilities, Style 1 is excellent.
- Selling (S2): The leader explains their decisions and allows team members to raise questions. Style 2 is best suited to followers who are driven to finish the work despite a lack of necessary information or skills.
- Participating (S3): Team members are encouraged to provide ideas and participate in decision-making. Style 3 suits followers with the necessary knowledge and skills to finish a task but who need more drive or motivation.
- Delegating (S4): The leader delegated greater responsibility to team members, allowing them to take ownership of the work. When dealing with high-commitment team members who are highly skilled and driven, Style 4 is acceptable since they have the knowledge, abilities, and desire to finish the assignment without much input from the leader.
While knowing the different situational leadership styles is important, their implementation may determine how effective a leader seems to their team. Examine its impact on team loyalty and the qualities of effective situational leaders.
The qualities of situational leaders

The qualities of situational leaders
- Flexibility: Situational leaders are adaptable enough to change their approach depending on the level of growth of each team member.
- Trustworthiness: Good situational leaders are capable of acquiring the trust of others.
- Ability to delegate:You must be able to delegate successfully to team members with high levels of competence and commitment to employ the situational leadership approach.
- Coaching skills: When working with team members who lack confidence or ability, one must deliver clear directions for task accomplishment.
- Courage: It takes courage to change your leadership style when everyone else is comfortable with the same stale approach.
Situational Leadership: Team Development
Situational leadership is a wonderful way of establishing your team. But first, figure out how you’ll address the learning needs of your project team members, who make up your core team.
Leadership team development provides your core project team with the abilities necessary to complete the duties assigned to them. As a situational leader, you can examine what is needed at any given time. One of the most critical areas to concentrate on is assisting the team in overcoming complacency.
Final Thoughts
Successfully using the situational leadership theory is an excellent method for becoming a competent leader. The idea divides leadership into several parts, explains each, and makes it simpler to increase one’s leadership skills successfully. It also demonstrates that leadership skills may be developed with appropriate training.
Situational leadership is a concept that may help any company, especially those that are already successful, enhance its performance and development. However, when done right, incorporating situational leadership into daily operations cannot affect a company. Instead, it can only help the company’s employees and, thus, its growth.
Finally, a leader must first come to know the employees to lead and inspire them successfully. Understanding leadership and motivation is the theoretical cornerstone of being a successful leader, but knowing one’s followers is equally important. To properly apply leadership and motivating concepts, leaders must understand their members’ personalities, cultural backgrounds, and developmental levels. Frequent personal interaction with their employees is the best way for a leader to get to know them, which is quickly done when the leader becomes a team member.
Feel free to check out my discussion on this topic with Justin Buckwalter in YouTube
For any questions related to your Project Management career, training, and certifications, you can book an obligation free 15 minutes session with me by visiting talktodharam.com
You can subscribe to the vCare Project Management YouTube Channel to catch future videos of our Q&A series and certification success stories: https://bit.ly/2YF0wJl
You can subscribe to and follow my podcasts and interviews with Project Management Experts on YouTube at https://bit.ly/2NDY8wd

















Recent Comments